Darwinian Aesthetics Informs Traditional Aesthetics
... nonrandomness has differential reproductive consequences. When design differences among individuals reflect genetic differences, selection accumulates genes in subsequent generations that (through the geneenvironment interactions that constitute ontogeny) lead to increased fit of individuals to thei ...
... nonrandomness has differential reproductive consequences. When design differences among individuals reflect genetic differences, selection accumulates genes in subsequent generations that (through the geneenvironment interactions that constitute ontogeny) lead to increased fit of individuals to thei ...
Chapter 16 notes
... genes within a population Relative frequency- How often something happens divided by all outcomes. Example: Your team has won 9 games from a total of 12 games played: the Frequency of winning is 9. the Relative Frequency of winning is 9/12 = 75% ...
... genes within a population Relative frequency- How often something happens divided by all outcomes. Example: Your team has won 9 games from a total of 12 games played: the Frequency of winning is 9. the Relative Frequency of winning is 9/12 = 75% ...
Spring 2012 Biology Final Exam Review Guide Mrs. Hawkins What
... “Are We Still Evolving”? –Why is the rate of evolution in developing countries different than the rate of evolution in the western world? What is the connection between Hemochromatosis and Alzheimers? What does the “Evolutionary Arms race” refer to? Why is this statement a misconception: Evoluti ...
... “Are We Still Evolving”? –Why is the rate of evolution in developing countries different than the rate of evolution in the western world? What is the connection between Hemochromatosis and Alzheimers? What does the “Evolutionary Arms race” refer to? Why is this statement a misconception: Evoluti ...
Teacher`s Guide - Life Sciences Outreach Program
... Specify island conditions and set up cards at each island that benefits a particular trait and harms its opposite, according to the island’s environment o I.e. light colored turtles on island with light sand or smaller, more maneuverable turtles on islands with rocky land Incorporating Hardy-Wei ...
... Specify island conditions and set up cards at each island that benefits a particular trait and harms its opposite, according to the island’s environment o I.e. light colored turtles on island with light sand or smaller, more maneuverable turtles on islands with rocky land Incorporating Hardy-Wei ...
WORKING WITH THE FIGURES 1. Examining Figure 20
... type quoted on page 731. What ideas do they have in common? Answer: The ideas of Darwin and Wallace were remarkably similar. Both authors recognized a struggle for existence and that survival and reproduction were not assured. Both also recognized the existence of variations that could confer a repr ...
... type quoted on page 731. What ideas do they have in common? Answer: The ideas of Darwin and Wallace were remarkably similar. Both authors recognized a struggle for existence and that survival and reproduction were not assured. Both also recognized the existence of variations that could confer a repr ...
Differences between individuals of the same species
... physiological or biochemical. They can be caused by two separate factors: there is genetic variation (also known as inherited variation) and there is also environmental variation. Genetic variation is all to do with the genes we inherit from our parents, which define our characteristics. The differe ...
... physiological or biochemical. They can be caused by two separate factors: there is genetic variation (also known as inherited variation) and there is also environmental variation. Genetic variation is all to do with the genes we inherit from our parents, which define our characteristics. The differe ...
Biology Performance Level Descriptors
... Standards for Biology. A student at this level has a sophisticated ability to describe genetic patterns of inheritance and how traits are defined by instructions encoded in many discrete genes, explain that Earth’s present-day species descended from common ancestral species due to variation and the ...
... Standards for Biology. A student at this level has a sophisticated ability to describe genetic patterns of inheritance and how traits are defined by instructions encoded in many discrete genes, explain that Earth’s present-day species descended from common ancestral species due to variation and the ...
Computational Intelligence.
... the Intelligent Robotics Laboratory. Students interesting in studying computational intelligence must enroll in: ECE 559 (Genetic Algorithms) ECE 555 (Neural Networks I) ECE 556 (Neural Networks II) ECE 578 (Intelligent Robotics I) ECE 579 (Intelligent Robotics II) A good mathematics background in g ...
... the Intelligent Robotics Laboratory. Students interesting in studying computational intelligence must enroll in: ECE 559 (Genetic Algorithms) ECE 555 (Neural Networks I) ECE 556 (Neural Networks II) ECE 578 (Intelligent Robotics I) ECE 579 (Intelligent Robotics II) A good mathematics background in g ...
Natural Selection Worksheet
... 7. Lots of factors play roles in how species change over time including ________________________, 8. ______________________, and the process of _______________________________. 9. Natural selection is the most powerful and important cause of ___________________________________. 10. Name 3 things Dar ...
... 7. Lots of factors play roles in how species change over time including ________________________, 8. ______________________, and the process of _______________________________. 9. Natural selection is the most powerful and important cause of ___________________________________. 10. Name 3 things Dar ...
IN MEMORIAM Charles M. Rick Jr.
... As a first step in the formal genetics of the many gene mutations he discovered or obtained, he determined their chromosome linkage (association). This was expedited by synthesizing trisomics (one extra chromosome) for each of the twelve chromosome pairs of the tomato genome. By personally marching ...
... As a first step in the formal genetics of the many gene mutations he discovered or obtained, he determined their chromosome linkage (association). This was expedited by synthesizing trisomics (one extra chromosome) for each of the twelve chromosome pairs of the tomato genome. By personally marching ...
Plant Ecology 03-55-468
... the result of phenotypic plasticity. (10) The experiment would take the form of a “common garden” growth experiment or a reciprocal transplant experiment. In the former, plants from Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan and Alberta would all be moved (probably by planting seeds from all sources) in a comm ...
... the result of phenotypic plasticity. (10) The experiment would take the form of a “common garden” growth experiment or a reciprocal transplant experiment. In the former, plants from Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan and Alberta would all be moved (probably by planting seeds from all sources) in a comm ...
L T P/S SW/FW TOTAL CREDIT UNITS 3 1 2
... Course Objectives: Theory: This course aims at introducing the students to the basics of biological anthropology, its historical background, how it evolved as a science, its important branches, scope and applications to the welfare of mankind. It provides a background canvas in understanding the sto ...
... Course Objectives: Theory: This course aims at introducing the students to the basics of biological anthropology, its historical background, how it evolved as a science, its important branches, scope and applications to the welfare of mankind. It provides a background canvas in understanding the sto ...
Section 2: Energy Flow in Ecosystems
... • Put another way, each species becomes adapted to its environment as a result of living in it over time. ...
... • Put another way, each species becomes adapted to its environment as a result of living in it over time. ...
Ch 15
... Evolution can be detected and measured by noting the amount of deviation from a HardyWeinberg equilibrium of allele frequencies in the gene pool of a population. ...
... Evolution can be detected and measured by noting the amount of deviation from a HardyWeinberg equilibrium of allele frequencies in the gene pool of a population. ...
Class Notes
... The tetraploid cannot mate with diploids from the original population because of abnormal meiosis by the triploid hybrid offspring. ...
... The tetraploid cannot mate with diploids from the original population because of abnormal meiosis by the triploid hybrid offspring. ...
lecture outline
... The tetraploid cannot mate with diploids from the original population because of abnormal meiosis by the triploid hybrid offspring. ...
... The tetraploid cannot mate with diploids from the original population because of abnormal meiosis by the triploid hybrid offspring. ...
chapter 24 - Phillips Scientific Methods
... The tetraploid cannot mate with diploids from the original population because of abnormal meiosis by the triploid hybrid offspring. ...
... The tetraploid cannot mate with diploids from the original population because of abnormal meiosis by the triploid hybrid offspring. ...
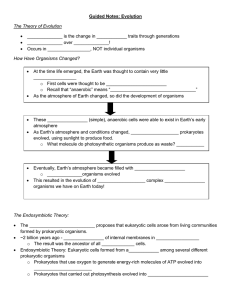
Evolution Guided Notes
... Genetic Recombination: Dominant and Recessive alleles in genes, along with polygenetic traits and complex genetics, lead to individual organisms with different ________________ (and thus, adaptations) ...
... Genetic Recombination: Dominant and Recessive alleles in genes, along with polygenetic traits and complex genetics, lead to individual organisms with different ________________ (and thus, adaptations) ...
Biology
... Describe how ecosystems can be reasonably stable over hundreds or thousands of years. Understand that if a disaster such as flood or fire occurs, the damaged ecosystem is likely to recover in stages that eventually result in a system similar to the original one. Understand and explain that like many ...
... Describe how ecosystems can be reasonably stable over hundreds or thousands of years. Understand that if a disaster such as flood or fire occurs, the damaged ecosystem is likely to recover in stages that eventually result in a system similar to the original one. Understand and explain that like many ...
File
... Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection NATURAL SELECTION is the way in which nature favours the reproductive success of some individuals within a population over others ...
... Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection NATURAL SELECTION is the way in which nature favours the reproductive success of some individuals within a population over others ...
DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY Dr. Carmen Hernandez Retires College of Arts and Sciences
... then used this genetic deficiency to screen for a knockout mutation in the muscle gene. “Carmen came to my lab with a strong background in Drosophila genetics and she played a key role in designing and conducting the genetic screens that turned out to be immensely valuable to our research”, says Dr. ...
... then used this genetic deficiency to screen for a knockout mutation in the muscle gene. “Carmen came to my lab with a strong background in Drosophila genetics and she played a key role in designing and conducting the genetic screens that turned out to be immensely valuable to our research”, says Dr. ...
Notes Chapter 18 Classification
... A. Organisms were first named and classified more than 2,000 years ago by the Greek philosopher Aristotle. He classified everything as either a plant or an animal and then grouped them into land dwellers, water dwellers, and air dwellers. This system worked very well for a period of time but eventua ...
... A. Organisms were first named and classified more than 2,000 years ago by the Greek philosopher Aristotle. He classified everything as either a plant or an animal and then grouped them into land dwellers, water dwellers, and air dwellers. This system worked very well for a period of time but eventua ...
The major histocompatibility complex in Old World Camelids: low
... Camelus bactrianus, Camelus dromedarius and Camelus ferus were retrieved. In general, very little interspecific differences manifested by high degree of sequence similarity and by high extent of allele sharing across all three species were observed. In addition, unexpectedly low level of polymorphis ...
... Camelus bactrianus, Camelus dromedarius and Camelus ferus were retrieved. In general, very little interspecific differences manifested by high degree of sequence similarity and by high extent of allele sharing across all three species were observed. In addition, unexpectedly low level of polymorphis ...
Koinophilia

Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis concerning sexual selection which proposes that animals seeking mate preferentially choose individuals with a minimum of unusual features. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek, koinos, ""the usual"", and philos, ""fondness"".Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common and eventually replace their disadvantageous counterparts. A sexually-reproducing animal would be expected to avoid individuals with unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. This means that mates displaying mutant features are also avoided. This is advantageous because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functionality or behavior, are disadvantageous. Because it is impossible to judge whether a new mutation is beneficial or not, koinophilic animals avoid them all, at the cost of avoiding the occasional beneficial mutation. Thus, koinophilia, although not infallible in its ability to distinguish fit from unfit mates, is a good strategy when choosing a mate. A koinophilic choice ensures that offspring are likely to inherit features that have been successful in the past.Koinophilia differs from assortative mating, where ""like prefers like"". If like preferred like, leucistic animals (such as white peacocks) would be sexually attracted to one another, and a leucistic subspecies would come into being. Koinophilia predicts that this is unlikely because leucistic animals are attracted to the average in the same way as other animals. Since non-leucistic animals are not attracted by leucism, few leucistic individuals find mates, and leucistic lineages will rarely form.Koinophilia provides simple explanations for the rarity of speciation (in particular Darwin's Dilemma), evolutionary stasis, punctuated equilibria, and the evolution of cooperation. Koinophilia might also contribute to the maintenance of sexual reproduction, preventing its reversion to the much simpler and inherently more advantageous asexual form of reproduction.The koinophilia hypothesis is supported by research into the physical attractiveness of human faces by Judith Langlois and her co-workers. They found that the average of two human faces was more attractive than either of the faces from which that average was derived. The more faces (of the same gender and age) that were used in the averaging process the more attractive and appealing the average face became. This work into averageness supports koinophilia as an explanation of what constitutes a beautiful face, and how the individuality of a face is recognized.