MTHFR C677T and A1298C: Explained In Plain
... MTHFR is also essential to convert folate and folic acid – each a form of Vitamin B9 – into the biologically active form called L-methylfolate (or 5-MTHF). Not to be confused with the enzyme, the MTHFR gene provides the instructions for making that MTHFR enzyme. In other words, it “triggers” product ...
... MTHFR is also essential to convert folate and folic acid – each a form of Vitamin B9 – into the biologically active form called L-methylfolate (or 5-MTHF). Not to be confused with the enzyme, the MTHFR gene provides the instructions for making that MTHFR enzyme. In other words, it “triggers” product ...
Memes
... seem to be precisely the type of things that might enable us to gain insight into the transmission and reception of facts across time and between disciplines. Added to which, they are apparently a scientific way to talk about this. But there are problems. It’s not entirely clear how seriously we are ...
... seem to be precisely the type of things that might enable us to gain insight into the transmission and reception of facts across time and between disciplines. Added to which, they are apparently a scientific way to talk about this. But there are problems. It’s not entirely clear how seriously we are ...
Prof. Kamakaka`s Lecture 12 Notes
... two or more wild-type alleles is polymorphic. The vast majority of traits are determined by alleles of more than one gene. This means that most traits are multifactorial. A Heterogeneous Trait is One That May be caused by mutations in more than one gene. Human deafness is an example of a heterogeneo ...
... two or more wild-type alleles is polymorphic. The vast majority of traits are determined by alleles of more than one gene. This means that most traits are multifactorial. A Heterogeneous Trait is One That May be caused by mutations in more than one gene. Human deafness is an example of a heterogeneo ...
Differential Enzyme Targeting As an Evolutionary Adaptation to
... mammals, apparently under the influence of dietary selection pressure. There is a tendency for AGT to be mitochondrial in carnivores (including insectivores), peroxisomal in herbivores, and both mitochondrial and peroxisomal in omnivores (Danpure et al. 1990,1994). AGT catalyses the detoxification o ...
... mammals, apparently under the influence of dietary selection pressure. There is a tendency for AGT to be mitochondrial in carnivores (including insectivores), peroxisomal in herbivores, and both mitochondrial and peroxisomal in omnivores (Danpure et al. 1990,1994). AGT catalyses the detoxification o ...
The infinitesimal model
... In one of the earliest quantitative discussions of heredity, Fleeming Jenkin (1867) argued that blending inheritance could have no effect in the long term: a white man stranded on a tropical island would leave offspring who, over successive generations, would approach ever closer to the dark-skinned n ...
... In one of the earliest quantitative discussions of heredity, Fleeming Jenkin (1867) argued that blending inheritance could have no effect in the long term: a white man stranded on a tropical island would leave offspring who, over successive generations, would approach ever closer to the dark-skinned n ...
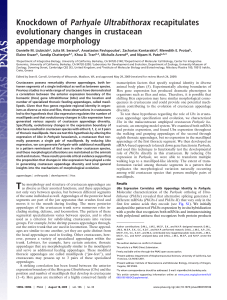
Knockdown of Parhyale Ultrabithorax - IMBB
... these branches in wild-type Parhyale, but PhUbx siRNA-treated animals develop T2 and T3 appendages with branches on the basis and ischium (arrow in Fig. 3D and asterisks in Fig. 4F, G, I, and J). In addition, the branches on transformed appendages have shapes and bristle patterns similar to those of ...
... these branches in wild-type Parhyale, but PhUbx siRNA-treated animals develop T2 and T3 appendages with branches on the basis and ischium (arrow in Fig. 3D and asterisks in Fig. 4F, G, I, and J). In addition, the branches on transformed appendages have shapes and bristle patterns similar to those of ...
conte et al 2015 genetics - UBC Zoology
... gene studies of repeated phenotypic evolution are prone to publication bias and have focused mainly on a small number of genes with mostly unknown effect sizes. Mapping studies of repeated phenotypic evolution have tended to focus on a small number of traits controlled by genes of apparently large e ...
... gene studies of repeated phenotypic evolution are prone to publication bias and have focused mainly on a small number of genes with mostly unknown effect sizes. Mapping studies of repeated phenotypic evolution have tended to focus on a small number of traits controlled by genes of apparently large e ...
RFT and evolution - Association for Contextual Behavioral Science
... • Selectionism involves an emphasis on the role historical context and consequences play in shaping the form and function of the phenomenon of interest in the current setting—an emphasis that clearly reflects both the root metaphor and truth criterion of ...
... • Selectionism involves an emphasis on the role historical context and consequences play in shaping the form and function of the phenomenon of interest in the current setting—an emphasis that clearly reflects both the root metaphor and truth criterion of ...
Human mutations in glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase reflect
... archive of The Institute of Genomic Research. The complete sequence from Rhodobacter capsulatus was retrieved from the archive of University of Chicago. The full genomes of Archaeoglobus fulgidus, Methanococcus jannaschii, Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum, Mycoplasma genitalium, Mycoplasma pneum ...
... archive of The Institute of Genomic Research. The complete sequence from Rhodobacter capsulatus was retrieved from the archive of University of Chicago. The full genomes of Archaeoglobus fulgidus, Methanococcus jannaschii, Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum, Mycoplasma genitalium, Mycoplasma pneum ...
Control of Lysogenization by Phage P22. II. Mutations (clyA) in the c1 Gene that Cause Increased Lysogenization
... tests are done under conditions in which each parent was infected at @I) into the ely-non-permissive host DB7000 and each parent carried a mutation in a P22 late gene. In every case. one parent carried a 5-am mutation carried an a-am mutation. In this way, only cells that were co-infected by each a ...
... tests are done under conditions in which each parent was infected at @I) into the ely-non-permissive host DB7000 and each parent carried a mutation in a P22 late gene. In every case. one parent carried a 5-am mutation carried an a-am mutation. In this way, only cells that were co-infected by each a ...
Review: Is genetic screening for hemochromatosis worthwhile?
... [62]. However, not all subjects with iron overload carry the C282Y mutation. This mutation is mainly found in Caucasians. This limits the application of this screening test to other ethnic groups. On the other hand, phenotypic measures such as biochemical iron levels are early indicators of disease ...
... [62]. However, not all subjects with iron overload carry the C282Y mutation. This mutation is mainly found in Caucasians. This limits the application of this screening test to other ethnic groups. On the other hand, phenotypic measures such as biochemical iron levels are early indicators of disease ...
Mar19
... "Variation is a feature of natural populations and every population produces more progeny than its environment can manage. The consequences of this overproduction is that those individuals with the best genetic fitness for the environment will produce offspring that can more successfully compete in ...
... "Variation is a feature of natural populations and every population produces more progeny than its environment can manage. The consequences of this overproduction is that those individuals with the best genetic fitness for the environment will produce offspring that can more successfully compete in ...
Evolution of Preferences - Northwestern University
... 5. While Ok and Vega-Redondo (2001) do not directly allow for different assumptions on observability, some aspects of those differences can be seen through variations in their matching technology. They use this to argue that preference evolution has no effect on outcomes when preferences are not obs ...
... 5. While Ok and Vega-Redondo (2001) do not directly allow for different assumptions on observability, some aspects of those differences can be seen through variations in their matching technology. They use this to argue that preference evolution has no effect on outcomes when preferences are not obs ...
Dissecting the Evolutionary Process of GENN
... This NN produces a classification error, just as a protein produces a phenotype within an organism. Function: In GE a lower classification error indicates higher fitness. Natural selection will work at the level of reproductive fitness, forcing changes in the heritable material of both biological or ...
... This NN produces a classification error, just as a protein produces a phenotype within an organism. Function: In GE a lower classification error indicates higher fitness. Natural selection will work at the level of reproductive fitness, forcing changes in the heritable material of both biological or ...
Designs for QTL detection in livestock and their implications for MAS
... Creating additional recombinations: experimental crosses. For experimental crosses, two strategies can be used to increase the number of recombinations around the QTL region. 1) An advanced intercross line (AIL) where the animals from an F2 are crossed to create an F3 and so on, until Fn. Every two ...
... Creating additional recombinations: experimental crosses. For experimental crosses, two strategies can be used to increase the number of recombinations around the QTL region. 1) An advanced intercross line (AIL) where the animals from an F2 are crossed to create an F3 and so on, until Fn. Every two ...
Henry David Thoreau: The Darwinian Naturalist
... “the play within the play” technique—but performed in triplicate. It seemed to me that Dr. Edge had undergone the same process that this tale beckoned forth in us: So through a myth a truth was told by a philosophy professor who understood the vision of a shadow that raised him to the light of self- ...
... “the play within the play” technique—but performed in triplicate. It seemed to me that Dr. Edge had undergone the same process that this tale beckoned forth in us: So through a myth a truth was told by a philosophy professor who understood the vision of a shadow that raised him to the light of self- ...
Untitled - System Components
... PER–TIM might dissociate, and PER physically disrupts the transcription factor CLK–CYC, leading to a fall in per and tim levels. (d) Nuclear TIM and, later, PER are then degraded, and this degradation enables the derepression of per and tim promoters via CLK–CYC, so the molecular cycle starts again ...
... PER–TIM might dissociate, and PER physically disrupts the transcription factor CLK–CYC, leading to a fall in per and tim levels. (d) Nuclear TIM and, later, PER are then degraded, and this degradation enables the derepression of per and tim promoters via CLK–CYC, so the molecular cycle starts again ...
Consulta: creatorFacets:"Leitao, Alexandra" Registros recuperados
... A microarray-based analysis was performed with the objective of describing genomic features of oocytes and looking for potential markers of oocyte quality in the economically important European clam, Ruditapes decussatus. Oocytes of 25 females from Ria de Aveiro, Western coast of Portugal (40°42′N; ...
... A microarray-based analysis was performed with the objective of describing genomic features of oocytes and looking for potential markers of oocyte quality in the economically important European clam, Ruditapes decussatus. Oocytes of 25 females from Ria de Aveiro, Western coast of Portugal (40°42′N; ...
Heritability - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
... In non-human populations it is often possible to collect information in a controlled way. For example, among farm animals it is easy to arrange for a bull to produce offspring from a large number of cows and to control environments. Such experimental control is impossible when gathering human data, ...
... In non-human populations it is often possible to collect information in a controlled way. For example, among farm animals it is easy to arrange for a bull to produce offspring from a large number of cows and to control environments. Such experimental control is impossible when gathering human data, ...
Molecular Identification of Vibrio harveyi From Larval Stage of
... Vibrio campbellii, Vibrio alginolyticus, Vibrio ...
... Vibrio campbellii, Vibrio alginolyticus, Vibrio ...
1 RUNNING TITLE Diversity and selection of
... and Cockerham, 1984) analyses. We found that the STRUCTURE clusters were significantly different from one another, strongly supporting the genetic grouping (Table S5). Based on Nei’s genetic distances (Nei, 1978), one of the most distinct STRUCTURE groups was represented by cluster 5, comprised of c ...
... and Cockerham, 1984) analyses. We found that the STRUCTURE clusters were significantly different from one another, strongly supporting the genetic grouping (Table S5). Based on Nei’s genetic distances (Nei, 1978), one of the most distinct STRUCTURE groups was represented by cluster 5, comprised of c ...
Untitled
... interested in wild fish populations is - Does the incursion of farm fish into a wild stock threaten the viability of the wild stock, or cause a loss of genetic diversity? This paper will only deal with the genetic aspects of this question, which is limited to the interaction between wild and farm fi ...
... interested in wild fish populations is - Does the incursion of farm fish into a wild stock threaten the viability of the wild stock, or cause a loss of genetic diversity? This paper will only deal with the genetic aspects of this question, which is limited to the interaction between wild and farm fi ...
The Peppered moth: decline of a Darwinian disciple
... evidence were obtained that seriously undermined the qualitative accuracy of the case, it would be of such importance in academic circles that I can not imagine any scientist speaking of it ‘quietly’. The Matthews article numerous scientific inaccuracies, misquotations and misrepresentations, but th ...
... evidence were obtained that seriously undermined the qualitative accuracy of the case, it would be of such importance in academic circles that I can not imagine any scientist speaking of it ‘quietly’. The Matthews article numerous scientific inaccuracies, misquotations and misrepresentations, but th ...
An Inclusive Fitness Model for Dispersal of Offspring 1. Introduction
... each of her patch mates (which may have been altered by her own mutant behaviour). Her inclusive fitness increment A W is her own fitness change plus the sum o f the fitness changes of each of her neighbours, each of these weighted by the coefficient of relatedness of that neighbour to the mutant in ...
... each of her patch mates (which may have been altered by her own mutant behaviour). Her inclusive fitness increment A W is her own fitness change plus the sum o f the fitness changes of each of her neighbours, each of these weighted by the coefficient of relatedness of that neighbour to the mutant in ...
Koinophilia

Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis concerning sexual selection which proposes that animals seeking mate preferentially choose individuals with a minimum of unusual features. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek, koinos, ""the usual"", and philos, ""fondness"".Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common and eventually replace their disadvantageous counterparts. A sexually-reproducing animal would be expected to avoid individuals with unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. This means that mates displaying mutant features are also avoided. This is advantageous because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functionality or behavior, are disadvantageous. Because it is impossible to judge whether a new mutation is beneficial or not, koinophilic animals avoid them all, at the cost of avoiding the occasional beneficial mutation. Thus, koinophilia, although not infallible in its ability to distinguish fit from unfit mates, is a good strategy when choosing a mate. A koinophilic choice ensures that offspring are likely to inherit features that have been successful in the past.Koinophilia differs from assortative mating, where ""like prefers like"". If like preferred like, leucistic animals (such as white peacocks) would be sexually attracted to one another, and a leucistic subspecies would come into being. Koinophilia predicts that this is unlikely because leucistic animals are attracted to the average in the same way as other animals. Since non-leucistic animals are not attracted by leucism, few leucistic individuals find mates, and leucistic lineages will rarely form.Koinophilia provides simple explanations for the rarity of speciation (in particular Darwin's Dilemma), evolutionary stasis, punctuated equilibria, and the evolution of cooperation. Koinophilia might also contribute to the maintenance of sexual reproduction, preventing its reversion to the much simpler and inherently more advantageous asexual form of reproduction.The koinophilia hypothesis is supported by research into the physical attractiveness of human faces by Judith Langlois and her co-workers. They found that the average of two human faces was more attractive than either of the faces from which that average was derived. The more faces (of the same gender and age) that were used in the averaging process the more attractive and appealing the average face became. This work into averageness supports koinophilia as an explanation of what constitutes a beautiful face, and how the individuality of a face is recognized.