theory of plate tectonics text
... flows very slowly. This movement occurs because of changes in density within the asthenosphere. These density changes are caused by the outward flow of thermal energy from deep within the Earth. When rock is heated, it expands, becomes less dense, and tends to rise to the surface of the Earth. As th ...
... flows very slowly. This movement occurs because of changes in density within the asthenosphere. These density changes are caused by the outward flow of thermal energy from deep within the Earth. When rock is heated, it expands, becomes less dense, and tends to rise to the surface of the Earth. As th ...
Deformation in the Lower Crust of the San Andreas Fault System in
... of the LCL along the margin with a detachment beneath all of coastal California slipping at up to the total SAF motion. Although contraction across the SAF at 5 to 6 mm/year (22) since 30 Ma can match the extent of the high-velocity lowermost crustal layer, such a detachment without recorded seismic ...
... of the LCL along the margin with a detachment beneath all of coastal California slipping at up to the total SAF motion. Although contraction across the SAF at 5 to 6 mm/year (22) since 30 Ma can match the extent of the high-velocity lowermost crustal layer, such a detachment without recorded seismic ...
Geology: Fluids in the lower crust following Mendocino triple
... layer which has velocities typical of mafic lithologies, while the deeper reflections are at the level of Moho formation. This is similar to the midocean ridges where melt due to upwelling asthenosphere is found in discrete bodies, both shallow and near the oceanic Moho (Kent et al., 1993; Garmany, ...
... layer which has velocities typical of mafic lithologies, while the deeper reflections are at the level of Moho formation. This is similar to the midocean ridges where melt due to upwelling asthenosphere is found in discrete bodies, both shallow and near the oceanic Moho (Kent et al., 1993; Garmany, ...
6th Grade Math Lesson Plans
... along plate boundaries? I can identify the three types of plate boundaries and what type of geologic formations are associated with each one ...
... along plate boundaries? I can identify the three types of plate boundaries and what type of geologic formations are associated with each one ...
Chapter 22 Plate Tectonics
... • Most transform faults join two segments of a mid-ocean ridge. • Transform faults are oriented perpendicular to mid-ocean ...
... • Most transform faults join two segments of a mid-ocean ridge. • Transform faults are oriented perpendicular to mid-ocean ...
convergent boundary
... proposed the hypothesis of sea-floor spreading, in which basaltic magma from the mantle rises to create new ocean floor at mid-ocean ridges. On each side of the ridge, sea floor moves from the ridge towards the deep-sea trenches, where it is subducted and recycled back into the mantle ...
... proposed the hypothesis of sea-floor spreading, in which basaltic magma from the mantle rises to create new ocean floor at mid-ocean ridges. On each side of the ridge, sea floor moves from the ridge towards the deep-sea trenches, where it is subducted and recycled back into the mantle ...
Intra-arc extension in Central America: Links between plate motions
... occurred in this region. Abundant basin-parallel fault-like features are seen north of the Nicaraguan graben (Fig. 3), which could certainly have been generated by normal faulting during basin extension. What is missing in Nicaragua (in contrast to the Taupo belt in NZ) is seismic evidence of active ...
... occurred in this region. Abundant basin-parallel fault-like features are seen north of the Nicaraguan graben (Fig. 3), which could certainly have been generated by normal faulting during basin extension. What is missing in Nicaragua (in contrast to the Taupo belt in NZ) is seismic evidence of active ...
6.7 Plate Tectonics
... Highlight each boundary on questions 2, 3, and 4 using a different color. Use the same color to highlight the arrows that represent convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries on the map at the top of the handout ...
... Highlight each boundary on questions 2, 3, and 4 using a different color. Use the same color to highlight the arrows that represent convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries on the map at the top of the handout ...
The Origins of Plate Tectonics Theory
... Mapping the ocean floor Before the 1920s, the crust below the seas was thought to be flat and featureless. During World War I, however, ships equipped with sonar began to produce data about the topography of the seafloor. These sonar maps showed the seafloor to be anything but featureless – instead, ...
... Mapping the ocean floor Before the 1920s, the crust below the seas was thought to be flat and featureless. During World War I, however, ships equipped with sonar began to produce data about the topography of the seafloor. These sonar maps showed the seafloor to be anything but featureless – instead, ...
Geochemistry of Serpentinized Peridotites from the Mariana Forearc
... Guest Editors: Gray Bebout, Jonathan Martin, and Tim Elliott ...
... Guest Editors: Gray Bebout, Jonathan Martin, and Tim Elliott ...
Deep Origin of Hotspots— the Mantle Plume Model
... Hawaii must also be 200 to 300 K hothydrous minerals. The water, when reter than the surrounding mantle to leased by metamorphism, causes already achieve the required large melt frac1000 hot rock material beneath island arcs to tions at depths below the 80-km-thick melt (2). lithosphere (6). Such ho ...
... Hawaii must also be 200 to 300 K hothydrous minerals. The water, when reter than the surrounding mantle to leased by metamorphism, causes already achieve the required large melt frac1000 hot rock material beneath island arcs to tions at depths below the 80-km-thick melt (2). lithosphere (6). Such ho ...
d6 Lithosphere, asthenosphere, mesosphere - e
... same rate of deformation, rock behaves elastically and, being brittle, it can break (fault). The shell of rock above the asthenosphere is called the lithosphere (Gk. lithos, stone). The lithosphere as its name implies is more rigid than the asthenosphere. It is important to remember that the names c ...
... same rate of deformation, rock behaves elastically and, being brittle, it can break (fault). The shell of rock above the asthenosphere is called the lithosphere (Gk. lithos, stone). The lithosphere as its name implies is more rigid than the asthenosphere. It is important to remember that the names c ...
ODP`s 100 greatest hits: The past and future of the Ocean Drilling
... ever really succeeded in drilling in fractured rock or much deeper than 2 km into either sediments or basement because of hole instability problems. In addition, it has not been possible to drill in shallow water, in high temperature formations or in pack ice. Thus because of platform limitations, t ...
... ever really succeeded in drilling in fractured rock or much deeper than 2 km into either sediments or basement because of hole instability problems. In addition, it has not been possible to drill in shallow water, in high temperature formations or in pack ice. Thus because of platform limitations, t ...
Subduction and collision processes in the Central Andes
... crustal shortening (equivalent to some 70% of the width of the Altiplano7±9) and only some 75 km of shortening at the latitude of Puna10. Our aim was to resolve crustal and mantle structures associated with the plateau building and subduction processes in the Central Andes. Several seismic networks ...
... crustal shortening (equivalent to some 70% of the width of the Altiplano7±9) and only some 75 km of shortening at the latitude of Puna10. Our aim was to resolve crustal and mantle structures associated with the plateau building and subduction processes in the Central Andes. Several seismic networks ...
proposal
... Since it is highly likely that most of the primitive alkaline volcanic rocks come from the TBL and the TBL coincides with the LAB, the main questions raised in this project are (i) what can we learn about partial melting depths, processes and sources involved during petrogenesis based on isotope and ...
... Since it is highly likely that most of the primitive alkaline volcanic rocks come from the TBL and the TBL coincides with the LAB, the main questions raised in this project are (i) what can we learn about partial melting depths, processes and sources involved during petrogenesis based on isotope and ...
The role of subduction in the evolution of the Apennines foreland basin
... than the wavelength of the flexure (thin plate approximation). The deflection of the top of our model plate is fitted to the base of the Plio-Pleistocene foreland basin of the Apennines. Model parameters (e.g. loads, densities, rheologies), which are not closely constrained by observations are being ...
... than the wavelength of the flexure (thin plate approximation). The deflection of the top of our model plate is fitted to the base of the Plio-Pleistocene foreland basin of the Apennines. Model parameters (e.g. loads, densities, rheologies), which are not closely constrained by observations are being ...
Mountain Building
... – Large strike-slip fault that cuts through the lithosphere – Often associated with plate boundaries ...
... – Large strike-slip fault that cuts through the lithosphere – Often associated with plate boundaries ...
Insight into collision zone dynamics from topography
... record from the overriding plate contains Upper OligoceneLower Miocene marine carbonates deposited between terrestrial clastic sedimentary rocks, in units such as the Qom Formation and its lateral equivalents. This stratigraphy shows that during the Late Oligocene–Early Miocene the surface of the ov ...
... record from the overriding plate contains Upper OligoceneLower Miocene marine carbonates deposited between terrestrial clastic sedimentary rocks, in units such as the Qom Formation and its lateral equivalents. This stratigraphy shows that during the Late Oligocene–Early Miocene the surface of the ov ...
Plate Tectonics as a Far- From- Equilibrium Self
... crust) fractures the lithosphere when it experiences even limited horizontal extension (18,36) The thickening of oceanic plates as they cool generates gravitational forces which drives the plates and, in general, puts them into lateral compression, holding out the surrounding fluids, and keeping the ...
... crust) fractures the lithosphere when it experiences even limited horizontal extension (18,36) The thickening of oceanic plates as they cool generates gravitational forces which drives the plates and, in general, puts them into lateral compression, holding out the surrounding fluids, and keeping the ...
Lower plate deformation at the Chile Triple Junction from the
... 4. Structure of the Ocean Floor in the CTJ Region 4.1. Bathymetry of the SCR North of the CTJ The SCR offshore southern Chile consists of spreading segments trending ~N160°, separated by a series of parallel fracture zones, from north to south: the Guamblin, Darwin, Taitao, and Tres Montes FZs (Figu ...
... 4. Structure of the Ocean Floor in the CTJ Region 4.1. Bathymetry of the SCR North of the CTJ The SCR offshore southern Chile consists of spreading segments trending ~N160°, separated by a series of parallel fracture zones, from north to south: the Guamblin, Darwin, Taitao, and Tres Montes FZs (Figu ...
Basin Analysis
... the rocks that fill sedimentary basins. • A sedimentary basin is an area in which sediments have accumulated during a -me span to significantly greater thickness than in the surrounding areas. • ...
... the rocks that fill sedimentary basins. • A sedimentary basin is an area in which sediments have accumulated during a -me span to significantly greater thickness than in the surrounding areas. • ...
CHAPTER 3 ELASTICITY AND FLEXURE
... The plot of (w/wb) vs. (x-xo)/(xb/xo) defines a universal flexure profile which is valid for any two-dimensional elastic flexure of the lithosphere under end loading. ...
... The plot of (w/wb) vs. (x-xo)/(xb/xo) defines a universal flexure profile which is valid for any two-dimensional elastic flexure of the lithosphere under end loading. ...
as a PDF - Dipartimento di Scienze della Terra
... subduction zones have mostly continental lithosphere in the upper plate and the dip of the first 125 km is mostly constrained by the thickness and shape of the upper continental plate when present, and by the angle of the slab with respect to the convergence direction as previously mentioned. The wes ...
... subduction zones have mostly continental lithosphere in the upper plate and the dip of the first 125 km is mostly constrained by the thickness and shape of the upper continental plate when present, and by the angle of the slab with respect to the convergence direction as previously mentioned. The wes ...
Chapter 4
... theory of Plate Tectonics, hi h de nes the outer ortion of the earth as a rittle outer layer that is broken into moving pieces called tectonic plates. This theory is supported by many lines of evidence including the shape of the continents, the distribution of fossils and rocks, the distribution of ...
... theory of Plate Tectonics, hi h de nes the outer ortion of the earth as a rittle outer layer that is broken into moving pieces called tectonic plates. This theory is supported by many lines of evidence including the shape of the continents, the distribution of fossils and rocks, the distribution of ...
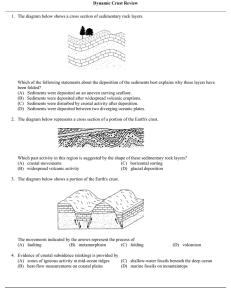
Dynamic Crust Review
... (C) New oceanic crust will form. (B) Earths circumference will increase. (D) Earths magnetic field will reverse direction. 37. Which inference is supported by a study of the Earth's magnetic rock record? (A) The Earth's magnetic poles appear to have changed location over time. (B) The Earth's magnet ...
... (C) New oceanic crust will form. (B) Earths circumference will increase. (D) Earths magnetic field will reverse direction. 37. Which inference is supported by a study of the Earth's magnetic rock record? (A) The Earth's magnetic poles appear to have changed location over time. (B) The Earth's magnet ...
Oceanic trench
The oceanic trenches are hemispheric-scale long but narrow topographic depressions of the sea floor. They are also the deepest parts of the ocean floor. Oceanic trenches are a distinctive morphological feature of convergent plate boundaries, along which lithospheric plates move towards each other at rates that vary from a few mm to over ten cm per year. A trench marks the position at which the flexed, subducting slab begins to descend beneath another lithospheric slab. Trenches are generally parallel to a volcanic island arc, and about 200 km (120 mi) from a volcanic arc. Oceanic trenches typically extend 3 to 4 km (1.9 to 2.5 mi) below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor. The greatest ocean depth to be sounded is in the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench, at a depth of 11,034 m (36,201 ft) below sea level. Oceanic lithosphere moves into trenches at a global rate of about 3 km2/yr.