Layers of the Earth Poster Project Instructions and
... Should be one paragraph (about 4 sentences) describing some feature, function, or miscellaneous fact about the interior of the Earth and/or its layers. ...
... Should be one paragraph (about 4 sentences) describing some feature, function, or miscellaneous fact about the interior of the Earth and/or its layers. ...
Ocean waves that wear away an island`s shoreline
... 2. Scientists think that the outer core made of liquid iron and nickel, contains convention currents which produce Earth’s magnetic field. 3. The part of the mantle called the asthenosphere is made of soft rock that bends like plastic. 4. Oceanic crust is made up mostly of dense rock called basalt. ...
... 2. Scientists think that the outer core made of liquid iron and nickel, contains convention currents which produce Earth’s magnetic field. 3. The part of the mantle called the asthenosphere is made of soft rock that bends like plastic. 4. Oceanic crust is made up mostly of dense rock called basalt. ...
Lecture32_webpost - UA Atmospheric Sciences
... Pole over thousands of years Changes in the orbital parameters change the incoming solar radiation at the North Pole by about 15% This is likely coupled with a biological response which affects the uptake of carbon dioxide in the ocean These two effects probably are responsible for the regular occur ...
... Pole over thousands of years Changes in the orbital parameters change the incoming solar radiation at the North Pole by about 15% This is likely coupled with a biological response which affects the uptake of carbon dioxide in the ocean These two effects probably are responsible for the regular occur ...
1-Unit4Part1EarthsInterior
... • 3 Sources of Energy that led to the Earth’s hot interior: 1) Kinetic energy of moving bodies striking the Earth (think meteorite impacts) 2) Compression of rock materials due to enormous pressure from material above *3) The decay of unstable, radioactive elements within the rock of the earth * Thi ...
... • 3 Sources of Energy that led to the Earth’s hot interior: 1) Kinetic energy of moving bodies striking the Earth (think meteorite impacts) 2) Compression of rock materials due to enormous pressure from material above *3) The decay of unstable, radioactive elements within the rock of the earth * Thi ...
Chapter 8: Volcanoes The Big Idea: Volcanoes form as a result of
... Section 1: Why Volcanoes Form VOCABULARY: 1. Volcano: a vent or fissure in Earth’s surface through which magma and gases are expelled. 2. Magma: liquid rock produced under Earth’s surface, in the crust and mantle. Igneous rocks form from magma. ...
... Section 1: Why Volcanoes Form VOCABULARY: 1. Volcano: a vent or fissure in Earth’s surface through which magma and gases are expelled. 2. Magma: liquid rock produced under Earth’s surface, in the crust and mantle. Igneous rocks form from magma. ...
Layers of the Earth
... deep; more fluid layer, but not liquid 3. Mesosphere- lowest layer; rigid rock; 660-2900 km deep -temperature increases with depth, as does density ...
... deep; more fluid layer, but not liquid 3. Mesosphere- lowest layer; rigid rock; 660-2900 km deep -temperature increases with depth, as does density ...
Chapter 7, Section 1 - Answer Key
... while the densest compounds make up the core? Heavier elements are pulled to the center of the Earth by gravity. The elements with less mass are further from the center. 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical composition. Crust, mantle, core (outer and inner) 5. Complete Sent ...
... while the densest compounds make up the core? Heavier elements are pulled to the center of the Earth by gravity. The elements with less mass are further from the center. 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical composition. Crust, mantle, core (outer and inner) 5. Complete Sent ...
Due: Monday, January 28, 2013 Quarter 2.5 Assessment Study Guide
... 24. Write an equation that shows how to find the difference in arrival times between the P waves and the surface waves shown in the graph? ...
... 24. Write an equation that shows how to find the difference in arrival times between the P waves and the surface waves shown in the graph? ...
the earth`s life support systems - sohs
... • The biosphere consists of several physical layers that contain: – Air – Water – Soil – Minerals – Life Figure 3-6 ...
... • The biosphere consists of several physical layers that contain: – Air – Water – Soil – Minerals – Life Figure 3-6 ...
Earth 1
... together to form sedimentary rock. c. Characteristics: These rocks are layered. The layers tell the story about how the rock was formed. ...
... together to form sedimentary rock. c. Characteristics: These rocks are layered. The layers tell the story about how the rock was formed. ...
UNIT 5 – Earth`s Internal Structure
... It consists of partially molten rock. It is believed that this is the surface on which the tectonic plates move (the movement of continents). ...
... It consists of partially molten rock. It is believed that this is the surface on which the tectonic plates move (the movement of continents). ...
Translate the text from English into Russian.
... combination of physical and chemical processes led to the differentiation of the earth into major parts: the core, the mantle, and the crust. This is believed to have occurred approximately 4 billion years ago. The Earth’s core is believed to consist of two regions. The inner core is solid, while th ...
... combination of physical and chemical processes led to the differentiation of the earth into major parts: the core, the mantle, and the crust. This is believed to have occurred approximately 4 billion years ago. The Earth’s core is believed to consist of two regions. The inner core is solid, while th ...
The Dynamic Crust Topic 4 Topic 12 in Review Book
... Orogeny refers to times of mountain building ...
... Orogeny refers to times of mountain building ...
The History of Continental Drift
... Errors in Wegener’s data led to easy arguments against some conclusions. ...
... Errors in Wegener’s data led to easy arguments against some conclusions. ...
Document
... (we now know that they are moving apart at a rate up to 3 cm per year) The second Biggest problem: the mechanism that Wegener proposed was impossible and easily demonstrated to be so. ...
... (we now know that they are moving apart at a rate up to 3 cm per year) The second Biggest problem: the mechanism that Wegener proposed was impossible and easily demonstrated to be so. ...
Continental Drift
... (we now know that they are moving apart at a rate up to 3 cm per year) The second Biggest problem: the mechanism that Wegener proposed was impossible and easily demonstrated to be so. ...
... (we now know that they are moving apart at a rate up to 3 cm per year) The second Biggest problem: the mechanism that Wegener proposed was impossible and easily demonstrated to be so. ...
Markville CGC 1D1
... The fast moving, high-altitude air that forms a boundary between cold and warm air masses is called: a) an air mass b) the prevailing Westerlies c) the polar jet stream d) the Gulf Stream ...
... The fast moving, high-altitude air that forms a boundary between cold and warm air masses is called: a) an air mass b) the prevailing Westerlies c) the polar jet stream d) the Gulf Stream ...
Article - Cross Section of the Earth
... Scientists believe that Earth began as a molten ball over 4.5 billion years ago. Like any other molten body, as Earth cooled, the lighter materials floated to the surface and the heavier materials sank toward the interior. You may have observed the same process after letting gravy sit for a while. A ...
... Scientists believe that Earth began as a molten ball over 4.5 billion years ago. Like any other molten body, as Earth cooled, the lighter materials floated to the surface and the heavier materials sank toward the interior. You may have observed the same process after letting gravy sit for a while. A ...
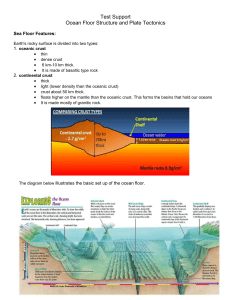
Unit 5: Ocean Floor Structure and Plate Tectonics
... Test Support Ocean Floor Structure and Plate Tectonics Sea Floor Features: Earth's rocky surface is divided into two types: 1. oceanic crust thin dense crust 6 km-10 km thick. It is made of basaltic type rock 2. continental crust thick light (lower density than the oceanic crust) crust ...
... Test Support Ocean Floor Structure and Plate Tectonics Sea Floor Features: Earth's rocky surface is divided into two types: 1. oceanic crust thin dense crust 6 km-10 km thick. It is made of basaltic type rock 2. continental crust thick light (lower density than the oceanic crust) crust ...
Unit 7 Earth`s Interior
... The Four Layers The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, or is under the ocean. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow (like hot pudding). The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into ...
... The Four Layers The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, or is under the ocean. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow (like hot pudding). The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.