Measuring variation (sample size, mean, median, standard deviation, variance, standard... know the equations and how they are calculated Principles of Ecology
... Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium- How to calculate, violations and rules Know processes that change allele frequencies Other terms: genetic drift, directional selection, gene flow, mutation Estimating a population size Terms: immigration vs. emigration Mark-recapture method (pg. 53) Lincoln-Peterson Index ...
... Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium- How to calculate, violations and rules Know processes that change allele frequencies Other terms: genetic drift, directional selection, gene flow, mutation Estimating a population size Terms: immigration vs. emigration Mark-recapture method (pg. 53) Lincoln-Peterson Index ...
Ecology Review
... 1. Mimicry is an example of a(n) ___________________________ adaptation. 2. Animals with ______________________________ that benefit them often live longer than other animals in the same species. 3. A population cannot exceed the _____________________________ of its environment, which is the largest ...
... 1. Mimicry is an example of a(n) ___________________________ adaptation. 2. Animals with ______________________________ that benefit them often live longer than other animals in the same species. 3. A population cannot exceed the _____________________________ of its environment, which is the largest ...
Evolution for Beginners
... • 3 conditions for natural selection to occur – Variation must exist among individuals in a population – Variation among individuals must result in differences in the number of offspring surviving – Variation must be genetically inherited ...
... • 3 conditions for natural selection to occur – Variation must exist among individuals in a population – Variation among individuals must result in differences in the number of offspring surviving – Variation must be genetically inherited ...
013368718X_CH17_267
... 8. All of the genes in a population make up the allele frequency of the population. 9. Traits controlled by two or more genes are polygenic traits. 10. Reproductive isolation occurs when members of two populations do not interbreed and produce fertile offspring. 11. The separation of two populations ...
... 8. All of the genes in a population make up the allele frequency of the population. 9. Traits controlled by two or more genes are polygenic traits. 10. Reproductive isolation occurs when members of two populations do not interbreed and produce fertile offspring. 11. The separation of two populations ...
013368718X_CH17_267
... 8. All of the genes in a population make up the allele frequency of the population. 9. Traits controlled by two or more genes are polygenic traits. 10. Reproductive isolation occurs when members of two populations do not interbreed and produce fertile offspring. 11. The separation of two populations ...
... 8. All of the genes in a population make up the allele frequency of the population. 9. Traits controlled by two or more genes are polygenic traits. 10. Reproductive isolation occurs when members of two populations do not interbreed and produce fertile offspring. 11. The separation of two populations ...
Chapter Vocabulary Review
... 8. All of the genes in a population make up the allele frequency of the population. 9. Traits controlled by two or more genes are polygenic traits. 10. Reproductive isolation occurs when members of two populations do not interbreed and produce fertile offspring. 11. The separation of two populations ...
... 8. All of the genes in a population make up the allele frequency of the population. 9. Traits controlled by two or more genes are polygenic traits. 10. Reproductive isolation occurs when members of two populations do not interbreed and produce fertile offspring. 11. The separation of two populations ...
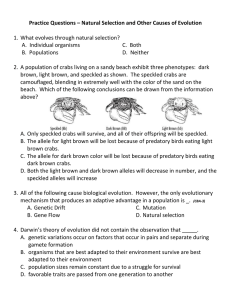
Evolution Practice Questions
... D. A flock of migrating geese loses its way to its wintering grounds, leaving other geese without competition for resources and enabling those geese to produce more offspring. 8. What affect does natural selection have on the variation of a species? A. It increases it C. It has random effects on it ...
... D. A flock of migrating geese loses its way to its wintering grounds, leaving other geese without competition for resources and enabling those geese to produce more offspring. 8. What affect does natural selection have on the variation of a species? A. It increases it C. It has random effects on it ...
File
... 4. Two related species live on different continents, but still look similar because they adapted in similar ways to similar environments. Example: Jaguars and leopards. 5. Two UNRELATED species look similar because they evolved in similar ways to similar environments. Example: sharks and dolphins. 6 ...
... 4. Two related species live on different continents, but still look similar because they adapted in similar ways to similar environments. Example: Jaguars and leopards. 5. Two UNRELATED species look similar because they evolved in similar ways to similar environments. Example: sharks and dolphins. 6 ...
1) Give a brief explanation and examples of: Incomplete dominance
... and Human Genetic Disorders on pgs. 125 – 132 Write and Answer: ...
... and Human Genetic Disorders on pgs. 125 – 132 Write and Answer: ...
22.0Evidence Evolution
... “There is grandeur in this view of life, with its several powers, having been originally breathed by the Creator into a few forms or into one; and that, whilst this planet has gone cycling on according to the fixed law of gravity, from so simple a beginning endless forms most beautiful and most wond ...
... “There is grandeur in this view of life, with its several powers, having been originally breathed by the Creator into a few forms or into one; and that, whilst this planet has gone cycling on according to the fixed law of gravity, from so simple a beginning endless forms most beautiful and most wond ...
How the Theory Developed - The Teacher
... Ernst Mayr (German/American, 19042005) studied species, speciation, and punctuated equilibrium. In his book Systematics and the Origin of Species (1942), he wrote that a species is not just a group of morphologically similar individuals, but a group that can breed only among themselves, excluding al ...
... Ernst Mayr (German/American, 19042005) studied species, speciation, and punctuated equilibrium. In his book Systematics and the Origin of Species (1942), he wrote that a species is not just a group of morphologically similar individuals, but a group that can breed only among themselves, excluding al ...
Theories of Evolution
... Beneficial traits were passed on to the offspring of those organisms. ...
... Beneficial traits were passed on to the offspring of those organisms. ...
Evolution is a Threat to Modern Science
... Georges Cuvier came up with this science and believed it showed the bodies of ____ and ______________ have certain basic similarities in their overall designs. ____________________ use comparative anatomy to say that one organism evolved from another because they are __________. There are some ...
... Georges Cuvier came up with this science and believed it showed the bodies of ____ and ______________ have certain basic similarities in their overall designs. ____________________ use comparative anatomy to say that one organism evolved from another because they are __________. There are some ...
скачати
... environment prevailed and reproduced, leaving those who did not adapt, extinct. In his book, On the Origin of Species, Darwin presented the idea that species evolve from more primitive species through the process of natural selection, which works spontaneously in nature. Darwinism states that not al ...
... environment prevailed and reproduced, leaving those who did not adapt, extinct. In his book, On the Origin of Species, Darwin presented the idea that species evolve from more primitive species through the process of natural selection, which works spontaneously in nature. Darwinism states that not al ...
Evolution through natural selection
... Small, hereditary variations (adaptations) are the basis for evolution in a population ...
... Small, hereditary variations (adaptations) are the basis for evolution in a population ...
Mechanisms of Divergence •Natural selection •Genetic Drift •Sexual
... Bottlenecks are periods of very low population size or near extinction. This is a special case of genetic drift The result of a population bottleneck is that even if the population regains its original numbers, genetic variation is drastically reduced ...
... Bottlenecks are periods of very low population size or near extinction. This is a special case of genetic drift The result of a population bottleneck is that even if the population regains its original numbers, genetic variation is drastically reduced ...
Evolution of Populations
... Contribution an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation relative to the contributions of others Natural selection is not survival of the fittest ...
... Contribution an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation relative to the contributions of others Natural selection is not survival of the fittest ...
Population genetics
... Runaway sexual selection posits that extreme male traits (such as the male peacock's tail, or the huge antlers of the now-extinct Irish Elk) can evolve through a process in which the male trait and the female preference for that trait become genetically linked. The male trait does not necessarily ...
... Runaway sexual selection posits that extreme male traits (such as the male peacock's tail, or the huge antlers of the now-extinct Irish Elk) can evolve through a process in which the male trait and the female preference for that trait become genetically linked. The male trait does not necessarily ...
Ch. 12 - Mechanisms of Speciation All life originated from a single
... • Example of the snapping shrimp species pairs found on either side of the Isthmus of Panama Ø Changes in chromosomes as barrier to gene flow § Sometimes called saltation events - polyploidization or other changes in ...
... • Example of the snapping shrimp species pairs found on either side of the Isthmus of Panama Ø Changes in chromosomes as barrier to gene flow § Sometimes called saltation events - polyploidization or other changes in ...
Neo-Darwinism: Is There A Mechanism For Macroevolution?
... dominated the Mesozoic Era. They included the crocodilians, pterosaurs, thecodonts, dinosaurs and allegedly, birds. Enzymes: Complex proteins that are produced by living cells and catalyze specific biochemical reactions at body temperatures. Mutation: Changes in the molecular nature of DNA. Mutation ...
... dominated the Mesozoic Era. They included the crocodilians, pterosaurs, thecodonts, dinosaurs and allegedly, birds. Enzymes: Complex proteins that are produced by living cells and catalyze specific biochemical reactions at body temperatures. Mutation: Changes in the molecular nature of DNA. Mutation ...
Big Ideas in Biology - juan-roldan
... Descent from a common ancestor with modification Natural Selection as the main mechanism that drives the evolution of adaptive evolutionary novelties ...
... Descent from a common ancestor with modification Natural Selection as the main mechanism that drives the evolution of adaptive evolutionary novelties ...
Taxonomic Issues in Conservation and Using Phylogenies to
... adaptive). H2 is heritability and gives us an idea of how much of the variation is genetically based. The implication of this is that these populations are locally adapted to environmental conditions. Natural selection has altered their morphology. ...
... adaptive). H2 is heritability and gives us an idea of how much of the variation is genetically based. The implication of this is that these populations are locally adapted to environmental conditions. Natural selection has altered their morphology. ...
Koinophilia

Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis concerning sexual selection which proposes that animals seeking mate preferentially choose individuals with a minimum of unusual features. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek, koinos, ""the usual"", and philos, ""fondness"".Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common and eventually replace their disadvantageous counterparts. A sexually-reproducing animal would be expected to avoid individuals with unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. This means that mates displaying mutant features are also avoided. This is advantageous because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functionality or behavior, are disadvantageous. Because it is impossible to judge whether a new mutation is beneficial or not, koinophilic animals avoid them all, at the cost of avoiding the occasional beneficial mutation. Thus, koinophilia, although not infallible in its ability to distinguish fit from unfit mates, is a good strategy when choosing a mate. A koinophilic choice ensures that offspring are likely to inherit features that have been successful in the past.Koinophilia differs from assortative mating, where ""like prefers like"". If like preferred like, leucistic animals (such as white peacocks) would be sexually attracted to one another, and a leucistic subspecies would come into being. Koinophilia predicts that this is unlikely because leucistic animals are attracted to the average in the same way as other animals. Since non-leucistic animals are not attracted by leucism, few leucistic individuals find mates, and leucistic lineages will rarely form.Koinophilia provides simple explanations for the rarity of speciation (in particular Darwin's Dilemma), evolutionary stasis, punctuated equilibria, and the evolution of cooperation. Koinophilia might also contribute to the maintenance of sexual reproduction, preventing its reversion to the much simpler and inherently more advantageous asexual form of reproduction.The koinophilia hypothesis is supported by research into the physical attractiveness of human faces by Judith Langlois and her co-workers. They found that the average of two human faces was more attractive than either of the faces from which that average was derived. The more faces (of the same gender and age) that were used in the averaging process the more attractive and appealing the average face became. This work into averageness supports koinophilia as an explanation of what constitutes a beautiful face, and how the individuality of a face is recognized.