Geography 12
... fracture or cracking the earth’s crust, usually occurring where plates are separating, sliding past one another, or colliding Vulcanism: the movement of molten rock, or magma, beneath or above the earth’s surface Hot Spot: a point on the earth’s surface where strong upward convection currents or plu ...
... fracture or cracking the earth’s crust, usually occurring where plates are separating, sliding past one another, or colliding Vulcanism: the movement of molten rock, or magma, beneath or above the earth’s surface Hot Spot: a point on the earth’s surface where strong upward convection currents or plu ...
Earth’s Layers
... • Located below the crust. (Egg White) • It is the largest layer (about 2900 km thick). Rock layers are movable. (plastic) ...
... • Located below the crust. (Egg White) • It is the largest layer (about 2900 km thick). Rock layers are movable. (plastic) ...
First Hour Exam, Fall, 2015
... d. are the principal minerals in basalt and gabbro. e. all of the above. 15. Most plutonic rocks tend to be intermediate or felsic in character. Dikes and sills, however, are often mafic. This is because a. mafic magmas are always more likely to crystallize underground. b. mafic magmas are normally ...
... d. are the principal minerals in basalt and gabbro. e. all of the above. 15. Most plutonic rocks tend to be intermediate or felsic in character. Dikes and sills, however, are often mafic. This is because a. mafic magmas are always more likely to crystallize underground. b. mafic magmas are normally ...
Chapter 17 Review game
... plant required a more temperate climate, so areas like Antarctica must have been closer to the Equator. ...
... plant required a more temperate climate, so areas like Antarctica must have been closer to the Equator. ...
Little Ice Age Module: Cycle A Group
... How should humans protect themselves from the harmful effects of volcanoes without reversing any beneficial or necessary natural processes? Was this eruption caused by an earthquake? If so, could something like this occur to Seattle with Mt. Rainier? Were there other events that were occurring aroun ...
... How should humans protect themselves from the harmful effects of volcanoes without reversing any beneficial or necessary natural processes? Was this eruption caused by an earthquake? If so, could something like this occur to Seattle with Mt. Rainier? Were there other events that were occurring aroun ...
The Next Pangaea
... to an end—in about 100 million years. That’s the theory put forth by Ross Mitchell, a geologist at Yale University, in a new study published in the journal Nature. In the early 1900s Alfred Wegener famously proposed the idea that Earth’s tectonic plates are slowly moving around the planet. About 300 ...
... to an end—in about 100 million years. That’s the theory put forth by Ross Mitchell, a geologist at Yale University, in a new study published in the journal Nature. In the early 1900s Alfred Wegener famously proposed the idea that Earth’s tectonic plates are slowly moving around the planet. About 300 ...
Name - mrspilkington
... mountains have a deep crack that runs through them. It is called a rift valley. Seafloor spreading happens here. It is a slow, regular process. There are no explosive bursts like volcanic eruptions on land. ...
... mountains have a deep crack that runs through them. It is called a rift valley. Seafloor spreading happens here. It is a slow, regular process. There are no explosive bursts like volcanic eruptions on land. ...
Plate Tectonics Tutoiral Questions
... plates move at the surface. Both Earth’s surface and interior are in motion. Solid rock in the mantle can be softened and shaped when subjected to the heat and pressure within Earth’s interior over millions of years. Subduction processes are believed by many scientists to be the driving force of pla ...
... plates move at the surface. Both Earth’s surface and interior are in motion. Solid rock in the mantle can be softened and shaped when subjected to the heat and pressure within Earth’s interior over millions of years. Subduction processes are believed by many scientists to be the driving force of pla ...
2017-Earth Forces-Study Guide and Web Quest
... Some of the plates contain ________________ and others are mostly under the __________. The type of crust that underlies the continents is called ________________ crust, while the type found under the oceans is called ____________ crust. ________________ crust is thicker — about _______________ (35 ...
... Some of the plates contain ________________ and others are mostly under the __________. The type of crust that underlies the continents is called ________________ crust, while the type found under the oceans is called ____________ crust. ________________ crust is thicker — about _______________ (35 ...
Lithosphere
... effective penetration depth to about 0.5 m for diurnal oscillations and to about 10 m for year around seasonal oscillations. A few meters below ground, diurnal and seasonal temperature variations are so damped that caves (and thick walls) on temperate climates are warm in winter and fresh in summer, ...
... effective penetration depth to about 0.5 m for diurnal oscillations and to about 10 m for year around seasonal oscillations. A few meters below ground, diurnal and seasonal temperature variations are so damped that caves (and thick walls) on temperate climates are warm in winter and fresh in summer, ...
this process
... 12. What outgassed molecule chemically reacted with the O2 produced through photochemical dissociation, helped to created even more nitrogen in our atmosphere? ANS: Ammonia (NH3) 13. Where is Earth’s biosphere? ANS: It is above, on, and under the surface of the Earth…wherever there is life. ...
... 12. What outgassed molecule chemically reacted with the O2 produced through photochemical dissociation, helped to created even more nitrogen in our atmosphere? ANS: Ammonia (NH3) 13. Where is Earth’s biosphere? ANS: It is above, on, and under the surface of the Earth…wherever there is life. ...
ppt
... Weathering refers to the breaking down of rock into small particles, which results from physical and chemical forces such as ________, grinding, flowing water, oxygen etc. Plants and __________ also contribute actively to weathering. These smaller particles are then subject to being washed or blown ...
... Weathering refers to the breaking down of rock into small particles, which results from physical and chemical forces such as ________, grinding, flowing water, oxygen etc. Plants and __________ also contribute actively to weathering. These smaller particles are then subject to being washed or blown ...
Name Youngblood, Period
... where on the Earth each type is occurring. (Four parts to each type of boundaries) ...
... where on the Earth each type is occurring. (Four parts to each type of boundaries) ...
Geology Test08
... present location of part of the Hawaiian Island chain. These volcanic islands may have formed as the Pacific Plate moved over a mantle hot spot. This diagram provides evidence that the Pacific Crustal Plate was moving toward the ...
... present location of part of the Hawaiian Island chain. These volcanic islands may have formed as the Pacific Plate moved over a mantle hot spot. This diagram provides evidence that the Pacific Crustal Plate was moving toward the ...
Earth Science Vocabulary Chapter 9: Plate Tectonics Section 9.1
... Divergent Boundary- a region where the rigid plates are moving apart, typified by the oceanic ridges Convergent Boundary- a boundary in which two plates move together Transform Fault Boundary- a boundary in which two plates slide past eachother without creating or destroying lithosphere Section 9.3: ...
... Divergent Boundary- a region where the rigid plates are moving apart, typified by the oceanic ridges Convergent Boundary- a boundary in which two plates move together Transform Fault Boundary- a boundary in which two plates slide past eachother without creating or destroying lithosphere Section 9.3: ...
1. Divergent Boundary
... Also known as spreading boundary, a divergent boundary occurs where two plates move apart, allowing magma, or molten rock, to rise from the Earth's interior to fill in the gap. The two plates move away from each other like two conveyor belts moving in opposite directions. The Earth's longest mountai ...
... Also known as spreading boundary, a divergent boundary occurs where two plates move apart, allowing magma, or molten rock, to rise from the Earth's interior to fill in the gap. The two plates move away from each other like two conveyor belts moving in opposite directions. The Earth's longest mountai ...
UNIT 5 Text Where to Look for Petroleum Grammar Revision
... the former, water is water and in the latter, water is ice. 2. The earth movement that causes earthquakes may be either volcanic or tectonic; the latter type being more common. 3. Even a casual observer of nature knows from common experience that certain animals and plants are confined to definite p ...
... the former, water is water and in the latter, water is ice. 2. The earth movement that causes earthquakes may be either volcanic or tectonic; the latter type being more common. 3. Even a casual observer of nature knows from common experience that certain animals and plants are confined to definite p ...
Geological time scale is hierarchical
... • The widths of alternating magnetic stripes on the opposite sides of a ridge are often roughly symmetrical, and the stripes are generally parallel to the long axis of the ridge. • The banding pattern of any one ocean closely matches that of the others, and the ocean patterns correspond approximatel ...
... • The widths of alternating magnetic stripes on the opposite sides of a ridge are often roughly symmetrical, and the stripes are generally parallel to the long axis of the ridge. • The banding pattern of any one ocean closely matches that of the others, and the ocean patterns correspond approximatel ...
Midterm Exam - Heritage Collegiate
... (D) The rock unit above is older than the rock unit below. 3. Volcanic ash was deposited at the bottom of a lake as varves. If the sequence contains 240 alternating layers of light and dark sediment, how many years ago did the volcanic eruption occur? (A) 30 (B) 60 (C) 120 (D) 240 4. Which represent ...
... (D) The rock unit above is older than the rock unit below. 3. Volcanic ash was deposited at the bottom of a lake as varves. If the sequence contains 240 alternating layers of light and dark sediment, how many years ago did the volcanic eruption occur? (A) 30 (B) 60 (C) 120 (D) 240 4. Which represent ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics and Convection Currents
... In the late 1800s, a German scientist, Alfred Wegener, began studying this question. In 1912, he proposed a hypothesis known as continental drift. According to Wegener’s hypothesis, Earth’s continents were once joined in a single landmass and gradually moved, or drifted, apart. For many years, peopl ...
... In the late 1800s, a German scientist, Alfred Wegener, began studying this question. In 1912, he proposed a hypothesis known as continental drift. According to Wegener’s hypothesis, Earth’s continents were once joined in a single landmass and gradually moved, or drifted, apart. For many years, peopl ...
CHAPTER 15: GEOLOGY AND NONRENEWABLE MINERAL
... 1. The crust is soil and rock that floats on a mantle of partly melted and solid rock. 2. The core is intensely hot. It has a solid inner part surrounded by a liquid core of molten or semisolid material. 3. The mantle is a thick, solid zone. It is mostly solid rock, but an area called the asthenosph ...
... 1. The crust is soil and rock that floats on a mantle of partly melted and solid rock. 2. The core is intensely hot. It has a solid inner part surrounded by a liquid core of molten or semisolid material. 3. The mantle is a thick, solid zone. It is mostly solid rock, but an area called the asthenosph ...
mantle - Uplift Mighty Prep
... When it all began… • 4.5 billion years ago, the Earth was in a fluid state. • As the Earth began to cool, the materials began to separate because of their densities. What do you think happened to the more dense materials during the separation? What about the less dense materials? ...
... When it all began… • 4.5 billion years ago, the Earth was in a fluid state. • As the Earth began to cool, the materials began to separate because of their densities. What do you think happened to the more dense materials during the separation? What about the less dense materials? ...
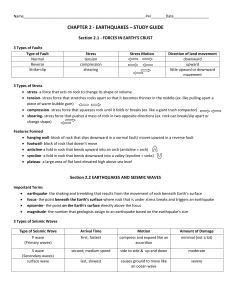
CHAPTER 2 - EARTHQUAKES – STUDY GUIDE
... seismogram- pattern of lines on a seismograph friction- force that opposes the motion of one surface as it moves across another surface ...
... seismogram- pattern of lines on a seismograph friction- force that opposes the motion of one surface as it moves across another surface ...
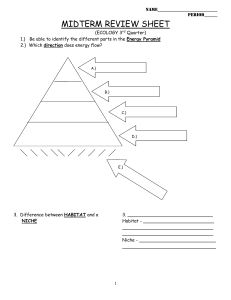
midterm review sheet
... 9.) Be able to explain/draw the Convection Cycle and how it causes plate movement. Also understand Seafloor Spreading and how it is evidence of Plate Tectonics. ...
... 9.) Be able to explain/draw the Convection Cycle and how it causes plate movement. Also understand Seafloor Spreading and how it is evidence of Plate Tectonics. ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.