Plate Tectonics Lecture Notes Page
... approximately 10,000+ foot high volcanic mountain chain that bisects the oceans). 2. The ocean floor is young (less than 200 million years old, compared to the 4 billion age of the continents). 3. Age progression on sea floor (oldest adjacent to the continents and youngest at mid-ocean ridges). ...
... approximately 10,000+ foot high volcanic mountain chain that bisects the oceans). 2. The ocean floor is young (less than 200 million years old, compared to the 4 billion age of the continents). 3. Age progression on sea floor (oldest adjacent to the continents and youngest at mid-ocean ridges). ...
Applying Concepts 33. a. Index fossils in each sequence can be
... 9. Fossils of coastal organisms, such as stromatolites, have been found along the Rocky Mountains. Also present are sedimentary rocks, which are indicative of coastal river deltas. And, finally, the presence of ripple marks, cracks, and salt crystals provide evidence of an ancient coastline. 10. Ear ...
... 9. Fossils of coastal organisms, such as stromatolites, have been found along the Rocky Mountains. Also present are sedimentary rocks, which are indicative of coastal river deltas. And, finally, the presence of ripple marks, cracks, and salt crystals provide evidence of an ancient coastline. 10. Ear ...
19.1 Forces Within Earth
... 30 to 100+ years by studying historic records & seismic gaps, based on the idea earthquakes are cyclical, help in determination of building codes; Are predictions accurate? What is a seismic gap? ...
... 30 to 100+ years by studying historic records & seismic gaps, based on the idea earthquakes are cyclical, help in determination of building codes; Are predictions accurate? What is a seismic gap? ...
beyond_the_volcano
... exemplars of the crosscutting concept. A weak connection indicates that there is either no part of the crosscutting concepts applies to the activity or the activity would have to be modified to develop these connections. ...
... exemplars of the crosscutting concept. A weak connection indicates that there is either no part of the crosscutting concepts applies to the activity or the activity would have to be modified to develop these connections. ...
color
... (Sun & most planets; Uranus exception) Planets contain 98% of angular momentum Spacing and Composition Spacing increases with distance (roughly logarithmic) Composition varies with distance inner 4: rocky, small, thin atmospheres outer 4: gaseous, large, mostly atmosphere Sun contains 99.9% of mass ...
... (Sun & most planets; Uranus exception) Planets contain 98% of angular momentum Spacing and Composition Spacing increases with distance (roughly logarithmic) Composition varies with distance inner 4: rocky, small, thin atmospheres outer 4: gaseous, large, mostly atmosphere Sun contains 99.9% of mass ...
06 Science FMA March 11
... 20 Imagine that you can travel to the center of the Earth. The diagram above lists the average thickness of each layer of the Earth. How far from the center of the Earth would you be if you were leaving the lithosphere and entering the asthenosphere in kilometers? Record and bubble your answer. ...
... 20 Imagine that you can travel to the center of the Earth. The diagram above lists the average thickness of each layer of the Earth. How far from the center of the Earth would you be if you were leaving the lithosphere and entering the asthenosphere in kilometers? Record and bubble your answer. ...
Go to the following link to start the activity http://www.learner.org
... 50‐40 million years ago ...
... 50‐40 million years ago ...
Study questions for Quiz 8 Plate Tectonics – more questions on
... What was the paleontological evidence for continental drift? What is the evidence from structure and rock type for continental drift? What is the evidence from glaciation for continental drift? What is paleomagnetism? What two lines of paleomagnetic data support the idea of seafloor spreading? What ...
... What was the paleontological evidence for continental drift? What is the evidence from structure and rock type for continental drift? What is the evidence from glaciation for continental drift? What is paleomagnetism? What two lines of paleomagnetic data support the idea of seafloor spreading? What ...
Plate Tectonics Part 1
... • Fossils from same or similar species found on continents separated by oceans today. ...
... • Fossils from same or similar species found on continents separated by oceans today. ...
MS Word
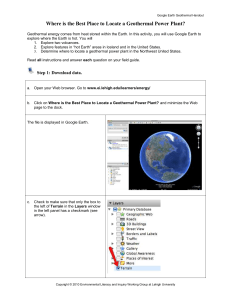
... Geothermal energy comes from heat stored within the Earth. In this activity, you will use Google Earth to explore where the Earth is hot. You will 1. Explore two volcanoes. 2. Explore features in “hot Earth” areas in Iceland and in the United States. 3. Determine where to locate a geothermal power p ...
... Geothermal energy comes from heat stored within the Earth. In this activity, you will use Google Earth to explore where the Earth is hot. You will 1. Explore two volcanoes. 2. Explore features in “hot Earth” areas in Iceland and in the United States. 3. Determine where to locate a geothermal power p ...
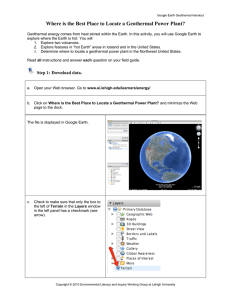
Where is the Best Place to Locate a Geothermal Power Plant?
... A hotspot is an area with high volcanic activity because of high heat flow from within the Earth. The country of Iceland is located on a hotspot. b. Double-click on Askja in the Places window to view it. NOTE: Uncheck the box to the left of Iceland Hotspot in the Places window. This will turn off th ...
... A hotspot is an area with high volcanic activity because of high heat flow from within the Earth. The country of Iceland is located on a hotspot. b. Double-click on Askja in the Places window to view it. NOTE: Uncheck the box to the left of Iceland Hotspot in the Places window. This will turn off th ...
Plate Tectonics Review Sheet
... pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant. slow motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle There are _3_ kinds of plate boundaries. convergent boundary - a place where two plates come together, or converge divergent boundary - a place where two plates move apart, or diverge: sea floor s ...
... pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant. slow motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle There are _3_ kinds of plate boundaries. convergent boundary - a place where two plates come together, or converge divergent boundary - a place where two plates move apart, or diverge: sea floor s ...
Chapter 3 section 1 2015
... and transported form one place to another by a natural agent, such as wind, water, ice or gravity. • Erosion wears down rocks and makes them smoother as times passes. Older mountains are therefore smoother than younger ones. ...
... and transported form one place to another by a natural agent, such as wind, water, ice or gravity. • Erosion wears down rocks and makes them smoother as times passes. Older mountains are therefore smoother than younger ones. ...
Mountain Belts formed at Divergent and Convergent Boundaries
... Mid Ocean Ridges • Continuous underwater mountain chains that extend up to 60,000 km around the globe. • Generally around 1500km wide and have peaks around 3km high. • Site of most volcanism on earth ...
... Mid Ocean Ridges • Continuous underwater mountain chains that extend up to 60,000 km around the globe. • Generally around 1500km wide and have peaks around 3km high. • Site of most volcanism on earth ...
continent, continental drift, seafloor, ocean floor, tectonic
... E.SE.06.51 Explain plate tectonic movement and that the lithospheric plates move centimeters each year. Instructional Clarifications 1. Explain is to clearly describe by means of illustrations (drawing), demonstrations, written reports, or verbally the movement of lithospheric plates. 2. The Earth’s ...
... E.SE.06.51 Explain plate tectonic movement and that the lithospheric plates move centimeters each year. Instructional Clarifications 1. Explain is to clearly describe by means of illustrations (drawing), demonstrations, written reports, or verbally the movement of lithospheric plates. 2. The Earth’s ...
The Terrestrial Worlds
... Moon was formed) by large impacts cracking through the crust and the consequent magma flow from the Moon’s mantle. Asymmetry of maria between the two sides of Moon is caused by differences in crust thickness (which ranges in depth from 60-100 km and is thinner on Earth-facing side). This asymmetry a ...
... Moon was formed) by large impacts cracking through the crust and the consequent magma flow from the Moon’s mantle. Asymmetry of maria between the two sides of Moon is caused by differences in crust thickness (which ranges in depth from 60-100 km and is thinner on Earth-facing side). This asymmetry a ...
Dr. Thorsten Becker, UT Austin Abstract: Plate tectonics can be
... Plate tectonics can be understood from the dynamics of the cold, top thermal boundary layer of Earth's mantle which is convecting over timescales of millions of years. However, how forces are transmitted depends on the flow strength of rocks (viscosity). For example, the low viscosity of the region ...
... Plate tectonics can be understood from the dynamics of the cold, top thermal boundary layer of Earth's mantle which is convecting over timescales of millions of years. However, how forces are transmitted depends on the flow strength of rocks (viscosity). For example, the low viscosity of the region ...
Dynamic Crust
... 3. ________________________________________: results from the ______________________ movement of a tectonic plate over a “fixed” point in the mantel that is _________________________ than the mantel around it. a) Causes: (1) A narrow _____________________ of hot ______________________ convecting up ...
... 3. ________________________________________: results from the ______________________ movement of a tectonic plate over a “fixed” point in the mantel that is _________________________ than the mantel around it. a) Causes: (1) A narrow _____________________ of hot ______________________ convecting up ...
Plate Tectonics - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Divergent Plate Boundaries • Plates are being pulled apart by convection currents in the mantle. • As the plates separate along the boundary, the block between the ...
... Divergent Plate Boundaries • Plates are being pulled apart by convection currents in the mantle. • As the plates separate along the boundary, the block between the ...
Using Earthquakes To Study the Earth`s Interior
... Ever since its formation—some 4.5 billion years ago—the earth has been losing heat. The deeper one goes inside the earth, the greater the temperature becomes. The pressure rises, too. The earth’s outer layer, or crust, is the coolest and least dense of all the layers inside the earth. (You might com ...
... Ever since its formation—some 4.5 billion years ago—the earth has been losing heat. The deeper one goes inside the earth, the greater the temperature becomes. The pressure rises, too. The earth’s outer layer, or crust, is the coolest and least dense of all the layers inside the earth. (You might com ...
plate tectonics
... A hot spot is a very hot region deep within the Earth. It is usually responsible for volcanic activity. Volcanic activity happens whenever red-hot material from the Earths thickest layer, the mantle, rises up and leaks through to the Earths surface, the crust. The red-hot material, called magma, som ...
... A hot spot is a very hot region deep within the Earth. It is usually responsible for volcanic activity. Volcanic activity happens whenever red-hot material from the Earths thickest layer, the mantle, rises up and leaks through to the Earths surface, the crust. The red-hot material, called magma, som ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.