References
... We first investigated whether there is evidence for indirect genetic effects in offspring ...
... We first investigated whether there is evidence for indirect genetic effects in offspring ...
Computer Simulation using AlleleA1
... harmful, is not eliminated from this population but instead is maintained at a very low frequency. (Note: You can confirm this by running this simulation over 100,000 generations). There are two possible hypotheses for why allele A1 is not lost completely. First, mutation from A2 to A1 may be recrea ...
... harmful, is not eliminated from this population but instead is maintained at a very low frequency. (Note: You can confirm this by running this simulation over 100,000 generations). There are two possible hypotheses for why allele A1 is not lost completely. First, mutation from A2 to A1 may be recrea ...
DNA Sequence Changes of Mutations Altering
... mechanism of the histidine operon are presented. These mutations are discussed in terms of a model for operon regulation that involves a his leader peptide gene whose translation regulates formation of alternative stem-loop structures in the his leader messenger RNA. Three suppressible mutations gen ...
... mechanism of the histidine operon are presented. These mutations are discussed in terms of a model for operon regulation that involves a his leader peptide gene whose translation regulates formation of alternative stem-loop structures in the his leader messenger RNA. Three suppressible mutations gen ...
The Frequency Distribution of Nucleotide Variation in Drosophila
... Introduction An early result of theoretical population genetics was the expected frequency distribution of mutations under a neutral, equilibrium model of evolution (e.g., Wright 1938; Kimura 1983). Unfortunately, violations of any one (or several) of the assumptions of the neutral, equilibrium mode ...
... Introduction An early result of theoretical population genetics was the expected frequency distribution of mutations under a neutral, equilibrium model of evolution (e.g., Wright 1938; Kimura 1983). Unfortunately, violations of any one (or several) of the assumptions of the neutral, equilibrium mode ...
Castric et al. (MBE 2010) - GEPV
... recombination among allelic lines with low versus High sequence divergence, whereas only cases of the latter are typically found when comparing functionally distinct SI specificities. In contrast to gametophytic SI, sporophytic SI allows the spontaneous generation of homozygote genotypes for a given ...
... recombination among allelic lines with low versus High sequence divergence, whereas only cases of the latter are typically found when comparing functionally distinct SI specificities. In contrast to gametophytic SI, sporophytic SI allows the spontaneous generation of homozygote genotypes for a given ...
Philosophy of Biology: A Contemporary Introduction
... will be philosophical arguments, as traditionally understood. Like biology, philosophy is divided into subdisciplines: metaphysics studies the basic kinds of things, processes, and properties in the universe, and addresses questions about them such as: What are numbers? Does God exist? Are all event ...
... will be philosophical arguments, as traditionally understood. Like biology, philosophy is divided into subdisciplines: metaphysics studies the basic kinds of things, processes, and properties in the universe, and addresses questions about them such as: What are numbers? Does God exist? Are all event ...
General Biology II
... 13.2 Explain why individuals cannot evolve and why evolution does not lead to perfectly adapted organisms. 13.3 Describe two examples of natural selection known to occur in nature. Note two key points about how natural selection works. 13.4 Explain how fossils form, noting examples of each process. ...
... 13.2 Explain why individuals cannot evolve and why evolution does not lead to perfectly adapted organisms. 13.3 Describe two examples of natural selection known to occur in nature. Note two key points about how natural selection works. 13.4 Explain how fossils form, noting examples of each process. ...
Spectrum of [beta] thalassemia mutations and HbF levels in the
... and one compound heterozygote  thal/Hb Newcastle, in 46 Moroccan families with at least one  thalassemia patient is reported. Six major mutations:  0 39 (C→T), 0FsCD8(−AA), +IVS1,nt6 (T→C) and 0IVS1,nt1 (G→A), 0FsCD6 (−A) and +-29 (A→G) cap site account for 75% of the 86 independent  thal c ...
... and one compound heterozygote  thal/Hb Newcastle, in 46 Moroccan families with at least one  thalassemia patient is reported. Six major mutations:  0 39 (C→T), 0FsCD8(−AA), +IVS1,nt6 (T→C) and 0IVS1,nt1 (G→A), 0FsCD6 (−A) and +-29 (A→G) cap site account for 75% of the 86 independent  thal c ...
Giant viruses, giant chimeras: The multiple evolutionary histories of
... beings (i.e. cellular) and, therefore, do not belong to the tree of life [7,10]. Moreover, there is compelling evidence for the polyphyletic origin of viruses, which further complicates the issue [11]. These debates have recently gained an unprecedented impetus when Raoult and co-workers published t ...
... beings (i.e. cellular) and, therefore, do not belong to the tree of life [7,10]. Moreover, there is compelling evidence for the polyphyletic origin of viruses, which further complicates the issue [11]. These debates have recently gained an unprecedented impetus when Raoult and co-workers published t ...
MARINE MALADIES? Worms, Germs, and Other Symbionts From
... Figures 1 and 2. Hermit crabs with symbionts on theU molluscan shells. Top, two individuals of an anemone (Calllactls tricolor) on the moon snail Inhabited by Pagurus longlcarpus. Bottom, a hydroid covering the shell housing Pagurus ...
... Figures 1 and 2. Hermit crabs with symbionts on theU molluscan shells. Top, two individuals of an anemone (Calllactls tricolor) on the moon snail Inhabited by Pagurus longlcarpus. Bottom, a hydroid covering the shell housing Pagurus ...
Student Page Name: Title: Planaria Asexual Reproduction Lab
... Title: Planaria Asexual Reproduction Lab Introduction: Planaria are a nonparasitic flatworm. They can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Planaria have many stem cells which gives them the ability to regenerate tissues. In this lab you may cut your planaria to observe regeneration of tissue from ...
... Title: Planaria Asexual Reproduction Lab Introduction: Planaria are a nonparasitic flatworm. They can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Planaria have many stem cells which gives them the ability to regenerate tissues. In this lab you may cut your planaria to observe regeneration of tissue from ...
Gene Section JAK3 (janus kinase 3 or just another kinase 3)
... some cases of acute megakaryoblastic leukemia with or without Down syndrome. Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia is a type of acute leukemia where more than 50% of the blasts are of megakaryocytic lineage. The exact role of JAK3 in this disease is not completely ...
... some cases of acute megakaryoblastic leukemia with or without Down syndrome. Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia is a type of acute leukemia where more than 50% of the blasts are of megakaryocytic lineage. The exact role of JAK3 in this disease is not completely ...
Methods for detecting positive selection and examples among fungi
... Measuring the dN/dS ratio (number of nonsynonymous substitutions over number of synonymous substitutions) provides a direct way to measure the selective pressure acting on codons. Evaluating whether dN/dS is significantly higher than 1 constitutes a test for the action of positive selection. The earl ...
... Measuring the dN/dS ratio (number of nonsynonymous substitutions over number of synonymous substitutions) provides a direct way to measure the selective pressure acting on codons. Evaluating whether dN/dS is significantly higher than 1 constitutes a test for the action of positive selection. The earl ...
Testing Guidelines for molecular diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis.
... When the CFTR gene was cloned and its major mutation, p.Phe508del (F508del) identified in 1989, it was widely believed that there might be another half dozen mutations that would account for the remaining 30% or so of CF mutations. Perhaps that was founded more on wishful thinking than on sound scie ...
... When the CFTR gene was cloned and its major mutation, p.Phe508del (F508del) identified in 1989, it was widely believed that there might be another half dozen mutations that would account for the remaining 30% or so of CF mutations. Perhaps that was founded more on wishful thinking than on sound scie ...
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (GGPD) Mutations
... types of mutation are responsible for G6PD deficiency in the Chinese population of Taiwan. The finding that several polymorphic sites are located near or within the G6PD gene may provide a haplotype pattern that would enable us to analyze the linkage disequilibrium between mutations and polymorphism ...
... types of mutation are responsible for G6PD deficiency in the Chinese population of Taiwan. The finding that several polymorphic sites are located near or within the G6PD gene may provide a haplotype pattern that would enable us to analyze the linkage disequilibrium between mutations and polymorphism ...
Solid Tumour Section Inflammatory fibroid polyps Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... granulocytes. These lesions show a plenty of spindle cells but only little collagen. We and others have shown that there is another morphological subtype ("intestinal type") which, in contrast, is paucicellular and collagen-rich. ...
... granulocytes. These lesions show a plenty of spindle cells but only little collagen. We and others have shown that there is another morphological subtype ("intestinal type") which, in contrast, is paucicellular and collagen-rich. ...
A Century of Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium
... A and a in regard to some trait, gave a first generation resembling one of the two parents (A) identically and that crosses among members of this first generation gave a ratio of 3:1 of the two parental types, the more frequent type being the same as this first generation (A). He had described the f ...
... A and a in regard to some trait, gave a first generation resembling one of the two parents (A) identically and that crosses among members of this first generation gave a ratio of 3:1 of the two parental types, the more frequent type being the same as this first generation (A). He had described the f ...
Androgen insensitivity syndrome
... Individuals with partial androgen insensitivity, unlike those with the complete or mild forms, present at birth with ambiguous genitalia, and the decision to raise the child as male or female is often not obvious.[1][45][66] Unfortunately, it is often the case that little information regarding pheno ...
... Individuals with partial androgen insensitivity, unlike those with the complete or mild forms, present at birth with ambiguous genitalia, and the decision to raise the child as male or female is often not obvious.[1][45][66] Unfortunately, it is often the case that little information regarding pheno ...
A Century of Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium
... A and a in regard to some trait, gave a first generation resembling one of the two parents (A) identically and that crosses among members of this first generation gave a ratio of 3:1 of the two parental types, the more frequent type being the same as this first generation (A). He had described the f ...
... A and a in regard to some trait, gave a first generation resembling one of the two parents (A) identically and that crosses among members of this first generation gave a ratio of 3:1 of the two parental types, the more frequent type being the same as this first generation (A). He had described the f ...
Work1
... Pc was chosen to be 1, as experiments with different values showed, the cross-over is a good thing, it increases diversity with little damaging effect, so that lower mutation rates can be used, which more damaging. Population size does bring slightly better results (when the rest of the parameters a ...
... Pc was chosen to be 1, as experiments with different values showed, the cross-over is a good thing, it increases diversity with little damaging effect, so that lower mutation rates can be used, which more damaging. Population size does bring slightly better results (when the rest of the parameters a ...
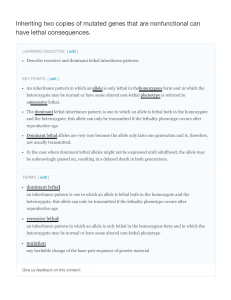
Inheriting two copies of mutated genes that are
... hypothetical essential gene. In one quarter of their offspring, we would expect to observe individuals that are homozygous recessive for the nonfunctional allele. Because the gene is essential, these individuals might fail to develop past fertilization, die in utero, or die later in life, depending ...
... hypothetical essential gene. In one quarter of their offspring, we would expect to observe individuals that are homozygous recessive for the nonfunctional allele. Because the gene is essential, these individuals might fail to develop past fertilization, die in utero, or die later in life, depending ...
The phenotypic consequences of MECP2 mutations extend beyond
... strikes females, Rett syndrome (RTT) has been an enigmatic disorder since it was first recognized. The identification of mutation in MECP2 as the cause of most cases of RTT affords us the opportunity to explore the mechanisms that underlie the disorder both clinically and molecularly. However, the g ...
... strikes females, Rett syndrome (RTT) has been an enigmatic disorder since it was first recognized. The identification of mutation in MECP2 as the cause of most cases of RTT affords us the opportunity to explore the mechanisms that underlie the disorder both clinically and molecularly. However, the g ...
Genetics of Epilepsy - Center for Neurosciences
... 7 good candidate pathogenic de novo variants based on gene function 2 probands have de novo variants possibly ...
... 7 good candidate pathogenic de novo variants based on gene function 2 probands have de novo variants possibly ...
C. elegans DAF-2 as a Model for Human Insulin Receptoropathies
... Mutation Project (MMP) in C. elegans provides such a resource, consisting of a distributed collection of genetic alleles generated by chemical mutagenesis and selected only for viability at room temperature (T H O M P S O N et al. 2013). Each MMP strain has been clonally selected and expanded for te ...
... Mutation Project (MMP) in C. elegans provides such a resource, consisting of a distributed collection of genetic alleles generated by chemical mutagenesis and selected only for viability at room temperature (T H O M P S O N et al. 2013). Each MMP strain has been clonally selected and expanded for te ...
Koinophilia

Koinophilia is an evolutionary hypothesis concerning sexual selection which proposes that animals seeking mate preferentially choose individuals with a minimum of unusual features. Koinophilia intends to explain the clustering of organisms into species and other issues described by Darwin's Dilemma. The term derives from the Greek, koinos, ""the usual"", and philos, ""fondness"".Natural selection causes beneficial inherited features to become more common and eventually replace their disadvantageous counterparts. A sexually-reproducing animal would be expected to avoid individuals with unusual features, and to prefer to mate with individuals displaying a predominance of common or average features. This means that mates displaying mutant features are also avoided. This is advantageous because most mutations that manifest themselves as changes in appearance, functionality or behavior, are disadvantageous. Because it is impossible to judge whether a new mutation is beneficial or not, koinophilic animals avoid them all, at the cost of avoiding the occasional beneficial mutation. Thus, koinophilia, although not infallible in its ability to distinguish fit from unfit mates, is a good strategy when choosing a mate. A koinophilic choice ensures that offspring are likely to inherit features that have been successful in the past.Koinophilia differs from assortative mating, where ""like prefers like"". If like preferred like, leucistic animals (such as white peacocks) would be sexually attracted to one another, and a leucistic subspecies would come into being. Koinophilia predicts that this is unlikely because leucistic animals are attracted to the average in the same way as other animals. Since non-leucistic animals are not attracted by leucism, few leucistic individuals find mates, and leucistic lineages will rarely form.Koinophilia provides simple explanations for the rarity of speciation (in particular Darwin's Dilemma), evolutionary stasis, punctuated equilibria, and the evolution of cooperation. Koinophilia might also contribute to the maintenance of sexual reproduction, preventing its reversion to the much simpler and inherently more advantageous asexual form of reproduction.The koinophilia hypothesis is supported by research into the physical attractiveness of human faces by Judith Langlois and her co-workers. They found that the average of two human faces was more attractive than either of the faces from which that average was derived. The more faces (of the same gender and age) that were used in the averaging process the more attractive and appealing the average face became. This work into averageness supports koinophilia as an explanation of what constitutes a beautiful face, and how the individuality of a face is recognized.







![Spectrum of [beta] thalassemia mutations and HbF levels in the](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014164939_1-79827c78cbc8128eaad3fd6fece2f656-300x300.png)