Plate Tectonics Vocabulary Continental Drift The
... The hypothesis that the continents slowly move across Earth’s Surface A plate boundary where two plants move toward each other A deep valley along the ocean floor which oceanic crust slowly sinks toward the mantle A plate boundary where two plates move away from each other A break or crack in Earth’ ...
... The hypothesis that the continents slowly move across Earth’s Surface A plate boundary where two plants move toward each other A deep valley along the ocean floor which oceanic crust slowly sinks toward the mantle A plate boundary where two plates move away from each other A break or crack in Earth’ ...
Name - Schoolwires.net
... Island arcs- volcanic arc--formed as one oceanic tectonic plate subducts under another one and, in most cases, produces magma below the plate above it. Result of friction between converging plates ! Glomar challenger-a deep sea research and scientific drilling vessel for oceanography and marine geol ...
... Island arcs- volcanic arc--formed as one oceanic tectonic plate subducts under another one and, in most cases, produces magma below the plate above it. Result of friction between converging plates ! Glomar challenger-a deep sea research and scientific drilling vessel for oceanography and marine geol ...
Ocean secret (Geography)
... Part 1 Do you know the name of the four oceans in the world? Point them on a world map? Paciific, Atlantic, Indian, and Arctic Oceans Part 2 Do you know where is the highest and lowest places on Earth's crust? They may name Mt. Everest and the Grand Canyon, respectively. Tell them that the tallest m ...
... Part 1 Do you know the name of the four oceans in the world? Point them on a world map? Paciific, Atlantic, Indian, and Arctic Oceans Part 2 Do you know where is the highest and lowest places on Earth's crust? They may name Mt. Everest and the Grand Canyon, respectively. Tell them that the tallest m ...
Chapter 13 Exploring the Oceans
... Explain how the mouth of a river opening into the ocean effects salinity and why. Explain the relationship between movement and salinity of ocean water. ...
... Explain how the mouth of a river opening into the ocean effects salinity and why. Explain the relationship between movement and salinity of ocean water. ...
How can there be life
... sea — a vast realm of frigid temperatures, intense pressure, and near-total darkness — is almost unknown to humans. Since only 1% of all sunlight penetrates more than about 100 m below the surface, and since most life on Earth is fueled by the Sun, people in centuries past presumed that the deep sea ...
... sea — a vast realm of frigid temperatures, intense pressure, and near-total darkness — is almost unknown to humans. Since only 1% of all sunlight penetrates more than about 100 m below the surface, and since most life on Earth is fueled by the Sun, people in centuries past presumed that the deep sea ...
Student Notes
... -very deep, narrow areas of the ocean where old oceanic crust ____________________ (see the map on pages 60 and 61 for large trenches) 6.What is seafloor spreading? -occurs at _____________________ where new crust is formed from rising magma 7.What are subduction zones? -areas where ocean crust is p ...
... -very deep, narrow areas of the ocean where old oceanic crust ____________________ (see the map on pages 60 and 61 for large trenches) 6.What is seafloor spreading? -occurs at _____________________ where new crust is formed from rising magma 7.What are subduction zones? -areas where ocean crust is p ...
Formation of Himalayas
... Volcanoes formed as magma rose from the subduction zone to the surface. ...
... Volcanoes formed as magma rose from the subduction zone to the surface. ...
What does the ocean floor look like
... A walk across the ocean floor Our journey begins with a shallow descent from a mid-Atlantic beach to the continental shelf, a narrow ribbon of seafloor that extends around the world’s continents and ranges between 30 and 1300 km wide. At the edge it’s only about 200m deep. A uniform layer of mud and ...
... A walk across the ocean floor Our journey begins with a shallow descent from a mid-Atlantic beach to the continental shelf, a narrow ribbon of seafloor that extends around the world’s continents and ranges between 30 and 1300 km wide. At the edge it’s only about 200m deep. A uniform layer of mud and ...
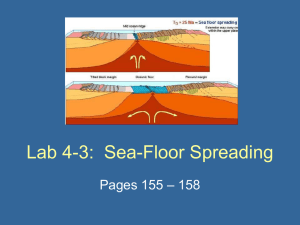
Lab 4-3: Sea-Floor Spreading
... What motion of the sea floor is responsible for the formation of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge’s rift valley? • The ocean crust is moving in opposite directions (diverging). ...
... What motion of the sea floor is responsible for the formation of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge’s rift valley? • The ocean crust is moving in opposite directions (diverging). ...
Name - Cedar Hill ISD
... 15. The oceanic plate is SUBDUCTED below the continental plate in a convergent boundary because the oceanic plate is MORE dense then the continental plate. When this happens, the oceanic plate returns to the MANTLE. 16. Why does subduction not occur when two continental plates converge? THEY ARE THE ...
... 15. The oceanic plate is SUBDUCTED below the continental plate in a convergent boundary because the oceanic plate is MORE dense then the continental plate. When this happens, the oceanic plate returns to the MANTLE. 16. Why does subduction not occur when two continental plates converge? THEY ARE THE ...
earthsciencechap17qu..
... 7: An island arc is a string of volcanic islands bordering on an ocean trench. 8: Ocean trenches are deep, V-shaped valleys in the sea floor. 9: A rift is a deep, narrow crack that splits the crust of some mid-ocean ridges. 10: A convergent boundary is the place where two plates meet. 11: The younge ...
... 7: An island arc is a string of volcanic islands bordering on an ocean trench. 8: Ocean trenches are deep, V-shaped valleys in the sea floor. 9: A rift is a deep, narrow crack that splits the crust of some mid-ocean ridges. 10: A convergent boundary is the place where two plates meet. 11: The younge ...
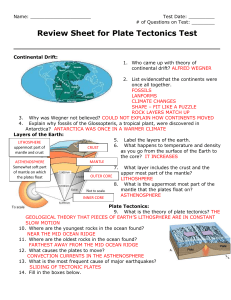
Plate Tectonics Review Sheet
... climate clues (glaciers in Africa and coal in Scandanavia) mountains with very similar structure on both sides of the Atlantic matching fossils on S. America and S. Africa they look like they fit together. ...
... climate clues (glaciers in Africa and coal in Scandanavia) mountains with very similar structure on both sides of the Atlantic matching fossils on S. America and S. Africa they look like they fit together. ...
Plate Tectonics Review Sheet
... climate clues (glaciers in Africa and coal in Scandanavia) mountains with very similar structure on both sides of the Atlantic matching fossils on S. America and S. Africa they look like they fit together. ...
... climate clues (glaciers in Africa and coal in Scandanavia) mountains with very similar structure on both sides of the Atlantic matching fossils on S. America and S. Africa they look like they fit together. ...
Kusky Tim
... Phanerozoic times but absent in the Precambrian, but overall, there have been few changes in the style of OPS accretion with time. Komatiites and banded iron formations occur predominantly in Archean orogenic belts, reflecting higher mantle temperatures and less oxic seawater composition, respective ...
... Phanerozoic times but absent in the Precambrian, but overall, there have been few changes in the style of OPS accretion with time. Komatiites and banded iron formations occur predominantly in Archean orogenic belts, reflecting higher mantle temperatures and less oxic seawater composition, respective ...
mid-ocean ridge
... flattest and smoothest regions and the least explored. • Abyssal plains result from the blanketing of an originally uneven surface of oceanic crust by fine-grained sediments, mainly clay and silt. • The remainder of the sediment comprises chiefly dust (clay particles) blown out to sea from land, and ...
... flattest and smoothest regions and the least explored. • Abyssal plains result from the blanketing of an originally uneven surface of oceanic crust by fine-grained sediments, mainly clay and silt. • The remainder of the sediment comprises chiefly dust (clay particles) blown out to sea from land, and ...
Journey to the bottom of the ocean (1)
... •They are more than 84,000 kilometers (52,000 miles) in length and they extend through the North and South of the Atlantic ocean, the Indian Ocean, and the South Pacific ocean. •According to the plate tectonics theory, volcanic rock is added to the sea floor as the mid-ocean ridge spreads apart. Bac ...
... •They are more than 84,000 kilometers (52,000 miles) in length and they extend through the North and South of the Atlantic ocean, the Indian Ocean, and the South Pacific ocean. •According to the plate tectonics theory, volcanic rock is added to the sea floor as the mid-ocean ridge spreads apart. Bac ...
Test 3 - Course World
... deep-sea garden of hot springs and towering spires they nicknamed the 'Lost City’. "If this were on land," Duke University geologist Jeff Karson said, "it would be a national park." The scientists spotted the formations on Dec. 4 more than 3,200 feet below the frigid, stormy Atlantic during a month- ...
... deep-sea garden of hot springs and towering spires they nicknamed the 'Lost City’. "If this were on land," Duke University geologist Jeff Karson said, "it would be a national park." The scientists spotted the formations on Dec. 4 more than 3,200 feet below the frigid, stormy Atlantic during a month- ...
GEOL 4110 Advanced Earth Science For Teachers Jim Miller
... Oceanic Crust - ~ 48% SiO2, high density rocks , “mafic” Lithospheric Mantle - ~ 40% ...
... Oceanic Crust - ~ 48% SiO2, high density rocks , “mafic” Lithospheric Mantle - ~ 40% ...
Table of Contents - Mr. Tobin`s Earth Science Class
... significance of magnetic patterns on the seafloor. Students will be able to explain the process of seafloor spreading. ...
... significance of magnetic patterns on the seafloor. Students will be able to explain the process of seafloor spreading. ...
biome sydney 4
... pelagic zone is where one can find wales because it is very far away from the land in contrast to the intertidal zone, and tends to be very cold due to its deepness. – Next is the Benthic Zone which is below the pelagic zone. Temperature drops drastically from the last zone and the ...
... pelagic zone is where one can find wales because it is very far away from the land in contrast to the intertidal zone, and tends to be very cold due to its deepness. – Next is the Benthic Zone which is below the pelagic zone. Temperature drops drastically from the last zone and the ...
PRESENTSS
... We can further divide the crust into Continental and Oceanic types based on their composition and densities. ...
... We can further divide the crust into Continental and Oceanic types based on their composition and densities. ...
Review of Plate Tectonics Name
... 10. Another example of a _____________ plate boundary can found in the middle of a continent, is in East Africa and is called the Great Rift Valley. Along this crack, the rift may someday split the eastern part of Africa away from the rest of the continent. As the rift valley widens, its floor gets ...
... 10. Another example of a _____________ plate boundary can found in the middle of a continent, is in East Africa and is called the Great Rift Valley. Along this crack, the rift may someday split the eastern part of Africa away from the rest of the continent. As the rift valley widens, its floor gets ...
12.740 Paleoceanography
... respect to the square root of the age of the seafloor. c. Beyond 70 m.y., underlying diffusion of geothermal heat in is balanced by heat diffusion out of the sea floor, so it does not get much deeper until it reaches a subduction zone. 2. Paleo-depth backtracking a. In order to make oceanic reconstr ...
... respect to the square root of the age of the seafloor. c. Beyond 70 m.y., underlying diffusion of geothermal heat in is balanced by heat diffusion out of the sea floor, so it does not get much deeper until it reaches a subduction zone. 2. Paleo-depth backtracking a. In order to make oceanic reconstr ...
Week 3 (Norton), part b (pdf, 5.7 MB)
... fire” that stretches from southern South America, round the northern Pacific through Japan, Indonesia, and to New Zealand. ...
... fire” that stretches from southern South America, round the northern Pacific through Japan, Indonesia, and to New Zealand. ...
Abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between 3000 and 6000 m. Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth’s surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest and least explored regions on Earth. Abyssal plains are key geologic elements of oceanic basins (the other elements being an elevated mid-ocean ridge and flanking abyssal hills). In addition to these elements, active oceanic basins (those that are associated with a moving plate tectonic boundary) also typically include an oceanic trench and a subduction zone.Abyssal plains were not recognized as distinct physiographic features of the sea floor until the late 1940s and, until very recently, none had been studied on a systematic basis. They are poorly preserved in the sedimentary record, because they tend to be consumed by the subduction process. The creation of the abyssal plain is the end result of spreading of the seafloor (plate tectonics) and melting of the lower oceanic crust. Magma rises from above the asthenosphere (a layer of the upper mantle) and as this basaltic material reaches the surface at mid-ocean ridges it forms new oceanic crust. This is constantly pulled sideways by spreading of the seafloor. Abyssal plains result from the blanketing of an originally uneven surface of oceanic crust by fine-grained sediments, mainly clay and silt. Much of this sediment is deposited by turbidity currents that have been channelled from the continental margins along submarine canyons down into deeper water. The remainder of the sediment is composed chiefly of pelagic sediments. Metallic nodules are common in some areas of the plains, with varying concentrations of metals, including manganese, iron, nickel, cobalt, and copper. These nodules may provide a significant resource for future mining ventures.Owing in part to their vast size, abyssal plains are currently believed to be a major reservoir of biodiversity. The abyss also exerts significant influence upon ocean carbon cycling, dissolution of calcium carbonate, and atmospheric CO2 concentrations over timescales of 100–1000 years. The structure and function of abyssal ecosystems are strongly influenced by the rate of flux of food to the seafloor and the composition of the material that settles. Factors such as climate change, fishing practices, and ocean fertilization are expected to have a substantial effect on patterns of primary production in the euphotic zone. This will undoubtedly impact the flux of organic material to the abyss in a similar manner and thus have a profound effect on the structure, function and diversity of abyssal ecosystems.