Earth Formation: Accretion
... Earth. The Apollo missions, where the astronauts examined the moon’s crust, played an important role in eliminating other hypothesis of the moon’s formation. ...
... Earth. The Apollo missions, where the astronauts examined the moon’s crust, played an important role in eliminating other hypothesis of the moon’s formation. ...
Name ____________ Date ______________ Period ________
... rocky crust that rest and moves on semi-liquid mantle. ...
... rocky crust that rest and moves on semi-liquid mantle. ...
Planetary Science
... of a large rocky planet, its internal heat takes billions of years to escape. • Compare this with smaller rocky worlds! ...
... of a large rocky planet, its internal heat takes billions of years to escape. • Compare this with smaller rocky worlds! ...
g. What do fossils show -evidence of the changing surface and
... j. how to conserve natural resources such as water, soil, and air. Fact: Soil is a valuable resource because it is important to all living things on land and is nonrenewable. The process of supplying water to areas of land to make them suitable for growing crops is a. conservation. b. coagulation. c ...
... j. how to conserve natural resources such as water, soil, and air. Fact: Soil is a valuable resource because it is important to all living things on land and is nonrenewable. The process of supplying water to areas of land to make them suitable for growing crops is a. conservation. b. coagulation. c ...
File
... 59) Luster- The way a mineral reflects light from its surface. 60) Magma- The molten mixture of rock-forming substances, gases, and water from the mantle. 61) Manipulated/Independent Variable- The one factor that a scientist changes during an experiment. 62) Mantle- The layer of hot, solid material ...
... 59) Luster- The way a mineral reflects light from its surface. 60) Magma- The molten mixture of rock-forming substances, gases, and water from the mantle. 61) Manipulated/Independent Variable- The one factor that a scientist changes during an experiment. 62) Mantle- The layer of hot, solid material ...
Earth
... that rises from Earth’s interior Usually near plate division or collision Can be on land or under water Under water may lead to island formation ...
... that rises from Earth’s interior Usually near plate division or collision Can be on land or under water Under water may lead to island formation ...
Powerpoint
... Plate Tectonic Theory Earth’s outer layer is comprised of several large, rigid but mobile chunks called tectonic plates There are 12 tectonic plates that make up the crust Divided into: Continental plates Oceanic plates ...
... Plate Tectonic Theory Earth’s outer layer is comprised of several large, rigid but mobile chunks called tectonic plates There are 12 tectonic plates that make up the crust Divided into: Continental plates Oceanic plates ...
Place on the Earth where seismic waves are first felt
... A body wave that can pass through all layers of the earth. It is fastest of all seismic waves. ...
... A body wave that can pass through all layers of the earth. It is fastest of all seismic waves. ...
Study Guide – Earth`s Changing Crust
... Physical or mechanical weathering: is the wearing away of rocks through wind, rain, ice or biological things (plants, animals, people) 18) What is erosion? Sediments or soil moving from one place to another through wind, water, or ice. 19) What are some causes of erosion? Wind, water, ice 20) What ...
... Physical or mechanical weathering: is the wearing away of rocks through wind, rain, ice or biological things (plants, animals, people) 18) What is erosion? Sediments or soil moving from one place to another through wind, water, or ice. 19) What are some causes of erosion? Wind, water, ice 20) What ...
Atmosphere Review - 6th Grade earth and space Sciencemrs
... (carbon dioxide, methane gas, water vapor) trap the infrared energy from the Sun and direct it back to Earth? ...
... (carbon dioxide, methane gas, water vapor) trap the infrared energy from the Sun and direct it back to Earth? ...
The Earth`s Interior
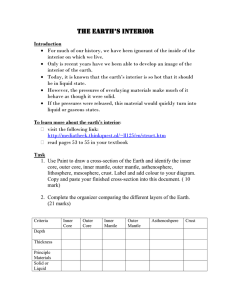
... The Earth’s Interior Introduction For much of our history, we have been ignorant of the inside of the interior on which we live. Only is recent years have we been able to develop an image of the interior of the earth. Today, it is known that the earth’s interior is so hot that it should be in ...
... The Earth’s Interior Introduction For much of our history, we have been ignorant of the inside of the interior on which we live. Only is recent years have we been able to develop an image of the interior of the earth. Today, it is known that the earth’s interior is so hot that it should be in ...
File
... Please review your notes and make sure you are comfortable with the following terms. While our Q Assessment is not a vocabulary test, being familiar with these terms, all of which are found in your notes and can be found on my website (rossbrownscience.com) will certainly help you answer the questio ...
... Please review your notes and make sure you are comfortable with the following terms. While our Q Assessment is not a vocabulary test, being familiar with these terms, all of which are found in your notes and can be found on my website (rossbrownscience.com) will certainly help you answer the questio ...
Abyssal plain- very level area of the deep ocean floor, usually lying
... composed of numerous interacting parts or subsystems. Environment - everything that surrounds and influences an organism Geological time scale - division of the earth history into books of time, eons, eras, periods, and epochs. Geology- the science that examines earth, its forms and composition and ...
... composed of numerous interacting parts or subsystems. Environment - everything that surrounds and influences an organism Geological time scale - division of the earth history into books of time, eons, eras, periods, and epochs. Geology- the science that examines earth, its forms and composition and ...
APES REV 4 - Bioenviroclasswiki
... 197. Serpentine soils lack potassium, an element required by most plants. There are some plants that can live on serpentine soils, but most cannot. In this case, potassium is a. part of the range of tolerance b. an example of Uniformitarianism c. a limiting factor d. a low-level toxin e. an example ...
... 197. Serpentine soils lack potassium, an element required by most plants. There are some plants that can live on serpentine soils, but most cannot. In this case, potassium is a. part of the range of tolerance b. an example of Uniformitarianism c. a limiting factor d. a low-level toxin e. an example ...
Document
... of people to material benefits and unlimited consumption of resources is a natural human feature. From ecological position the economic growth is a constant increase in the consumption of natural resources. At the same time progress can not be forbidden - it will always accompany human. ...
... of people to material benefits and unlimited consumption of resources is a natural human feature. From ecological position the economic growth is a constant increase in the consumption of natural resources. At the same time progress can not be forbidden - it will always accompany human. ...
File - Science by Shaw
... a system of deep depressions in the seafloor _________ 3rd largest ocean basin _________ the process by which the sea floor moves away from the mid-ocean ridges to create new sea floor. _________ the process of the earth’s plates moving apart _________ the mass of a given volume of a substance______ ...
... a system of deep depressions in the seafloor _________ 3rd largest ocean basin _________ the process by which the sea floor moves away from the mid-ocean ridges to create new sea floor. _________ the process of the earth’s plates moving apart _________ the mass of a given volume of a substance______ ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.