Section 1 The Earth System
... causes the air in the atmosphere to move. For example, cold air is denser than warm air. So, cold air in the atmosphere sinks. As the cold air sinks, it forces warm, less-dense air out of the way. This movement of air distributes energy throughout the atmosphere. The transfer of energy, especially h ...
... causes the air in the atmosphere to move. For example, cold air is denser than warm air. So, cold air in the atmosphere sinks. As the cold air sinks, it forces warm, less-dense air out of the way. This movement of air distributes energy throughout the atmosphere. The transfer of energy, especially h ...
Lecture 5
... • Air is held to the planet with gravity, so there is more air near surface • Bars are used to measure pressure ...
... • Air is held to the planet with gravity, so there is more air near surface • Bars are used to measure pressure ...
Erosion
... Pacific plate lies at the bottom of the ocean. Over time, the edges of these plates were forced under the edges of the plates surrounding the Pacific Ocean. ...
... Pacific plate lies at the bottom of the ocean. Over time, the edges of these plates were forced under the edges of the plates surrounding the Pacific Ocean. ...
Human Impact on the Ecosystem
... 20. List several ways we are trying to preserve endangered species. 21. List several ways we are trying to reduce air pollution. 22. Recognize that through a greater awareness and application of ecological principles, each individual can help assure that there will be suitable environments for futur ...
... 20. List several ways we are trying to preserve endangered species. 21. List several ways we are trying to reduce air pollution. 22. Recognize that through a greater awareness and application of ecological principles, each individual can help assure that there will be suitable environments for futur ...
01 - Middletown Public Schools
... 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _______________________________________________________________________ 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical composition. _____________________________________________________ ...
... 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _______________________________________________________________________ 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical composition. _____________________________________________________ ...
Level 2_ZOOL_03 - Marine Ecology
... • The Mariana Trench is located at a convergent plate boundary. • Here two converging lithospheric plates collide with one another. • At this collision point, one of the plates descends into the mantle. • At the line of contact between the two plates the downward flexure forms a trough known as an ...
... • The Mariana Trench is located at a convergent plate boundary. • Here two converging lithospheric plates collide with one another. • At this collision point, one of the plates descends into the mantle. • At the line of contact between the two plates the downward flexure forms a trough known as an ...
Document
... 13) _____ The picking up and removal of rock pieces and other particles. 14) _____ The dropping off of eroded particles in different locations from where they were picked up. 15) _____ A mixture of weathered rock, air, water, and humus that can support the growth of rooted plants. 16) _____ Decayed ...
... 13) _____ The picking up and removal of rock pieces and other particles. 14) _____ The dropping off of eroded particles in different locations from where they were picked up. 15) _____ A mixture of weathered rock, air, water, and humus that can support the growth of rooted plants. 16) _____ Decayed ...
Presentation
... • Cover about 2% of the earth’s land surface • Contain about 50% of the world’s known plant and animal species • Disruption will have three major harmful effects • Reduce biodiversity • Accelerate global warming • Change regional weather patterns ...
... • Cover about 2% of the earth’s land surface • Contain about 50% of the world’s known plant and animal species • Disruption will have three major harmful effects • Reduce biodiversity • Accelerate global warming • Change regional weather patterns ...
Solid, rocky crust covering entire planet.
... Estuaries are bodies of water and their surrounding coastal habitats typically found where rivers meet the sea. Estuaries harbor unique plant and animal communities because their waters are brackish—a mixture of fresh water draining from the land and ...
... Estuaries are bodies of water and their surrounding coastal habitats typically found where rivers meet the sea. Estuaries harbor unique plant and animal communities because their waters are brackish—a mixture of fresh water draining from the land and ...
Climate Test
... D. The climate on one side of a mountain range will never be different from the climate on the other side of the mountain range. ...
... D. The climate on one side of a mountain range will never be different from the climate on the other side of the mountain range. ...
Early Earth Quiz Prep
... 2. When the Americas bump into Asia in a few hundred million years _____________________________________________________________ 3. True or false (circle) – Continents keep changing, but never disappear? Vocabulary; Know the meaning of each word. Word Bank: molten landforms Pangaea plateau plate tec ...
... 2. When the Americas bump into Asia in a few hundred million years _____________________________________________________________ 3. True or false (circle) – Continents keep changing, but never disappear? Vocabulary; Know the meaning of each word. Word Bank: molten landforms Pangaea plateau plate tec ...
Climate - Humble ISD
... increases, the air temperature drops about 3.5°F for every 1,000 feet of height. Landforms also affect climate. This is especially true of mountain areas. As winds move up the side of a mountain, they cool and release moisture as rain or snow, on the windward side of the mountain. The winds that rea ...
... increases, the air temperature drops about 3.5°F for every 1,000 feet of height. Landforms also affect climate. This is especially true of mountain areas. As winds move up the side of a mountain, they cool and release moisture as rain or snow, on the windward side of the mountain. The winds that rea ...
LAB 2
... Shows us that the Earth is LAYERED The core must be made of a different material than the mantle to make the waves refract ...
... Shows us that the Earth is LAYERED The core must be made of a different material than the mantle to make the waves refract ...
AP Chapter 5 Study Guide - Bennatti
... epicenter-the location on the surface of the Earth directly above the focus magma- molten rock found within the Earth lava- molten rock that has reached the surface of the Earth ...
... epicenter-the location on the surface of the Earth directly above the focus magma- molten rock found within the Earth lava- molten rock that has reached the surface of the Earth ...
What on EARTH is going on here? (Mrs. Rodriguez tells the story of
... one big ocean and one SUPERcontinent! Well, that’s what scientists think Earth looked like. ...
... one big ocean and one SUPERcontinent! Well, that’s what scientists think Earth looked like. ...
Document
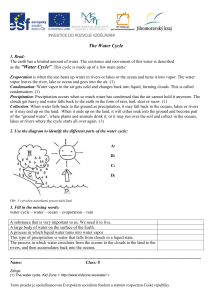
... The Water Cycle 1. Read: The earth has a limited amount of water. The existence and movement of this water is described as the "Water Cycle". This cycle is made up of a few main parts: Evaporation is when the sun heats up water in rivers or lakes or the ocean and turns it into vapor. The water vapor ...
... The Water Cycle 1. Read: The earth has a limited amount of water. The existence and movement of this water is described as the "Water Cycle". This cycle is made up of a few main parts: Evaporation is when the sun heats up water in rivers or lakes or the ocean and turns it into vapor. The water vapor ...
Chapter 4
... Alfred Wegener Continents can drift apart from one another and have done so in the past Pangea Greek word meaning “All Earth” Name for the single land mass that is the separate continents of today Panthelassa Name for the single ocean of the world that is the separate oceans of the world t ...
... Alfred Wegener Continents can drift apart from one another and have done so in the past Pangea Greek word meaning “All Earth” Name for the single land mass that is the separate continents of today Panthelassa Name for the single ocean of the world that is the separate oceans of the world t ...
Chapter 19 Section 1 Review Page 474
... Objective 1: Describe the unique physical features of Earth’s environment that make life on Earth possible. Objective 2: Analyze how ecosystems differ from each other due to abiotic and biotic factors. Objective 3: Examine Earth’s diversity of life as it changes over time. ...
... Objective 1: Describe the unique physical features of Earth’s environment that make life on Earth possible. Objective 2: Analyze how ecosystems differ from each other due to abiotic and biotic factors. Objective 3: Examine Earth’s diversity of life as it changes over time. ...
Document
... is mostly solid, but can move slowly The crust is cracked into tectonic plates How do tectonic plates move? 1. Radioactive processes occur in the core which release heat. 2. The heat travels through the mantle by convention currents. These convection currents cause the plates to move a few cm per ye ...
... is mostly solid, but can move slowly The crust is cracked into tectonic plates How do tectonic plates move? 1. Radioactive processes occur in the core which release heat. 2. The heat travels through the mantle by convention currents. These convection currents cause the plates to move a few cm per ye ...
earth*s shape, dimensions, and internal heat
... rocks - Friction between tectonic plates - Tidal stress from moon’s gravity ...
... rocks - Friction between tectonic plates - Tidal stress from moon’s gravity ...
forces of change
... Layers of the Earth: The super-hot solid inner layer of iron and nickel under extreme pressure The liquid layer of melted iron and nickel that surrounds the inner core. The thickest layer. This layer is made up of hot, dense rock – silicon, aluminum, iron, magnesium, and oxygen. This layer rises, co ...
... Layers of the Earth: The super-hot solid inner layer of iron and nickel under extreme pressure The liquid layer of melted iron and nickel that surrounds the inner core. The thickest layer. This layer is made up of hot, dense rock – silicon, aluminum, iron, magnesium, and oxygen. This layer rises, co ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.