Evolutionary relationships between Saccharomyces cerevisiae and
... study of evolution of eukaryotic organisms, among other merits of such scientific achievement. Annotation of the genes from the DNA sequence revealed that the function of about 40% of them was totally or partially unknown at that time. Less than ten years later, much more is known on the function of ...
... study of evolution of eukaryotic organisms, among other merits of such scientific achievement. Annotation of the genes from the DNA sequence revealed that the function of about 40% of them was totally or partially unknown at that time. Less than ten years later, much more is known on the function of ...
Presentation
... from minute to minute, hour to hour, day to day; just as a genome may. Please do not confuse this “change over time” with the belief of creationism. These are two different concepts that are confused with each other because of misconceptions of the definition. Darwin’s theory is Natural Selection. ...
... from minute to minute, hour to hour, day to day; just as a genome may. Please do not confuse this “change over time” with the belief of creationism. These are two different concepts that are confused with each other because of misconceptions of the definition. Darwin’s theory is Natural Selection. ...
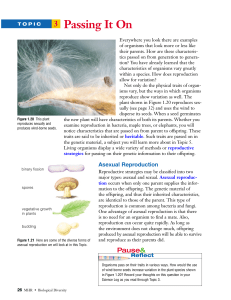
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction & Animal Development
... involves only one parent and produces offspring that are identical to the parent • Advantage- asexual reproduction limits the spread of detrimental characteristics • Disadvantage- is asexual reproduction the organism can not adapt to change in the ...
... involves only one parent and produces offspring that are identical to the parent • Advantage- asexual reproduction limits the spread of detrimental characteristics • Disadvantage- is asexual reproduction the organism can not adapt to change in the ...
Convergent evolution of `creepers`
... DNA (mtDNA) evidence ( Fleischer et al. 2001; James 2004) suggests these two species are evolutionarily quite distant, and instead points to a close relationship between O. mana and the cross-billed akepas or curve-billed amakihis. Pratt (2001) remarked that if the Kauai and Hawaii creepers derived ...
... DNA (mtDNA) evidence ( Fleischer et al. 2001; James 2004) suggests these two species are evolutionarily quite distant, and instead points to a close relationship between O. mana and the cross-billed akepas or curve-billed amakihis. Pratt (2001) remarked that if the Kauai and Hawaii creepers derived ...
Random Genetic Drift
... Random Genetic Drift and Migration: Effects 1. On average WITHIN one population, RGD DECREASES genetic variation, Migration INCREASES genetic variation: A) RGD makes INDIVIDUALS more homozygous, Migration makes INDIVIDUALS more heterozygous. B) the POPULATION reaches a STABLE LEVEL of genetic varia ...
... Random Genetic Drift and Migration: Effects 1. On average WITHIN one population, RGD DECREASES genetic variation, Migration INCREASES genetic variation: A) RGD makes INDIVIDUALS more homozygous, Migration makes INDIVIDUALS more heterozygous. B) the POPULATION reaches a STABLE LEVEL of genetic varia ...
Hardy Weinberg PPT File
... The Hardy-Weinberg equation (p² + 2pq + q² = 1), and the frequency of homozygous recessive individuals (aa) in a population is q². Therefore, in North America the following must be true for ...
... The Hardy-Weinberg equation (p² + 2pq + q² = 1), and the frequency of homozygous recessive individuals (aa) in a population is q². Therefore, in North America the following must be true for ...
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium: Bean Love
... the variation from the expected (5 heads and 5 tails) to chance. However, if you went on to flip 100,000 times, and the coin came up heads 80,000 times, you might just as reasonably wonder if the coin was haunted. It's not very likely that with so many coin flips, you'd still get that 80:20 ratio, i ...
... the variation from the expected (5 heads and 5 tails) to chance. However, if you went on to flip 100,000 times, and the coin came up heads 80,000 times, you might just as reasonably wonder if the coin was haunted. It's not very likely that with so many coin flips, you'd still get that 80:20 ratio, i ...
What the scientists say about evolution
... without."—*B. Leith, The Descent of Darwin: A Handbook of Doubts about Darwinism (1982), p. 11. "My attempts to demonstrate evolution by an experiment carried on for more than 40 years have completely failed. At least I should hardly be accused of having started from any preconceived anti-evolution ...
... without."—*B. Leith, The Descent of Darwin: A Handbook of Doubts about Darwinism (1982), p. 11. "My attempts to demonstrate evolution by an experiment carried on for more than 40 years have completely failed. At least I should hardly be accused of having started from any preconceived anti-evolution ...
Severe congenital neutropenia (SCN) and cyclic neutropenia
... 35-84% of individuals with SCN. SCN and cyclic neutropenia secondary to mutations in ELA2 are inherited as autosomal dominant conditions. ELA2 consists of five exons and encodes a 218 amino acid protein known as neutrophil elastase. Neutrophil elastase targets bacterial virulence proteins and serves ...
... 35-84% of individuals with SCN. SCN and cyclic neutropenia secondary to mutations in ELA2 are inherited as autosomal dominant conditions. ELA2 consists of five exons and encodes a 218 amino acid protein known as neutrophil elastase. Neutrophil elastase targets bacterial virulence proteins and serves ...
Unit 3_Lesson 80_Asexual Sexual
... ____Did you capitalize the beginning of every sentence and all proper nouns? ____Did you spell every word correctly that is spelled correctly on the page? ____Did you punctuate the end of every sentence? ____Did you write in complete sentences? (Subject, predicate, and complete ...
... ____Did you capitalize the beginning of every sentence and all proper nouns? ____Did you spell every word correctly that is spelled correctly on the page? ____Did you punctuate the end of every sentence? ____Did you write in complete sentences? (Subject, predicate, and complete ...
Physical Anthropology- 101 - Fullerton College Staff Web Pages
... Are the following statements true or false? Write an F or T next to each question (you will NOT be graded on this exercise). 1. Science can be used to explore any question that humans have. At this time there is enough evidence for scientists to state absolutely that UFO’s do not exist. 2. The age o ...
... Are the following statements true or false? Write an F or T next to each question (you will NOT be graded on this exercise). 1. Science can be used to explore any question that humans have. At this time there is enough evidence for scientists to state absolutely that UFO’s do not exist. 2. The age o ...
Selection on Developmental Genes
... see what happened to the biological phenotype after several generations. He chose as his test animal a species close to the wolf, namely the silver fox, Vulpes vulpes, an animal never before domesticated. The experiment began with 30 male foxes and 100 vixens from a commercial fur farm. (Such animal ...
... see what happened to the biological phenotype after several generations. He chose as his test animal a species close to the wolf, namely the silver fox, Vulpes vulpes, an animal never before domesticated. The experiment began with 30 male foxes and 100 vixens from a commercial fur farm. (Such animal ...
Two-point Linkage Analysis: a brief outline of theory
... the relationships between genes, this is not necessarily the same as relationships between species. • Your sequence data may not have the same phylogenetic history as the species from which they were isolated. • Different genes evolve at different speeds, and there is always the possibility of horiz ...
... the relationships between genes, this is not necessarily the same as relationships between species. • Your sequence data may not have the same phylogenetic history as the species from which they were isolated. • Different genes evolve at different speeds, and there is always the possibility of horiz ...
Article A Molecular Evolutionary Reference for the Human Variome
... acid state at a protein position (or each possible nucleotide state at a genomic position) in a given species using only the interspecific evolutionary history of the position. In the new method, population-level information on observed alleles is not needed when deriving EPs. This independence enab ...
... acid state at a protein position (or each possible nucleotide state at a genomic position) in a given species using only the interspecific evolutionary history of the position. In the new method, population-level information on observed alleles is not needed when deriving EPs. This independence enab ...
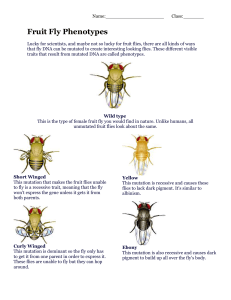
Fruit Fly Phenotypes
... Lucky for scientists, and maybe not so lucky for fruit flies, there are all kinds of ways that fly DNA can be mutated to create interesting looking flies. These different visible traits that result from mutated DNA are called phenotypes. ...
... Lucky for scientists, and maybe not so lucky for fruit flies, there are all kinds of ways that fly DNA can be mutated to create interesting looking flies. These different visible traits that result from mutated DNA are called phenotypes. ...
Slide 1
... males from the same population (left and right panels). Each male is essentially unique in his color pattern, and this variation is almost entirely genetically based. ...
... males from the same population (left and right panels). Each male is essentially unique in his color pattern, and this variation is almost entirely genetically based. ...
2 + pn
... have genetic signatures from a number of ancestral populations. East Asia had been somewhat isolated, with less migration from Middle East, Europe or Central Asia. It is also likely that genetic drift played a role. Human populations migrated out of Africa and Middle Eastern populations were ...
... have genetic signatures from a number of ancestral populations. East Asia had been somewhat isolated, with less migration from Middle East, Europe or Central Asia. It is also likely that genetic drift played a role. Human populations migrated out of Africa and Middle Eastern populations were ...
lecture 3 notes
... B. Type of reproductive behavior-eukaryotic microbes may be self-fertile, self-sterile (outcrossing), both or only asexual. Reproduction mostly occurs by conjugation. Transfer of nuclear material or whole cell fusion. ...
... B. Type of reproductive behavior-eukaryotic microbes may be self-fertile, self-sterile (outcrossing), both or only asexual. Reproduction mostly occurs by conjugation. Transfer of nuclear material or whole cell fusion. ...
Non-dominated Multi-objective Evolutionary Algorithm Based on
... (GFSs) [5], has attracted considerable attention in the computational intelligence community. GFSs provide an useful tools for pattern analysis and for the extraction of new types of useful information. In [7] a mono-objective GFS within the iterative rule learning approach for SD is presented with ...
... (GFSs) [5], has attracted considerable attention in the computational intelligence community. GFSs provide an useful tools for pattern analysis and for the extraction of new types of useful information. In [7] a mono-objective GFS within the iterative rule learning approach for SD is presented with ...
Inferring Process from Pattern In Fungal Population Genetics 3
... speciation can be inferred. We focus on fungal populations, but draw from the wider literature on population genetics, evolutionary statistics, and, of course, phylogeography (see Avise, 2000). We discuss the problems of gene duplication, paralogy, orthology, and deep coalescence as challenges to fi ...
... speciation can be inferred. We focus on fungal populations, but draw from the wider literature on population genetics, evolutionary statistics, and, of course, phylogeography (see Avise, 2000). We discuss the problems of gene duplication, paralogy, orthology, and deep coalescence as challenges to fi ...
File
... what do organisms have in common & why do similarities exist? common biochemistry & physiology evolutionary relationships connected through common ancestor ...
... what do organisms have in common & why do similarities exist? common biochemistry & physiology evolutionary relationships connected through common ancestor ...
Characteristics and Classification of Living Organisms (Extended)
... For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ ...
... For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ ...
Topic 3 - Science 9 Jones
... material. Many spores are produced to ensure that at least some of them survive. Some fungi and algae, such as the green algae Chlamydomonas and Ulva, produce zoospores, which move using tail-like flagella. Interestingly, fungi can also reproduce sexually — a process we will look at in more detail sh ...
... material. Many spores are produced to ensure that at least some of them survive. Some fungi and algae, such as the green algae Chlamydomonas and Ulva, produce zoospores, which move using tail-like flagella. Interestingly, fungi can also reproduce sexually — a process we will look at in more detail sh ...
Genetic Variation
... • When homologous chromosomes form pairs during prophase I of meiosis I, crossing-over can occur. Crossingover is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. It results in new combinations of genes on each chromosome. • When cells divide during meiosis, homologous chromosomes ar ...
... • When homologous chromosomes form pairs during prophase I of meiosis I, crossing-over can occur. Crossingover is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. It results in new combinations of genes on each chromosome. • When cells divide during meiosis, homologous chromosomes ar ...
Unit 1 Topic 3 - Holy Cross Collegiate
... material. Many spores are produced to ensure that at least some of them survive. Some fungi and algae, such as the green algae Chlamydomonas and Ulva, produce zoospores, which move using tail-like flagella. Interestingly, fungi can also reproduce sexually — a process we will look at in more detail sh ...
... material. Many spores are produced to ensure that at least some of them survive. Some fungi and algae, such as the green algae Chlamydomonas and Ulva, produce zoospores, which move using tail-like flagella. Interestingly, fungi can also reproduce sexually — a process we will look at in more detail sh ...
Koinophilia

Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis concerning sexual selection which proposes that animals seeking mate preferentially choose individuals with a minimum of unusual features. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek, koinos, ""the usual"", and philos, ""fondness"".Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common and eventually replace their disadvantageous counterparts. A sexually-reproducing animal would be expected to avoid individuals with unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. This means that mates displaying mutant features are also avoided. This is advantageous because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functionality or behavior, are disadvantageous. Because it is impossible to judge whether a new mutation is beneficial or not, koinophilic animals avoid them all, at the cost of avoiding the occasional beneficial mutation. Thus, koinophilia, although not infallible in its ability to distinguish fit from unfit mates, is a good strategy when choosing a mate. A koinophilic choice ensures that offspring are likely to inherit features that have been successful in the past.Koinophilia differs from assortative mating, where ""like prefers like"". If like preferred like, leucistic animals (such as white peacocks) would be sexually attracted to one another, and a leucistic subspecies would come into being. Koinophilia predicts that this is unlikely because leucistic animals are attracted to the average in the same way as other animals. Since non-leucistic animals are not attracted by leucism, few leucistic individuals find mates, and leucistic lineages will rarely form.Koinophilia provides simple explanations for the rarity of speciation (in particular Darwin's Dilemma), evolutionary stasis, punctuated equilibria, and the evolution of cooperation. Koinophilia might also contribute to the maintenance of sexual reproduction, preventing its reversion to the much simpler and inherently more advantageous asexual form of reproduction.The koinophilia hypothesis is supported by research into the physical attractiveness of human faces by Judith Langlois and her co-workers. They found that the average of two human faces was more attractive than either of the faces from which that average was derived. The more faces (of the same gender and age) that were used in the averaging process the more attractive and appealing the average face became. This work into averageness supports koinophilia as an explanation of what constitutes a beautiful face, and how the individuality of a face is recognized.