Plate tectonic phenomena in the Southern Poland and adjacent areas
... Gondwana, Laurussia and Oldredia). As a results of the closure of the Rheic Ocean the Variscan Orogen was created with Sudetes in its eastern part. The first stage of the Wilson Cycle in the Sudetes is represented by large bodies of Lustatian granitoids identified in the Western Sudetes which are in ...
... Gondwana, Laurussia and Oldredia). As a results of the closure of the Rheic Ocean the Variscan Orogen was created with Sudetes in its eastern part. The first stage of the Wilson Cycle in the Sudetes is represented by large bodies of Lustatian granitoids identified in the Western Sudetes which are in ...
Earth systems plate tectonics homework
... A _ zone is the place where two lithospheric plates converge, one riding over the other. Most volcanoes on land occur parallel to the boundary between the two plates. A. continental C. subduction B. convergent D. volcano Volcanoes are often formed at plate boundaries. This is a convergent plate boun ...
... A _ zone is the place where two lithospheric plates converge, one riding over the other. Most volcanoes on land occur parallel to the boundary between the two plates. A. continental C. subduction B. convergent D. volcano Volcanoes are often formed at plate boundaries. This is a convergent plate boun ...
SEISMIC ACTIVITY (mainly shallow earthquakes)
... introduction of new magnetic material occur in a zone with width from 0 til 10 km. Even in a relatively broad volcanic zone there is an identifiable magnetic anomaly-pattern The magnetic anomalies are among the best evidence for seafloor spreading. It is hard to explain this pattern in other ways, a ...
... introduction of new magnetic material occur in a zone with width from 0 til 10 km. Even in a relatively broad volcanic zone there is an identifiable magnetic anomaly-pattern The magnetic anomalies are among the best evidence for seafloor spreading. It is hard to explain this pattern in other ways, a ...
Crustal Features
... • Continental crust – Continental crust is older than oceanic crust. It has two layers, mostly igneous rock. The upper crust is mostly granite. The lower crust is mostly basalt and diorite. ...
... • Continental crust – Continental crust is older than oceanic crust. It has two layers, mostly igneous rock. The upper crust is mostly granite. The lower crust is mostly basalt and diorite. ...
Physical Geology
... • Where plates move toward each other, oceanic crust and the underlying lithosphere is subducted beneath the other plate (with either oceanic crust or continental crust) • Wet crust is partially melted to form silicic (Silicarich, iron-poor, i.e., granitic) magma ...
... • Where plates move toward each other, oceanic crust and the underlying lithosphere is subducted beneath the other plate (with either oceanic crust or continental crust) • Wet crust is partially melted to form silicic (Silicarich, iron-poor, i.e., granitic) magma ...
hydrothermal vents and chemosynthesis
... been found in the Atlantic, Indian, and most recently, the Arctic Ocean. Most occur at an average depth of about 2,100 meters (7,000 ft) in areas of seafloor spreading along the Mid-Ocean Ridge system — the underwater mountain chain that winds around the globe. How do hydrothermal vents form? In som ...
... been found in the Atlantic, Indian, and most recently, the Arctic Ocean. Most occur at an average depth of about 2,100 meters (7,000 ft) in areas of seafloor spreading along the Mid-Ocean Ridge system — the underwater mountain chain that winds around the globe. How do hydrothermal vents form? In som ...
Plate boudaries II
... Extrusion of basalt along faults floods the valleys with magma. Many volcanoes of the shield variety. Nonmarine sediments continue to accumulate. With continued basalt eruption the density of the crust in this region increases, and subsidence, or sinking, occurs. Flooding by ocean water creates a s ...
... Extrusion of basalt along faults floods the valleys with magma. Many volcanoes of the shield variety. Nonmarine sediments continue to accumulate. With continued basalt eruption the density of the crust in this region increases, and subsidence, or sinking, occurs. Flooding by ocean water creates a s ...
Plate tectonics
... What is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge? • Undersea mountain range, with a steep valley running down its center. • Part of an 80,000km system of mid-ocean ridges • In 1940s scientists found that none of the rock there was older than from 175MYA • Continental rock is from up to 4BYA! ...
... What is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge? • Undersea mountain range, with a steep valley running down its center. • Part of an 80,000km system of mid-ocean ridges • In 1940s scientists found that none of the rock there was older than from 175MYA • Continental rock is from up to 4BYA! ...
Tectonic Plates - Reading packet
... energy from Earth’s interior drives plate motion in a process called convection. As plates move and interact along plate boundaries, forces like slab pull, ridge push, and friction also contribute to the process. Radioactive elements in Earth's core and mantle decay and give off heat. As parts of th ...
... energy from Earth’s interior drives plate motion in a process called convection. As plates move and interact along plate boundaries, forces like slab pull, ridge push, and friction also contribute to the process. Radioactive elements in Earth's core and mantle decay and give off heat. As parts of th ...
1. Mantle convection causes tectonic plate motion and is
... another at a subduction zone? Slab pull occurs at subduction zones, where denser plate sinks beneath the less dense plate. The leading edge of the sinking plate continues to pull the rest of the plate down with it. 2. Plate tectonic forces are responsible for the slow movement of continents over geo ...
... another at a subduction zone? Slab pull occurs at subduction zones, where denser plate sinks beneath the less dense plate. The leading edge of the sinking plate continues to pull the rest of the plate down with it. 2. Plate tectonic forces are responsible for the slow movement of continents over geo ...
Slab pull occurs at subduction zones, where denser plate sinks
... another at a subduction zone? Slab pull occurs at subduction zones, where denser plate sinks beneath the less dense plate. The leading edge of the sinking plate continues to pull the rest of the plate down with it. 2. Plate tectonic forces are responsible for the slow movement of continents over geo ...
... another at a subduction zone? Slab pull occurs at subduction zones, where denser plate sinks beneath the less dense plate. The leading edge of the sinking plate continues to pull the rest of the plate down with it. 2. Plate tectonic forces are responsible for the slow movement of continents over geo ...
Marine Science a Modern Perspective
... > 4,000 new species found Measured temperatures at all depths Studied deep ocean currents Took 19 years to publish all of their findings Led by Scientist __________ __________ ...
... > 4,000 new species found Measured temperatures at all depths Studied deep ocean currents Took 19 years to publish all of their findings Led by Scientist __________ __________ ...
On November 29 - the National Sea Grant Library
... ranges in thickness from only about 3 kilometers (2 mi) in some areas of the ocean floor to some 120 kilometers (75 mi) deep under mountains on the continents. According to the theory of plate tectonics, the Earth’s crust is made up of about a dozen plates on which the continents and the oceans rest ...
... ranges in thickness from only about 3 kilometers (2 mi) in some areas of the ocean floor to some 120 kilometers (75 mi) deep under mountains on the continents. According to the theory of plate tectonics, the Earth’s crust is made up of about a dozen plates on which the continents and the oceans rest ...
Volcanoes Reading - SOEST
... suggests that these sources of magma likely originate at the core-mantle boundary as well as at the boundary between the upper and lower mantle. This is shown in the figure below depicting mantle plumes and large igneous provinces (LIPs). Interestingly, the rocks that make up LIPs and hot spot islan ...
... suggests that these sources of magma likely originate at the core-mantle boundary as well as at the boundary between the upper and lower mantle. This is shown in the figure below depicting mantle plumes and large igneous provinces (LIPs). Interestingly, the rocks that make up LIPs and hot spot islan ...
D o e i
... lack smoke is the hallmark of high-temperature mid-ocean ridge hydrothermal vents. The “smoke” consists of metalrich, microscopic particles that form when super hot vent fluid is quenched by cold, abyssal ocean water. Iron and sulfur minerals such as pyrite or “fool’s gold” form first, followed by s ...
... lack smoke is the hallmark of high-temperature mid-ocean ridge hydrothermal vents. The “smoke” consists of metalrich, microscopic particles that form when super hot vent fluid is quenched by cold, abyssal ocean water. Iron and sulfur minerals such as pyrite or “fool’s gold” form first, followed by s ...
Protecting Ocean Hotspots Lesson 3 Presentation Content
... The ocean looks similar everywhere … ...
... The ocean looks similar everywhere … ...
Plate Tectonics Review
... entire length of the Atlantic Ocean from north to south, and where new land forms. b) analyzing ocean rock and sediments Rocks near the Mid-Atlantic ridge are younger than rocks farther away from the ridge, and sediments at the edges are deeper (suggesting they are older). c) ...
... entire length of the Atlantic Ocean from north to south, and where new land forms. b) analyzing ocean rock and sediments Rocks near the Mid-Atlantic ridge are younger than rocks farther away from the ridge, and sediments at the edges are deeper (suggesting they are older). c) ...
COMPOSITION OF THE EARTH`S MANTLE - IDC
... The Earth’s mantle contains a huge amount of water (estimated to be far more than the ocean) in a supercritical fluid state at high temperatures and pressures. The mantle is a type of refractory or thermal insulation, that might act as a semiconductor due to the abundance of the oxides of silicon, a ...
... The Earth’s mantle contains a huge amount of water (estimated to be far more than the ocean) in a supercritical fluid state at high temperatures and pressures. The mantle is a type of refractory or thermal insulation, that might act as a semiconductor due to the abundance of the oxides of silicon, a ...
CRCT Review - Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics.
... _____ 10. What hypothesis by Alfred Wegener explains why continents seem to fit together? a. continental spreading c. Wegener’s puzzle b. plate tectonics d. continental drift _____ 11. What did Wegener hypothesize happened to the continents? a. They broke up and re-formed. b. They drifted together t ...
... _____ 10. What hypothesis by Alfred Wegener explains why continents seem to fit together? a. continental spreading c. Wegener’s puzzle b. plate tectonics d. continental drift _____ 11. What did Wegener hypothesize happened to the continents? a. They broke up and re-formed. b. They drifted together t ...
Slide 1 - Linn-Benton Community College
... Half/ocean- transition between Pacific & Atlantic models Shaped like collapsing teepee, India at top <1/4 Earth’s water Tectonically similar to Pacific in East- Atlantic in West (both active & passive margins) Has huge chunk of Africa (Madagascar) and another on the way (Horn of Africa) Narrow shelv ...
... Half/ocean- transition between Pacific & Atlantic models Shaped like collapsing teepee, India at top <1/4 Earth’s water Tectonically similar to Pacific in East- Atlantic in West (both active & passive margins) Has huge chunk of Africa (Madagascar) and another on the way (Horn of Africa) Narrow shelv ...
Platemovementrecapquiz 5.08MB 2017-03-29 12
... • Outer core is semi-molten/liquid (only part of the planet which is!) • Inner core is solid The Mantle • Separated from the core by the Gutenburg discontinuity • Largely composed of silicate rocks rich in iron and magnesium • Upper mantle (close to the crust) is rigid and together with the crust fo ...
... • Outer core is semi-molten/liquid (only part of the planet which is!) • Inner core is solid The Mantle • Separated from the core by the Gutenburg discontinuity • Largely composed of silicate rocks rich in iron and magnesium • Upper mantle (close to the crust) is rigid and together with the crust fo ...
1 Mountains and Mountain Ranges
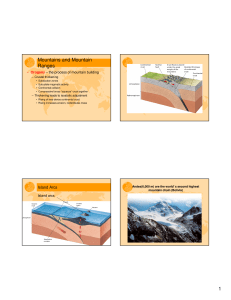
... • Rising magma – Some rises to form volcanoes – Some cools inside forming plutons – Thickening leads to isostatic rise ...
... • Rising magma – Some rises to form volcanoes – Some cools inside forming plutons – Thickening leads to isostatic rise ...
The Earth`s structure
... solid layer; the asthenosphere, which behaves plastically and flows slowly; and a solid upper layer. Partial melting within the asthenosphere generates magma (molten material), some of which rises to the surface because it is less dense than the surrounding material. The upper mantle and the crust m ...
... solid layer; the asthenosphere, which behaves plastically and flows slowly; and a solid upper layer. Partial melting within the asthenosphere generates magma (molten material), some of which rises to the surface because it is less dense than the surrounding material. The upper mantle and the crust m ...
Abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between 3000 and 6000 m. Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth’s surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest and least explored regions on Earth. Abyssal plains are key geologic elements of oceanic basins (the other elements being an elevated mid-ocean ridge and flanking abyssal hills). In addition to these elements, active oceanic basins (those that are associated with a moving plate tectonic boundary) also typically include an oceanic trench and a subduction zone.Abyssal plains were not recognized as distinct physiographic features of the sea floor until the late 1940s and, until very recently, none had been studied on a systematic basis. They are poorly preserved in the sedimentary record, because they tend to be consumed by the subduction process. The creation of the abyssal plain is the end result of spreading of the seafloor (plate tectonics) and melting of the lower oceanic crust. Magma rises from above the asthenosphere (a layer of the upper mantle) and as this basaltic material reaches the surface at mid-ocean ridges it forms new oceanic crust. This is constantly pulled sideways by spreading of the seafloor. Abyssal plains result from the blanketing of an originally uneven surface of oceanic crust by fine-grained sediments, mainly clay and silt. Much of this sediment is deposited by turbidity currents that have been channelled from the continental margins along submarine canyons down into deeper water. The remainder of the sediment is composed chiefly of pelagic sediments. Metallic nodules are common in some areas of the plains, with varying concentrations of metals, including manganese, iron, nickel, cobalt, and copper. These nodules may provide a significant resource for future mining ventures.Owing in part to their vast size, abyssal plains are currently believed to be a major reservoir of biodiversity. The abyss also exerts significant influence upon ocean carbon cycling, dissolution of calcium carbonate, and atmospheric CO2 concentrations over timescales of 100–1000 years. The structure and function of abyssal ecosystems are strongly influenced by the rate of flux of food to the seafloor and the composition of the material that settles. Factors such as climate change, fishing practices, and ocean fertilization are expected to have a substantial effect on patterns of primary production in the euphotic zone. This will undoubtedly impact the flux of organic material to the abyss in a similar manner and thus have a profound effect on the structure, function and diversity of abyssal ecosystems.