F2007_311_summary_V
... Milankovitch cycles, but amplitude (magnitude) of cycles not consistent with theory (100,000 year cycle is dominant, but should have weakest effect on sunshine) changes occurred in both hemispheres at same time but seasonality in southern hemisphere should be different from northern hemisphere appea ...
... Milankovitch cycles, but amplitude (magnitude) of cycles not consistent with theory (100,000 year cycle is dominant, but should have weakest effect on sunshine) changes occurred in both hemispheres at same time but seasonality in southern hemisphere should be different from northern hemisphere appea ...
ES Spring Exam Study
... 67. Why is the ozone layer important and what chemicals may destroy it? 68. In which layer does most weather occur? 69. What three things happen to solar radiation as it approaches or contacts Earth? 70. What is a temperature inversion and why may it be harmful? 71. Which type of solar radiation is ...
... 67. Why is the ozone layer important and what chemicals may destroy it? 68. In which layer does most weather occur? 69. What three things happen to solar radiation as it approaches or contacts Earth? 70. What is a temperature inversion and why may it be harmful? 71. Which type of solar radiation is ...
The Earth`s structure
... collide, deep trenches in the ocean occur. As the plate descends it melts to generate magma. As this magma rises, it may erupt at Earth’s surface, forming a chain of volcanoes. Where continental plates collide, mountain ranges such as the Himalayas arise. Mountain chains are also formed where one of ...
... collide, deep trenches in the ocean occur. As the plate descends it melts to generate magma. As this magma rises, it may erupt at Earth’s surface, forming a chain of volcanoes. Where continental plates collide, mountain ranges such as the Himalayas arise. Mountain chains are also formed where one of ...
Chapter 4 Mt. St. Helens: A Case Study
... The unloading of the summit of the volcano by the debris avalanche triggered the expansion of high temperature‐high pressure steam trapped in the cracks and voids in the volcano and the vesiculation of gases dissolved in the dacitic magma that had created th ...
... The unloading of the summit of the volcano by the debris avalanche triggered the expansion of high temperature‐high pressure steam trapped in the cracks and voids in the volcano and the vesiculation of gases dissolved in the dacitic magma that had created th ...
Lesson 3: The formation of mountains Factsheet for teachers
... The Himalayas: The Himalayan range was formed 25 million years ago when the Indo-Australian plate collided with the Eurasian plate. Mount Everest, located in the Himalayan range, is a fold mountain and is the highest mountain not only in Asia, but on Earth at 8849 metres above sea level. It is just ...
... The Himalayas: The Himalayan range was formed 25 million years ago when the Indo-Australian plate collided with the Eurasian plate. Mount Everest, located in the Himalayan range, is a fold mountain and is the highest mountain not only in Asia, but on Earth at 8849 metres above sea level. It is just ...
Lesson 3: The formation of mountains Factsheet for teachers
... The Himalayas: The Himalayan range was formed 25 million years ago when the Indo-Australian plate collided with the Eurasian plate. Mount Everest, located in the Himalayan range, is a fold mountain and is the highest mountain not only in Asia, but on Earth at 8849 metres above sea level. It is just ...
... The Himalayas: The Himalayan range was formed 25 million years ago when the Indo-Australian plate collided with the Eurasian plate. Mount Everest, located in the Himalayan range, is a fold mountain and is the highest mountain not only in Asia, but on Earth at 8849 metres above sea level. It is just ...
Differentiation of the Earth
... formation of an early enriched layer (at ~ 30 Myr) that subsequently sank back into the mantle; this hidden layer is not sampled today at either mid ocean ridge volcanism or ocean island volcanism. ...
... formation of an early enriched layer (at ~ 30 Myr) that subsequently sank back into the mantle; this hidden layer is not sampled today at either mid ocean ridge volcanism or ocean island volcanism. ...
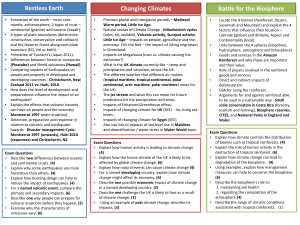
Restless Earth Changing Climates Battle for the Biosphere
... • Explain how the future climate of the UK is likely to be affected by global climate change. (6) • Explain how natural events can cause climate change (4) • For a named developing country, explain how climate change might affect its economy. (6) • Describe one possible economic impact of climate ch ...
... • Explain how the future climate of the UK is likely to be affected by global climate change. (6) • Explain how natural events can cause climate change (4) • For a named developing country, explain how climate change might affect its economy. (6) • Describe one possible economic impact of climate ch ...
244KB - NZQA
... cause of volcanic activity in the Kermadec Islands (Raoul), including explanation of the role of water in producing explosive eruptions due to lowered melting point of crust material. • Gives a comprehensive explanation that a dacite eruption would contain a higher percentage of overlying (AP) crust ...
... cause of volcanic activity in the Kermadec Islands (Raoul), including explanation of the role of water in producing explosive eruptions due to lowered melting point of crust material. • Gives a comprehensive explanation that a dacite eruption would contain a higher percentage of overlying (AP) crust ...
599KB - NZQA
... cause of volcanic activity in the Kermadec Islands (Raoul), including explanation of the role of water in producing explosive eruptions due to lowered melting point of crust material. • Gives a comprehensive explanation that a dacite eruption would contain a higher percentage of overlying (AP) crust ...
... cause of volcanic activity in the Kermadec Islands (Raoul), including explanation of the role of water in producing explosive eruptions due to lowered melting point of crust material. • Gives a comprehensive explanation that a dacite eruption would contain a higher percentage of overlying (AP) crust ...
The Earth - Cardinal Newman High School
... cracks or vents found on the Earth’s crust of the ocean floor (oceanic crust) these areas rise above the surrounding crust underwater mountains, but most are under hundreds of meters below surface a few are above the water (island of Iceland, islands in the Philippines) underwater volcanoes ...
... cracks or vents found on the Earth’s crust of the ocean floor (oceanic crust) these areas rise above the surrounding crust underwater mountains, but most are under hundreds of meters below surface a few are above the water (island of Iceland, islands in the Philippines) underwater volcanoes ...
17.3 Theory of plate Tectonics
... is subducted? What is created with the material? The subducted plate melts in the mantle. Some of the resulting magma is forced to the surface creating a series of volcanoes that are parallel to the subduction zone. Some of the magma is recycled into new oceanic crust at the ridge. ...
... is subducted? What is created with the material? The subducted plate melts in the mantle. Some of the resulting magma is forced to the surface creating a series of volcanoes that are parallel to the subduction zone. Some of the magma is recycled into new oceanic crust at the ridge. ...
1 Island Arc Magmatism
... Lesser Antilles arc lavas Pb ratios both higher and lower than Atlantic sediments source contamination and crustal assimilation? ...
... Lesser Antilles arc lavas Pb ratios both higher and lower than Atlantic sediments source contamination and crustal assimilation? ...
plate tectonics article from nat'l geo. fall 2012
... These convergent boundaries also occur where a plate of ocean dives, in a process called subduction, under a landmass. As the overlying plate lifts up, it also forms mountain ranges. In addition, the diving plate melts and is often spewed out in volcanic eruptions such as those that formed some of t ...
... These convergent boundaries also occur where a plate of ocean dives, in a process called subduction, under a landmass. As the overlying plate lifts up, it also forms mountain ranges. In addition, the diving plate melts and is often spewed out in volcanic eruptions such as those that formed some of t ...
Part B - Bakersfield College
... • The plate tectonic model describes surface features, geologic environments, and patterns of EQ’s and volcanism. • Ridged lithospheric plates (continents + ocean floor) ride along the soft layer (like hot wax) called the asthenosphere • Plates spread apart, collide, and slide past one another. • EQ ...
... • The plate tectonic model describes surface features, geologic environments, and patterns of EQ’s and volcanism. • Ridged lithospheric plates (continents + ocean floor) ride along the soft layer (like hot wax) called the asthenosphere • Plates spread apart, collide, and slide past one another. • EQ ...
TEST REVIEW KEY – Cat Events, W-E
... Physical (mechanical) weathering is caused by PLANT ROOTS growing, animals DIGGING, or ice WEDGING. ...
... Physical (mechanical) weathering is caused by PLANT ROOTS growing, animals DIGGING, or ice WEDGING. ...
PT Magic Squares - Welcome to Rossignols.net
... your answers by adding the numbers to see if the sums of each column and each row add up to the same “Magic Number”. 1. A boundary in which two plates slide past each other, neither creating nor destroying crust. 2. Supercontinent that began breaking up 200 million years ago. 3. Feature on seafloor ...
... your answers by adding the numbers to see if the sums of each column and each row add up to the same “Magic Number”. 1. A boundary in which two plates slide past each other, neither creating nor destroying crust. 2. Supercontinent that began breaking up 200 million years ago. 3. Feature on seafloor ...
Venus Entry Probe Initiative landing site proposal: a GIS approach
... points to a shallow crustal source (Hansen, 2005). It will be necessary to determinate the composition of this volcanic materials to better understand the possible processes that could originate this regionally important type of terrain. 2.3. Geochemical sampling of possible evolved materials: the c ...
... points to a shallow crustal source (Hansen, 2005). It will be necessary to determinate the composition of this volcanic materials to better understand the possible processes that could originate this regionally important type of terrain. 2.3. Geochemical sampling of possible evolved materials: the c ...
18.3 - Faculty Perry, Oklahoma
... divergent boundary occurs where tectonic plates move apart convergent boundary occurs where tectonic plates push together transform boundary occurs where tectonic plates scrape past each other rift valley a gap formed between two diverging plates magnetic reversal when Earth’s magnetic north and sou ...
... divergent boundary occurs where tectonic plates move apart convergent boundary occurs where tectonic plates push together transform boundary occurs where tectonic plates scrape past each other rift valley a gap formed between two diverging plates magnetic reversal when Earth’s magnetic north and sou ...
Geography and Society – First Discussions
... List and discuss at least three of the hazards associated with volcanoes. Relate the benefits associated with volcanoes and volcanism. Discuss which areas of the United States are at most risk from volcanic eruptions and why. Explain two of the techniques used to predict volcanic eruptions. ...
... List and discuss at least three of the hazards associated with volcanoes. Relate the benefits associated with volcanoes and volcanism. Discuss which areas of the United States are at most risk from volcanic eruptions and why. Explain two of the techniques used to predict volcanic eruptions. ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.