Chapter 2 – Plate Tectonics
... southern ocean. connected to the oceans are Mediterranean Sea, Gulf of Mexico, and South China Sea. ...
... southern ocean. connected to the oceans are Mediterranean Sea, Gulf of Mexico, and South China Sea. ...
File
... crust *More than 80% of Earth’s volcanic activity occurs on the ocean floor *Most volcanoes are found where the plates that make up Earth’s crust meet each other *Volcanoes tend to erupt where one plate is pushed under another plate *The Ring of Fire follows the boundaries of the plates that meet ar ...
... crust *More than 80% of Earth’s volcanic activity occurs on the ocean floor *Most volcanoes are found where the plates that make up Earth’s crust meet each other *Volcanoes tend to erupt where one plate is pushed under another plate *The Ring of Fire follows the boundaries of the plates that meet ar ...
Chapter 17 Vocabulary
... tectonic plates are moving apart; is associated with volcanism, earthquakes, and high heat flow, and is found primarily on the seafloor. Rift Valley (p. 456) Long, narrow depression that forms when continental crust begins to separate at a divergent boundary. Subduction (p. 457) Process by which one ...
... tectonic plates are moving apart; is associated with volcanism, earthquakes, and high heat flow, and is found primarily on the seafloor. Rift Valley (p. 456) Long, narrow depression that forms when continental crust begins to separate at a divergent boundary. Subduction (p. 457) Process by which one ...
PS review Earth
... • A warm front forms as a warm air mass moves over a slower cold air mass. • A cold front forms as a cold air mass moves under a slower warm air mass. • Tornadoes are high-speed rotating winds that form as air begins to rotate around quickly rising warm air. • Hurricanes are large storm systems tha ...
... • A warm front forms as a warm air mass moves over a slower cold air mass. • A cold front forms as a cold air mass moves under a slower warm air mass. • Tornadoes are high-speed rotating winds that form as air begins to rotate around quickly rising warm air. • Hurricanes are large storm systems tha ...
CRCT Review Warm Ups
... A. divergent boundaries only B. convergent boundaries only C. transform boundaries only D. all types of plate boundaries ...
... A. divergent boundaries only B. convergent boundaries only C. transform boundaries only D. all types of plate boundaries ...
Social Studies
... 2. Pangaea a. The name given to Earth’s landmasses when it formed one huge supercontinent. 3. Continental Drift Theory a. Forces within earth caused Pangaea to break apart into continental plates and drift apart. 4. Mountain formation a. tectonic plates push together b. two plates collide and one mo ...
... 2. Pangaea a. The name given to Earth’s landmasses when it formed one huge supercontinent. 3. Continental Drift Theory a. Forces within earth caused Pangaea to break apart into continental plates and drift apart. 4. Mountain formation a. tectonic plates push together b. two plates collide and one mo ...
Earth`s Structures and Earthquake Study Guide
... 30. A fold in rock that bends upward into an arch is called an anticline. 31. A place where two plates slip past each other, moving in opposite directions, is known as a transform boundary. 32. A rift valley forms at a divergent plate boundary. 33. Earth’s magnetic field is believed to result from r ...
... 30. A fold in rock that bends upward into an arch is called an anticline. 31. A place where two plates slip past each other, moving in opposite directions, is known as a transform boundary. 32. A rift valley forms at a divergent plate boundary. 33. Earth’s magnetic field is believed to result from r ...
The Planet Oceanus
... reflected at the boundaries between layers while others were bent. Seismic evidence shows that Earth is layered. ...
... reflected at the boundaries between layers while others were bent. Seismic evidence shows that Earth is layered. ...
Ocean Topography
... Active Continental Margin vs Passive Continental Margin Sediments: 4 kinds and how they are created Tectonic Plates: Features of Plate Boundaries -difference between Oceanic and Continental Crust-what they are made of (granite (cc)/Basalt (oc) 1. Convergent: Two plates colliding (Ocean-ocean, ocea ...
... Active Continental Margin vs Passive Continental Margin Sediments: 4 kinds and how they are created Tectonic Plates: Features of Plate Boundaries -difference between Oceanic and Continental Crust-what they are made of (granite (cc)/Basalt (oc) 1. Convergent: Two plates colliding (Ocean-ocean, ocea ...
ch6 humans in the world
... Natural Ecosystems Processes • Some Natural Ecosystem Processes which affect humans 1. maintenance of atmospheric quality 2. generation of soils 3. control of the water cycle 4. removal of wastes 5. energy flow 6. recycling of nutrients ** Humans have changed many of these ecosystem processes -freq ...
... Natural Ecosystems Processes • Some Natural Ecosystem Processes which affect humans 1. maintenance of atmospheric quality 2. generation of soils 3. control of the water cycle 4. removal of wastes 5. energy flow 6. recycling of nutrients ** Humans have changed many of these ecosystem processes -freq ...
Earthquakes
... Two of the crusts plates rub against each other and stick in one place. Pressure builds up as they try and move past each other. Suddenly, the pressure is too much and the plates jerk past each other. The place where this happens is called the focus. Vibrations go out in all directions through the r ...
... Two of the crusts plates rub against each other and stick in one place. Pressure builds up as they try and move past each other. Suddenly, the pressure is too much and the plates jerk past each other. The place where this happens is called the focus. Vibrations go out in all directions through the r ...
Changes to the Earth`s rocks and atmosphere
... movements of the Earth’s crust can cause changes in the surface rocks. The Earth consists of an inner and outer core, then a mantle and finally a thin crust. The Earth’s crust and the upper part of the mantle are cracked into a number of large pieces called tectonic plates. Convection currents withi ...
... movements of the Earth’s crust can cause changes in the surface rocks. The Earth consists of an inner and outer core, then a mantle and finally a thin crust. The Earth’s crust and the upper part of the mantle are cracked into a number of large pieces called tectonic plates. Convection currents withi ...
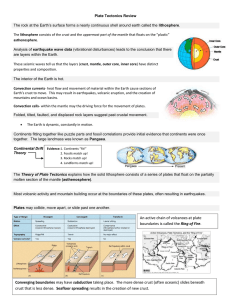
Plate Tectonics Review The rock at the Earth`s surface forms a
... The rock at the Earth’s surface forms a nearly continuous shell around earth called the lithosphere. The lithosphere consists of the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle that floats on the “plastic” asthenosphere. Analysis of earthquake wave data (vibrational disturbances) leads to the conclus ...
... The rock at the Earth’s surface forms a nearly continuous shell around earth called the lithosphere. The lithosphere consists of the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle that floats on the “plastic” asthenosphere. Analysis of earthquake wave data (vibrational disturbances) leads to the conclus ...
The Hadean Eon
... •Found incorporated into younger metamorphic rocks. •Zircon forms in granite - continental crust. •Eroded and incorporated into sedimentary rock. •Sedimentary rock metamorphosed into gneiss. ...
... •Found incorporated into younger metamorphic rocks. •Zircon forms in granite - continental crust. •Eroded and incorporated into sedimentary rock. •Sedimentary rock metamorphosed into gneiss. ...
Human Impact on ecosystems
... Algae are microscopic plants that are usually aquatic, unicellular, and lack true stems, roots, and leaves. Algal blooms occur in both marine and freshwater environments when an algal species outcompetes other species and reproduces rapidly. An algal bloom can still kill fish and other aquatic life ...
... Algae are microscopic plants that are usually aquatic, unicellular, and lack true stems, roots, and leaves. Algal blooms occur in both marine and freshwater environments when an algal species outcompetes other species and reproduces rapidly. An algal bloom can still kill fish and other aquatic life ...
Science Notes December 1, 2010 SOL 5.7 (b, c, d) Scientists are
... The extreme pressure and heat from the Earth can cause materials in the Earth to move or shift. This heat and pressure cause large continent-sized blocks called plates to move slowly about the Earth’s surface. They are not connected to one another, but move freely about. These plates can bump, push, ...
... The extreme pressure and heat from the Earth can cause materials in the Earth to move or shift. This heat and pressure cause large continent-sized blocks called plates to move slowly about the Earth’s surface. They are not connected to one another, but move freely about. These plates can bump, push, ...
Backward Design Learning Plan - UNC
... Earthquakes often occur along the boundaries between colliding plates, and molten rock from below creates pressure that is released by volcanic eruptions, helping to build up mountains. Under the ocean basins, molten rock may well up between separating plates to create new ocean floor. Volcanic acti ...
... Earthquakes often occur along the boundaries between colliding plates, and molten rock from below creates pressure that is released by volcanic eruptions, helping to build up mountains. Under the ocean basins, molten rock may well up between separating plates to create new ocean floor. Volcanic acti ...
Lecture #1
... Less dense than core. – Crust - cool, lightweight, brittle outermost layer. Floats on top of mantle. ...
... Less dense than core. – Crust - cool, lightweight, brittle outermost layer. Floats on top of mantle. ...
Chapter_1_Section1
... Geologists – scientists who study the forces that make and shape the planet Earth Rock – the material that forms Earth’s hard surface Geologists study: the processes that create Earth’s features search for clues about Earth’s history study the chemical and physical properties of rock map where diffe ...
... Geologists – scientists who study the forces that make and shape the planet Earth Rock – the material that forms Earth’s hard surface Geologists study: the processes that create Earth’s features search for clues about Earth’s history study the chemical and physical properties of rock map where diffe ...
The Earth was extensively molten in the first 100 million years after
... The Earth was extensively molten in the first 100 million years after its formation. In that span of time, it acquired much of its present-day structure: the metallic core segregated and sank towards the center, while the mantle and crust separated at the surface. The primordial evolution of the man ...
... The Earth was extensively molten in the first 100 million years after its formation. In that span of time, it acquired much of its present-day structure: the metallic core segregated and sank towards the center, while the mantle and crust separated at the surface. The primordial evolution of the man ...
Chapter 26
... Similarities in inner membrane structures and functions Both have their own circular DNA ...
... Similarities in inner membrane structures and functions Both have their own circular DNA ...
HISTORY OF THE OCEANS
... • 2/3rds of the earth’s land area is found in the Northern Hemisphere which is only 61% ocean. • About 80% of the Southern Hemisphere is ocean. • Oceans play a crucial role in regulating our climate and atmosphere. • Without water, life would be impossible. ...
... • 2/3rds of the earth’s land area is found in the Northern Hemisphere which is only 61% ocean. • About 80% of the Southern Hemisphere is ocean. • Oceans play a crucial role in regulating our climate and atmosphere. • Without water, life would be impossible. ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.