Science
... • Forces, or stresses, that cause rocks to break or move are: o Tension—forces that pull rocks apart o Compression—forces that push or squeeze rocks together o Shearing—forces that cause rocks on either side of faults to push in opposite directions • Forces or stresses (for example, tension and comp ...
... • Forces, or stresses, that cause rocks to break or move are: o Tension—forces that pull rocks apart o Compression—forces that push or squeeze rocks together o Shearing—forces that cause rocks on either side of faults to push in opposite directions • Forces or stresses (for example, tension and comp ...
Word
... 23. As a result of seismic waves interacting with the liquid layer mentioned in the previous question, within what region do seismographs show no record of the earthquake ever having occurred? A. the S-wave shadow zone B. the P-wave shadow zone C. the epicenter D. the opposite side of the earth to ...
... 23. As a result of seismic waves interacting with the liquid layer mentioned in the previous question, within what region do seismographs show no record of the earthquake ever having occurred? A. the S-wave shadow zone B. the P-wave shadow zone C. the epicenter D. the opposite side of the earth to ...
Plate Tectonics
... became accepted by the scientific community. Some continents fit together almost perfectly, e.g. South America and Africa. Similar fossils can be found on different continents. This shows these regions were once very close or joined together. Almost identical patterns of rock layers on different con ...
... became accepted by the scientific community. Some continents fit together almost perfectly, e.g. South America and Africa. Similar fossils can be found on different continents. This shows these regions were once very close or joined together. Almost identical patterns of rock layers on different con ...
Outline
... • The outermost portion of Earth is composed of a mosaic of thin rigid plates (pieces of lithosphere) that move horizontally with respect to one another • Plates interact with each other along their edges (called plate boundaries) • Plate boundaries have a high degree of tectonic activity (mountain ...
... • The outermost portion of Earth is composed of a mosaic of thin rigid plates (pieces of lithosphere) that move horizontally with respect to one another • Plates interact with each other along their edges (called plate boundaries) • Plate boundaries have a high degree of tectonic activity (mountain ...
Internal Structure of the Earth
... gradually (hard to detect, often due to phase changes or a gradual changes in composition). –Gravity: by using very sensitive measuring scales, geophysicists measure the strength of gravity, usually for exploration or missile-lobbing. These measurements have shown that most areas have nearly the sam ...
... gradually (hard to detect, often due to phase changes or a gradual changes in composition). –Gravity: by using very sensitive measuring scales, geophysicists measure the strength of gravity, usually for exploration or missile-lobbing. These measurements have shown that most areas have nearly the sam ...
EARTH`S INTERIOR 23. The average density of the Earth is 5.5 g/cm3
... 23. As a result of seismic waves interacting with the liquid layer mentioned in the previous question, within what region do seismographs show no record of the earthquake ever having occurred? A. the S-wave shadow zone B. the P-wave shadow zone C. the epicenter D. the opposite side of the earth to ...
... 23. As a result of seismic waves interacting with the liquid layer mentioned in the previous question, within what region do seismographs show no record of the earthquake ever having occurred? A. the S-wave shadow zone B. the P-wave shadow zone C. the epicenter D. the opposite side of the earth to ...
CV - Blake Dyer
... The goal of my research is to better understand how sediments record the Earth-system response to changing boundary conditions. The information stored in the sedimentary rock record offers a broad range of past environmental variability that serves as a powerful baseline to differentiate naturally o ...
... The goal of my research is to better understand how sediments record the Earth-system response to changing boundary conditions. The information stored in the sedimentary rock record offers a broad range of past environmental variability that serves as a powerful baseline to differentiate naturally o ...
File - WatchYourSteps
... tectonic boundaries: Convergent - where plates move into one another; Divergent - where plates move apart; Transform - where plates move sideways in relation to each other ...
... tectonic boundaries: Convergent - where plates move into one another; Divergent - where plates move apart; Transform - where plates move sideways in relation to each other ...
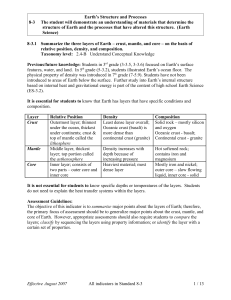
Layers Of The Earth
... 4,400-6,000 degrees Celsius. • The second innermost layer, the Outer Core, Is the liquid layer that creates the magnetic field by swirling around the Outer Core and is between 4,500 and 5,500 degrees Celcius. • The Mantle is the semi-liquid layer that create the majority of the Earths mass and allow ...
... 4,400-6,000 degrees Celsius. • The second innermost layer, the Outer Core, Is the liquid layer that creates the magnetic field by swirling around the Outer Core and is between 4,500 and 5,500 degrees Celcius. • The Mantle is the semi-liquid layer that create the majority of the Earths mass and allow ...
Main Idea: Types of Volcanoes
... the air and piles up around the vent. 2. Small in size less than 500 m high. 3. More explosive than shield volcanoes, because magma contains more water and silica. 4. Magma is more viscous, which leads to more gas ...
... the air and piles up around the vent. 2. Small in size less than 500 m high. 3. More explosive than shield volcanoes, because magma contains more water and silica. 4. Magma is more viscous, which leads to more gas ...
Unit Plan
... Earth’s layers using their data table. Graph thickness (0 to 3000 km) against continental crust, ocean crust, lithosphere, mantle, outer core, and inner core. Graphs should be well labeled and accurate. Discuss and list the characteristics of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Discuss how ...
... Earth’s layers using their data table. Graph thickness (0 to 3000 km) against continental crust, ocean crust, lithosphere, mantle, outer core, and inner core. Graphs should be well labeled and accurate. Discuss and list the characteristics of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Discuss how ...
Fall Semester Exam Review 2016 Define the following organisms
... Define the following organisms and give an example of each in the food web above. 1. Producer – Plants that produce their own energy through photosynthesis such as the Trees and Grasses 2. Consumer – Animals that have to eat to get energy such as the Elephants, Zebras, Hyenas, Cheetahs, Termites, an ...
... Define the following organisms and give an example of each in the food web above. 1. Producer – Plants that produce their own energy through photosynthesis such as the Trees and Grasses 2. Consumer – Animals that have to eat to get energy such as the Elephants, Zebras, Hyenas, Cheetahs, Termites, an ...
Soil
... On steeper slopes, erosion will increase, very little water gets into the soil, and the soil itself is very thin because much of it will be pulled down by gravity Flatter areas will have erosion decrease, lots of water in the soil, and the soil is generally thicker ...
... On steeper slopes, erosion will increase, very little water gets into the soil, and the soil itself is very thin because much of it will be pulled down by gravity Flatter areas will have erosion decrease, lots of water in the soil, and the soil is generally thicker ...
Activity: A Plate Tectonic Puzzle - American Museum of Natural History
... Activity: A Plate Tectonic Puzzle Introduction The Earth’s crust is not a solid shell. It is made up of thick, interconnecting pieces called tectonic plates that fit together like a puzzle. They move atop the underlying mantle, a really thick layer of hot flowing rock. By examining evidence such as ...
... Activity: A Plate Tectonic Puzzle Introduction The Earth’s crust is not a solid shell. It is made up of thick, interconnecting pieces called tectonic plates that fit together like a puzzle. They move atop the underlying mantle, a really thick layer of hot flowing rock. By examining evidence such as ...
Science 10 Provincial Exam Review Sheet Unit 1: Sustainability of
... Describe the following tectonic boundaries, including: transform boundaries, divergent boundaries, convergent boundaries ( oceanic-oceanic crust, oceanic-continental crust, and continental-continental crust) What are the tectonic mapping symbols? How does plate movement produce: epicenters and shall ...
... Describe the following tectonic boundaries, including: transform boundaries, divergent boundaries, convergent boundaries ( oceanic-oceanic crust, oceanic-continental crust, and continental-continental crust) What are the tectonic mapping symbols? How does plate movement produce: epicenters and shall ...
plate tectonics
... • Early 20th century geologists viewed continents as fixed features that could rise and fall, but not move around. • Slow shrinking of the Earth was considered to be the cause of mountain building. • Connections of former land bridges and seaways could explain all stratigraphy and distributions of f ...
... • Early 20th century geologists viewed continents as fixed features that could rise and fall, but not move around. • Slow shrinking of the Earth was considered to be the cause of mountain building. • Connections of former land bridges and seaways could explain all stratigraphy and distributions of f ...
Dynamic Earth
... -S waves cannot travel through • Inner core -iron and nickel -solid due to intense pressure ...
... -S waves cannot travel through • Inner core -iron and nickel -solid due to intense pressure ...
PlateTec1617 - Biloxi Public Schools
... remains in one place as plate above it moves creates chain of small volcanoes no longer active when not over the hot spot Hawaiian Islands--different ages of islands a wave of energy that travels away from the center of an earthquake in all directions increase going into Earth because they are movin ...
... remains in one place as plate above it moves creates chain of small volcanoes no longer active when not over the hot spot Hawaiian Islands--different ages of islands a wave of energy that travels away from the center of an earthquake in all directions increase going into Earth because they are movin ...
Unit Title: Physical Systems and Forces of Change
... In viewing this image (Slide # 6): There are three basic kinds of movement along plate boundaries. 1.) Some plates move toward one another; this is a converging plate boundary. There are two types of converging plate boundaries, one of which involves two of the same type of plate composition (contin ...
... In viewing this image (Slide # 6): There are three basic kinds of movement along plate boundaries. 1.) Some plates move toward one another; this is a converging plate boundary. There are two types of converging plate boundaries, one of which involves two of the same type of plate composition (contin ...
File - Mr Michael mccloskey
... • The Earth is made up of 3 main layers (core, mantle, crust) • On the surface of the Earth are tectonic plates that slowly move around the globe • Plates are made of crust and upper mantle ...
... • The Earth is made up of 3 main layers (core, mantle, crust) • On the surface of the Earth are tectonic plates that slowly move around the globe • Plates are made of crust and upper mantle ...
Unit Title: Physical Systems and Forces of Change
... In viewing this image (Slide # 6): There are three basic kinds of movement along plate boundaries. 1.) Some plates move toward one another; this is a converging plate boundary. There are two types of converging plate boundaries, one of which involves two of the same type of plate composition (contin ...
... In viewing this image (Slide # 6): There are three basic kinds of movement along plate boundaries. 1.) Some plates move toward one another; this is a converging plate boundary. There are two types of converging plate boundaries, one of which involves two of the same type of plate composition (contin ...
Case of the Split Personality Lab #20
... to the lab, notes and textbook pg. 235) 2. Explain what convection currents are by sketching and labeling a picture of convection current movement within the asthenosphere. (Refer to your handout on convection currents) 3. Read about the two models of mantle convection on pg. 270 of your textbook. E ...
... to the lab, notes and textbook pg. 235) 2. Explain what convection currents are by sketching and labeling a picture of convection current movement within the asthenosphere. (Refer to your handout on convection currents) 3. Read about the two models of mantle convection on pg. 270 of your textbook. E ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.