2nd_nine_weeks_exam_review_answers
... the ocean floor. Explain why the magnetism in the rocks alternates. Earth’s magnetic field has continually reversed. The alignment of the iron atoms alternates depending on the polarity of Earth at the time the seafloor was created. 4. List the four evidences for continental drift. a. Puzzle-like fi ...
... the ocean floor. Explain why the magnetism in the rocks alternates. Earth’s magnetic field has continually reversed. The alignment of the iron atoms alternates depending on the polarity of Earth at the time the seafloor was created. 4. List the four evidences for continental drift. a. Puzzle-like fi ...
Plate tectonics in a hotter Earth?
... Alternative tectonic models: Flake tectonics (Hoffman & Ranalli, 1988) Today, continental lithosphere shows ‘sandwich’ rheology. In past maybe all plates showed that, with less plate and more ductile material in between. The two layers might have started convecting separately. ...
... Alternative tectonic models: Flake tectonics (Hoffman & Ranalli, 1988) Today, continental lithosphere shows ‘sandwich’ rheology. In past maybe all plates showed that, with less plate and more ductile material in between. The two layers might have started convecting separately. ...
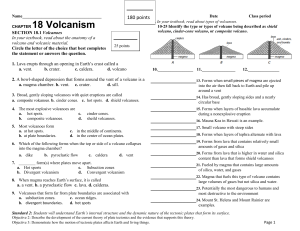
CHAPTER 18 Volcanism
... The greatest challenge for mountain climbers is Mt. Everest, whose peak rises 8,872 meters above sea level. This is the highest mountain in the world, though many mountains around it are almost as high. Mt. Everest is in the Himalayas, a series of massive ranges that extends 2,500 kilometers across ...
... The greatest challenge for mountain climbers is Mt. Everest, whose peak rises 8,872 meters above sea level. This is the highest mountain in the world, though many mountains around it are almost as high. Mt. Everest is in the Himalayas, a series of massive ranges that extends 2,500 kilometers across ...
Plate Tectonic, Earthquakes, and Volcanoes Test Review
... i. __Crust____________- the thinnest layer. We live on it. Made up of two types: continental (less dense/granite) and oceanic (more dense/ basalt). Lighter minerals (silicates) ii. ___Mantle_________- Magnesium and iron. Makes up most of Earth’s mass. We have never drilled to it. ...
... i. __Crust____________- the thinnest layer. We live on it. Made up of two types: continental (less dense/granite) and oceanic (more dense/ basalt). Lighter minerals (silicates) ii. ___Mantle_________- Magnesium and iron. Makes up most of Earth’s mass. We have never drilled to it. ...
File
... • Movement resembles ripples in a pond of water • Travels at high speeds( 500-800 km/hr) in deep seas, long wave-lengths • Cant be seen or detected from the air. • As they approach shores, speed is reuced and they attain enormous height>10 m to 30 m ...
... • Movement resembles ripples in a pond of water • Travels at high speeds( 500-800 km/hr) in deep seas, long wave-lengths • Cant be seen or detected from the air. • As they approach shores, speed is reuced and they attain enormous height>10 m to 30 m ...
Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10/e
... Plummer & Carlson Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Plummer & Carlson Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Slides - Powerpoint - University of Toronto Physics
... • Fourth heat transfer mechanism, not mentioned in Hewitt • Molecules in a liquid are continuously moving and jiggling against one another • At the surface, sometimes a collision is such that a molecule ends up with enough energy to escape • When the molecule leaves the liquid, it takes thermal ene ...
... • Fourth heat transfer mechanism, not mentioned in Hewitt • Molecules in a liquid are continuously moving and jiggling against one another • At the surface, sometimes a collision is such that a molecule ends up with enough energy to escape • When the molecule leaves the liquid, it takes thermal ene ...
Chapter 21 Guided Reading
... and has provided information on ________________________. Volcanoes and earthquakes often occur where ________________________ come together. At these ________________________, many other dramatic geological features, such as ___________________ and ___________________ can occur. ...
... and has provided information on ________________________. Volcanoes and earthquakes often occur where ________________________ come together. At these ________________________, many other dramatic geological features, such as ___________________ and ___________________ can occur. ...
ESVolcanoes - Cole Camp R-1
... Then an explosive eruption occurs, depositing large amounts of tephra around the vent. The explosive eruption is followed again by quiet lava flows. The resulting cone is formed of alternating layers of hardened lava flows and tephra. Composite cones, also known as ________________________________ ...
... Then an explosive eruption occurs, depositing large amounts of tephra around the vent. The explosive eruption is followed again by quiet lava flows. The resulting cone is formed of alternating layers of hardened lava flows and tephra. Composite cones, also known as ________________________________ ...
Volcanoes, Earthquakes, Islands . . . Oh My!
... What lies beneath the tectonic plates? • Below the lithosphere is the asthenosphere, a layer that is solid, but flows. ...
... What lies beneath the tectonic plates? • Below the lithosphere is the asthenosphere, a layer that is solid, but flows. ...
Practice Exam #1
... 4. Why must a planet with divergent plate boundaries also have convergent plate boundaries? 5. How does the temperature of a substance affect its volume, density and buoyancy? 6. What is the energy source and driving mechanism for the movement of plates? Describe how this process works. 7. Two ident ...
... 4. Why must a planet with divergent plate boundaries also have convergent plate boundaries? 5. How does the temperature of a substance affect its volume, density and buoyancy? 6. What is the energy source and driving mechanism for the movement of plates? Describe how this process works. 7. Two ident ...
New insights into volcanic activity on the ocean floor
... In the case of the break-up of America from Europe, massive volcanic activity occurred along The red zone indicates ancient eruptions that happened the rift because a previous geological event had when North America split from Europe thinned the plate, according to today's study. This provided a foc ...
... In the case of the break-up of America from Europe, massive volcanic activity occurred along The red zone indicates ancient eruptions that happened the rift because a previous geological event had when North America split from Europe thinned the plate, according to today's study. This provided a foc ...
Name
... What is a hot spot? What has it formed? A hot spot is an area of volcanic activity in the MIDDLE of a plate. The plate above the hotspot shifts and forms a chain of volcanoes. ...
... What is a hot spot? What has it formed? A hot spot is an area of volcanic activity in the MIDDLE of a plate. The plate above the hotspot shifts and forms a chain of volcanoes. ...
LFS,_201,_202,_204_Earth_Science,_Gr._9,_15_pgs
... Explain how the Earth is composed of a number of dynamic, interacting systems exchanging energy or matter. Lesson Essential Questions: How has the rock cycle created features that we see today? Competencies: Analyze features caused by interaction of processes that change Earth’s surface. (How wind a ...
... Explain how the Earth is composed of a number of dynamic, interacting systems exchanging energy or matter. Lesson Essential Questions: How has the rock cycle created features that we see today? Competencies: Analyze features caused by interaction of processes that change Earth’s surface. (How wind a ...
OCR ASA Level Geography Exploring Oceans Learner Resource 1
... In the North Atlantic, the Sohm Plain has an area of 900,000 km2. http://www.britannica.com/science/abyssal-plain ...
... In the North Atlantic, the Sohm Plain has an area of 900,000 km2. http://www.britannica.com/science/abyssal-plain ...
Group Quiz Review Game
... 1a. This is an area of volcanic activity created by a weakened area of the earth’s crust. 2a. It contains the oldest rocks known. 3a. It is located where magma rises to the surface of the oceanic crust. 4a. It creates composite volcanoes from the melting of low-density crust. 5a. It is the longest m ...
... 1a. This is an area of volcanic activity created by a weakened area of the earth’s crust. 2a. It contains the oldest rocks known. 3a. It is located where magma rises to the surface of the oceanic crust. 4a. It creates composite volcanoes from the melting of low-density crust. 5a. It is the longest m ...
Why Did the Dinosaurs Die Out?
... The reason no one knows for sure is because the whole thing happened about 65 million years ago. No one was around to see or hear what was going on back then, and no one was around to keep records. What we do know comes mainly from fossil records. Scientists study the fossils themselves, and they st ...
... The reason no one knows for sure is because the whole thing happened about 65 million years ago. No one was around to see or hear what was going on back then, and no one was around to keep records. What we do know comes mainly from fossil records. Scientists study the fossils themselves, and they st ...
How Do Diamonds Form?
... The high temperature and pressure conditions of such an impact are more than adequate to form diamonds. This theory of diamond formation has been supported by the discovery of tiny diamonds around several asteroid impact sites. See Location 3 in the diagrams above and at right. Tiny, sub-millimeter ...
... The high temperature and pressure conditions of such an impact are more than adequate to form diamonds. This theory of diamond formation has been supported by the discovery of tiny diamonds around several asteroid impact sites. See Location 3 in the diagrams above and at right. Tiny, sub-millimeter ...
Plate tectonics web quest Alfred Wegner noticed that Greenland had
... is generated as the plates pull away from each other. Convergent boundaries are where crust is destroyed as one plate dives under another. Transform boundaries are where crust is neither produced nor destroyed as the plates slide horizontally past each other. Plate boundary zones as in broad belts i ...
... is generated as the plates pull away from each other. Convergent boundaries are where crust is destroyed as one plate dives under another. Transform boundaries are where crust is neither produced nor destroyed as the plates slide horizontally past each other. Plate boundary zones as in broad belts i ...
World Geography 3202/3200
... two converging plates. The tremendous compressional forces literally fold the thin crust in to mountains. Remember this occurs over millions of years. Volcanoes can occur at subduction zones or at ridge zones. At subduction zones the compressional forces sometimes leave a crack in the crust that all ...
... two converging plates. The tremendous compressional forces literally fold the thin crust in to mountains. Remember this occurs over millions of years. Volcanoes can occur at subduction zones or at ridge zones. At subduction zones the compressional forces sometimes leave a crack in the crust that all ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.