CONSTRUCTING A SEA-FLOOR SPREADING MODEL
... The lithosphere is composed of the crust and upper mantle and is broken into large pieces know as plates. The lithospheric plates, carrying both oceanic and continental rock, “float” on the plastic part of the mantle below the lithosphere. Plates move together, separate, and slide past each other cr ...
... The lithosphere is composed of the crust and upper mantle and is broken into large pieces know as plates. The lithospheric plates, carrying both oceanic and continental rock, “float” on the plastic part of the mantle below the lithosphere. Plates move together, separate, and slide past each other cr ...
Alfred Wegener was a scientist who lived about 100 years ago
... tectonic plates by mapping the location of earthquakes all over the world. Volcanoes occur near plate boundaries if one plate is subducting beneath another plate. Where two continents converge, mountains are pushed up. Where an ocean plate converges with a continent, the ocean floor subducts beneath ...
... tectonic plates by mapping the location of earthquakes all over the world. Volcanoes occur near plate boundaries if one plate is subducting beneath another plate. Where two continents converge, mountains are pushed up. Where an ocean plate converges with a continent, the ocean floor subducts beneath ...
Weathering, Erosion, and Plate Tectonics
... wedging occurs when water freezes in between the pores of large sedimentary rocks. ...
... wedging occurs when water freezes in between the pores of large sedimentary rocks. ...
Inside Earth Chapter 1 Plate Tectonics Study Guide Notes
... - He said that at the mid-ocean ridge, molten materials rise from the mantle and erupt. The molten material then spreads out pushing older rock to both sides of the ridge. - Hess called the process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor sea-floor spreading. Evidence to support Sea-flo ...
... - He said that at the mid-ocean ridge, molten materials rise from the mantle and erupt. The molten material then spreads out pushing older rock to both sides of the ridge. - Hess called the process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor sea-floor spreading. Evidence to support Sea-flo ...
Section 1.1 Outline
... Inner core: a ball of hot, solid materials, enormous pressure; remains a solid Outer core: layer of liquid metals that surrounds inner core; remains a liquid due to lower pressure Mantle: thickest layer (2900 km or 1700 mi); hot rock that is less dense than core; top part is cool & rigid; below that ...
... Inner core: a ball of hot, solid materials, enormous pressure; remains a solid Outer core: layer of liquid metals that surrounds inner core; remains a liquid due to lower pressure Mantle: thickest layer (2900 km or 1700 mi); hot rock that is less dense than core; top part is cool & rigid; below that ...
lithosphere, mid-ocean ridge
... 9. Which is most likely to happen at G? a. Rising magma will create new crust. b. Subduction will cause a deep trench c. Colliding plates will cause rocks to crumple d. Moving plates will create island arcs. Extended Response (worth 6 points each on the test) Describing. Describe Earth’s crust an ...
... 9. Which is most likely to happen at G? a. Rising magma will create new crust. b. Subduction will cause a deep trench c. Colliding plates will cause rocks to crumple d. Moving plates will create island arcs. Extended Response (worth 6 points each on the test) Describing. Describe Earth’s crust an ...
- gst boces
... o Oceanic-Oceanic Divergence: Mid-Ocean Ridge, where new crust is created. Mid-ocean ridges: new, young, crust created; Trenches: holes where crust is subducted into mantle. Ring of Fire: Convergent boundaries around Pacific Plate where most earthquakes and volcanoes occur. ...
... o Oceanic-Oceanic Divergence: Mid-Ocean Ridge, where new crust is created. Mid-ocean ridges: new, young, crust created; Trenches: holes where crust is subducted into mantle. Ring of Fire: Convergent boundaries around Pacific Plate where most earthquakes and volcanoes occur. ...
Rocks - SchoolNotes
... •Glaciers are like big snow plows, and when they come through, they pick up rocks, and sediment and other such things an move them far away from where they started. •When the glacier starts to melt, it drops all this material. •These huge rocks are deposited that way. •It is how you can tell that th ...
... •Glaciers are like big snow plows, and when they come through, they pick up rocks, and sediment and other such things an move them far away from where they started. •When the glacier starts to melt, it drops all this material. •These huge rocks are deposited that way. •It is how you can tell that th ...
Plate Tectonics Review
... P-waves are underground seismic waves that travel the most quickly through Earth’s crust, causing the ground to move in the direction of the wave’s motion. They can travel through solids, liquids, and gases. S-waves are underground seismic waves that travel slower, causing the ground to move perpend ...
... P-waves are underground seismic waves that travel the most quickly through Earth’s crust, causing the ground to move in the direction of the wave’s motion. They can travel through solids, liquids, and gases. S-waves are underground seismic waves that travel slower, causing the ground to move perpend ...
The most important questions to study for the exam
... • the absorption by the CO2 gas of the planet's atmosphere of infrared radiation emitted by the hot planet surface, which itself is heated by sunlight. • the trapping of hot gases ejected by continuously active volcanoes under the dense cloud cover. • the absorption of solar visible radiation by the ...
... • the absorption by the CO2 gas of the planet's atmosphere of infrared radiation emitted by the hot planet surface, which itself is heated by sunlight. • the trapping of hot gases ejected by continuously active volcanoes under the dense cloud cover. • the absorption of solar visible radiation by the ...
Weathering in Iceland
... the Quaternary and Tertiary formations of Iceland, whereas a large part of the precipitation falling on ice-free land in the younger volcanic zones, covered by post-glacial lavas, inltrates and may discharge directly as groundwater into the ocean or emerge as springs to form spring-fed streams and ...
... the Quaternary and Tertiary formations of Iceland, whereas a large part of the precipitation falling on ice-free land in the younger volcanic zones, covered by post-glacial lavas, inltrates and may discharge directly as groundwater into the ocean or emerge as springs to form spring-fed streams and ...
The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics
... The subducting plate is bent downward to form a very deep depression in the ocean floor called a trench. The worlds deepest parts of the ocean are found along ...
... The subducting plate is bent downward to form a very deep depression in the ocean floor called a trench. The worlds deepest parts of the ocean are found along ...
Layers of the Earth
... – Lithosphere: Acts like a rigid, but still brittle solid. – Asthenosphere: Plastically (not liquid!) layer. ...
... – Lithosphere: Acts like a rigid, but still brittle solid. – Asthenosphere: Plastically (not liquid!) layer. ...
1AER200-MET1
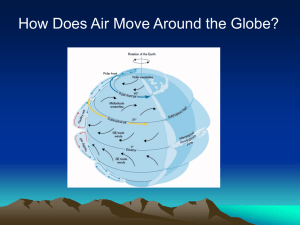
... Higher day temperatures, lower night temperatures Good visibility Cumulus type clouds Breezy ...
... Higher day temperatures, lower night temperatures Good visibility Cumulus type clouds Breezy ...
Energy In The Rock Cycle
... water harden sediments and __________ them together to form new rocks as water __________or moves away. • Chemical __________ within the earth’s crust __________rocks from one form to another. ...
... water harden sediments and __________ them together to form new rocks as water __________or moves away. • Chemical __________ within the earth’s crust __________rocks from one form to another. ...
Earth`s Interior notes
... solid rock that is very hot. It is separated into 3 layers. The lithosphere, the asthenosphere and lower mantle. thickness – almost 3,000 kilometers composition – silicon, magnesium and iron ...
... solid rock that is very hot. It is separated into 3 layers. The lithosphere, the asthenosphere and lower mantle. thickness – almost 3,000 kilometers composition – silicon, magnesium and iron ...
LAKE TOBA
... The destination for the 2015 trip will be Lake Toba on the island of Sumatra in Indonesia. Lake Toba, which is one of the biggest lakes in SE Asia, is the ‘hole’ left behind following the eruption(s) of a super volcano some 70,000 years ago. Whether there was anyone around at the time on the island ...
... The destination for the 2015 trip will be Lake Toba on the island of Sumatra in Indonesia. Lake Toba, which is one of the biggest lakes in SE Asia, is the ‘hole’ left behind following the eruption(s) of a super volcano some 70,000 years ago. Whether there was anyone around at the time on the island ...
thetheoryofplatetectonics
... • Plate- a large section of Earth’s oceanic or continental crust and rigid upper mantle that moves around the asthenosphere • Plate tectonics- theory that Earth’s crust and upper mantle are broken into plates that float and move around the plasticlike layer of the mantle • Seafloor spreading- Jess’s ...
... • Plate- a large section of Earth’s oceanic or continental crust and rigid upper mantle that moves around the asthenosphere • Plate tectonics- theory that Earth’s crust and upper mantle are broken into plates that float and move around the plasticlike layer of the mantle • Seafloor spreading- Jess’s ...
Rocks and Minerals
... formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals • The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another ...
... formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals • The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.