The structure of the earth – a plenary
... This liquid layer is made of iron and nickel. It is extremely hot in this layer. ...
... This liquid layer is made of iron and nickel. It is extremely hot in this layer. ...
One sentence or phrase only
... c) A right-lateral strike-slip fault is so-called because if you were to stand straddling the fault with one foot on each side of it, your right foot would move forward during an earthquake. d) A dip-slip fault is so called because it dips (is inclined rather than being vertical or ...
... c) A right-lateral strike-slip fault is so-called because if you were to stand straddling the fault with one foot on each side of it, your right foot would move forward during an earthquake. d) A dip-slip fault is so called because it dips (is inclined rather than being vertical or ...
The visual world atlas
... Earth is the largest rocky planet in the Solar System. It offers a variety of ever-changing landscapes. As the immense plates that form Earth’s crust slowly move toward and away from each other, mountains rise, oceans open up, volcanoes erupt. Erosion is also constantly shaping the planet’s relief f ...
... Earth is the largest rocky planet in the Solar System. It offers a variety of ever-changing landscapes. As the immense plates that form Earth’s crust slowly move toward and away from each other, mountains rise, oceans open up, volcanoes erupt. Erosion is also constantly shaping the planet’s relief f ...
Class 9 - Earth and Atmospheric Sciences
... basins’ depth decreases relative to midocean ridges and sea level rises relative to continents, flooding them with water that tends to buffer seasonal temperature fluctuations; when the midocean ridge system shortens and sea-floor spreading slows (as when oceans close and continents collide), ocean ...
... basins’ depth decreases relative to midocean ridges and sea level rises relative to continents, flooding them with water that tends to buffer seasonal temperature fluctuations; when the midocean ridge system shortens and sea-floor spreading slows (as when oceans close and continents collide), ocean ...
Continental Drift - Ms. Mosley
... plates float on this super-heated rock, but they don’t float like rafts float in a swimming pool. The melted rock is very thick like silly putty. So, the plates drift very slowly. ...
... plates float on this super-heated rock, but they don’t float like rafts float in a swimming pool. The melted rock is very thick like silly putty. So, the plates drift very slowly. ...
Bodies of Salt Water (cont.)
... In 1906 the booming city of San Francisco was destroyed by an earthquake that measured 8.6 on the Richter scale. Over 400 people were killed, and 28,000 buildings were reduced to rubble. Another slightly less forceful earthquake struck the city in 1989, doing far less damage and ...
... In 1906 the booming city of San Francisco was destroyed by an earthquake that measured 8.6 on the Richter scale. Over 400 people were killed, and 28,000 buildings were reduced to rubble. Another slightly less forceful earthquake struck the city in 1989, doing far less damage and ...
Geosphere - Oregon Department of Geology and Mineral Industries
... ⑥ Oregon and Washington are connected by 16 bridges that allo ...
... ⑥ Oregon and Washington are connected by 16 bridges that allo ...
Weathering, Erosion and Deposition
... Wind, water, and waves work together in the processes of deposition, weathering, and erosion. A: weathering breaks material apart, erosion carries the pieces away and deposition drops it somewhere else. O: We will investigate different types of deposition, weathering, and erosion. A: The strongest a ...
... Wind, water, and waves work together in the processes of deposition, weathering, and erosion. A: weathering breaks material apart, erosion carries the pieces away and deposition drops it somewhere else. O: We will investigate different types of deposition, weathering, and erosion. A: The strongest a ...
6. Earth`s Structure v2.0
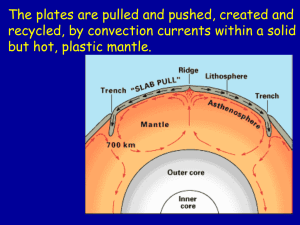
... The ocean floors are continually moving, spreading from the centre and sinking at the edges. Earthquakes and volcanoes occur at plate boundaries, where the tectonic plates meet. Convection currents in the mantle move the tectonic plates on the Earth’s surface. The source of the heat driving th ...
... The ocean floors are continually moving, spreading from the centre and sinking at the edges. Earthquakes and volcanoes occur at plate boundaries, where the tectonic plates meet. Convection currents in the mantle move the tectonic plates on the Earth’s surface. The source of the heat driving th ...
Earth`s structure File
... The ocean floors are continually moving, spreading from the centre and sinking at the edges. Earthquakes and volcanoes occur at plate boundaries, where the tectonic plates meet. Convection currents in the mantle move the tectonic plates on the Earth’s surface. The source of the heat driving th ...
... The ocean floors are continually moving, spreading from the centre and sinking at the edges. Earthquakes and volcanoes occur at plate boundaries, where the tectonic plates meet. Convection currents in the mantle move the tectonic plates on the Earth’s surface. The source of the heat driving th ...
Midterm Review Answers
... arrows represent the directions in which the cracks have widened due to weathering. ...
... arrows represent the directions in which the cracks have widened due to weathering. ...
Seafloor Spreading and Paleomagnetism
... said no • Wegener also thought the continents plowed through ocean floor but there was no evidence for that ...
... said no • Wegener also thought the continents plowed through ocean floor but there was no evidence for that ...
Teaching_Strategies_files/EARTH PROJECT
... You will be creating a 2-sided poster/large piece of paper project depicting various geographical details of the planet Earth. The goal of this project is to introduce you to the physical features of the world in which you live. This will be an extended project that is made up of 3 important steps. ...
... You will be creating a 2-sided poster/large piece of paper project depicting various geographical details of the planet Earth. The goal of this project is to introduce you to the physical features of the world in which you live. This will be an extended project that is made up of 3 important steps. ...
Ocean Bathymetry and Plate Tectonics
... at the ridge axes recycles the entire volume of the ocean in just a few million years and delivers nutrients for transient biological communities on the seafloor. Scientists believe that life originated in these hydrothermal environments and that hydrothermal circulation is critical for maintaining ...
... at the ridge axes recycles the entire volume of the ocean in just a few million years and delivers nutrients for transient biological communities on the seafloor. Scientists believe that life originated in these hydrothermal environments and that hydrothermal circulation is critical for maintaining ...
8.2 Continental Drift Theory and Sea-Floor Spreading
... is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 micro Tesla (0.25 to 0.65 Gauss). It is approximately the field of a magnetic dipole tilted a ...
... is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 micro Tesla (0.25 to 0.65 Gauss). It is approximately the field of a magnetic dipole tilted a ...
Introduction and Tectonic Plates
... influenced his observation that catastrophes may play a role in geologic processes. They observed uplift of 1-2 meters from the quake, suggesting that at 100 year intervals, this could produce the mountain range in roughly 100 million years! ...
... influenced his observation that catastrophes may play a role in geologic processes. They observed uplift of 1-2 meters from the quake, suggesting that at 100 year intervals, this could produce the mountain range in roughly 100 million years! ...
Geography Progress Sheet Earth Forces
... I can describe the crust, mantle, inner core and outer core I can describe why the Earth’s plates move I can discuss the effects of plate movements e.g. volcanoes, fold mountains and earthquakes I can discuss what is meant by Pangaea I can give four pieces of evidence which show that Pangaea existed ...
... I can describe the crust, mantle, inner core and outer core I can describe why the Earth’s plates move I can discuss the effects of plate movements e.g. volcanoes, fold mountains and earthquakes I can discuss what is meant by Pangaea I can give four pieces of evidence which show that Pangaea existed ...
Earth Formation
... Although the mantle is largely hidden from our view, we do see it in places where cracks open up, allowing the molten rock to escape. These are volcanoes, of course, and the liquid rock we see pouring out is the same as you’d find in the mantle. The Earth’s mantle is mostly composed of silicate rock ...
... Although the mantle is largely hidden from our view, we do see it in places where cracks open up, allowing the molten rock to escape. These are volcanoes, of course, and the liquid rock we see pouring out is the same as you’d find in the mantle. The Earth’s mantle is mostly composed of silicate rock ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.