AN-346 High-Performance Audio Applications
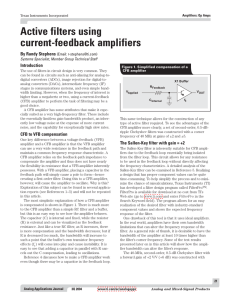
... The circuit of Figure 2(a) has a disadvantage: it cannot accurately follow the curve in Figure 1, no matter what values are chosen for the feedback resistors and capacitors. This is because the non-inverting amplifier cannot have a gain of less than unity, which means that the high frequency gain ca ...
... The circuit of Figure 2(a) has a disadvantage: it cannot accurately follow the curve in Figure 1, no matter what values are chosen for the feedback resistors and capacitors. This is because the non-inverting amplifier cannot have a gain of less than unity, which means that the high frequency gain ca ...
Lecture 18
... A chip has a 2-mm-long data bus of 0.6-mm wires on 1.2mm centers. Use the table values. Assume that the perpendicular wires on adjacent layers are all grounded. Each driver can be modeled as a voltage source in series with a 1-kW resistor. All lines switch simultaneously to random states. What is th ...
... A chip has a 2-mm-long data bus of 0.6-mm wires on 1.2mm centers. Use the table values. Assume that the perpendicular wires on adjacent layers are all grounded. Each driver can be modeled as a voltage source in series with a 1-kW resistor. All lines switch simultaneously to random states. What is th ...
Practical exercises for learning to construct NMR/MRI probe circuits
... where QL and QU are the loaded and unloaded values of Q. To impedance match the circuit to a 50 V resistive load, one needs to adjust the current through the load (or the voltage across the load) so the power dissipated in the external load is equal to the power dissipated in the loss of the tuned c ...
... where QL and QU are the loaded and unloaded values of Q. To impedance match the circuit to a 50 V resistive load, one needs to adjust the current through the load (or the voltage across the load) so the power dissipated in the external load is equal to the power dissipated in the loss of the tuned c ...
Full-Text PDF
... fundamental changes or deregulated markets, economic and environmental requirements have to be considered when analysing the performance of distance relays, selecting protection devices with distance functions and calculating their settings ...
... fundamental changes or deregulated markets, economic and environmental requirements have to be considered when analysing the performance of distance relays, selecting protection devices with distance functions and calculating their settings ...
Active GaAs FET Mixers Using the ATF-10136, ATF-13736, and ATF-13484 Application Note G005
... conversion gains from unity to nearly 5 dB depending on bandwidth requirements. The typical microwave communications system uses mixers for frequency up- or down- ...
... conversion gains from unity to nearly 5 dB depending on bandwidth requirements. The typical microwave communications system uses mixers for frequency up- or down- ...
Solution
... (a) Find the equivalent circuit referred to the low-voltage side of this transformer. (b) Calculate the voltage regulation of this transformer for a full-load current at power factor of 0.8 lagging. (c) Assume that the primary voltage of this transformer is a constant 15 kV, and plot the secondary v ...
... (a) Find the equivalent circuit referred to the low-voltage side of this transformer. (b) Calculate the voltage regulation of this transformer for a full-load current at power factor of 0.8 lagging. (c) Assume that the primary voltage of this transformer is a constant 15 kV, and plot the secondary v ...
CM1235 - Small Footprint ESD Clamp Array for
... copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A listing of SCILLC’s product/patent coverage may be accessed at www.onsemi.com/site/pdf/Patent−Marking.pdf. SCILLC reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. SCILLC makes no warranty, representation o ...
... copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A listing of SCILLC’s product/patent coverage may be accessed at www.onsemi.com/site/pdf/Patent−Marking.pdf. SCILLC reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. SCILLC makes no warranty, representation o ...
MAX2690 Low-Noise, 2.5GHz Downconverter Mixer _______________General Description
... the load using shunt inductors to VCC and series capacitors to the load. Most applications use a resistive termination of 500Ω (typical) resistors in parallel with the pull-up inductors to set a terminating impedance. The part’s conversion gain has been specified with the resistors in place (using t ...
... the load using shunt inductors to VCC and series capacitors to the load. Most applications use a resistive termination of 500Ω (typical) resistors in parallel with the pull-up inductors to set a terminating impedance. The part’s conversion gain has been specified with the resistors in place (using t ...
Differential PECL Series
... For Optimum Jitter Performance, Pletronics recommends: A ground plane under the device with any other signals below the ground plane Minimize other RF signals near device No large transient signals (both current and voltage) should be routed under the device Do not layout near a large magnetic field ...
... For Optimum Jitter Performance, Pletronics recommends: A ground plane under the device with any other signals below the ground plane Minimize other RF signals near device No large transient signals (both current and voltage) should be routed under the device Do not layout near a large magnetic field ...
Operating Instructions
... Use appropriate sealing materials depending upon installation method. The following points must be observed in order to prevent destruction of the printed circuit boards inside of the standpipe at the NIVOMAT FS 21/22.. fill level sensor: • The standpipe may not be bent during installation or opera ...
... Use appropriate sealing materials depending upon installation method. The following points must be observed in order to prevent destruction of the printed circuit boards inside of the standpipe at the NIVOMAT FS 21/22.. fill level sensor: • The standpipe may not be bent during installation or opera ...
SATA_backplane_design
... Smaller vias will impart less distortion to the SATA signal. For this reason blind or buried vias are preferred. However due to the cost increase for these vias, an RF type via may be used as a minimum. An RF via is the minimum diameter drill available from the selected board house and will increase ...
... Smaller vias will impart less distortion to the SATA signal. For this reason blind or buried vias are preferred. However due to the cost increase for these vias, an RF type via may be used as a minimum. An RF via is the minimum diameter drill available from the selected board house and will increase ...
AND8020/D Termination of ECL Devices with EF (Emitter Follower) OUTPUT Structure
... Near Standard Pair DC Current Return − Standard Pair Termination The near standard pair termination scheme uses a pull−down resistor, RE, located at each driver pin to return the output transistor bias current near the driver, and an impedance matching parallel resistor, RT, located at the receiver ...
... Near Standard Pair DC Current Return − Standard Pair Termination The near standard pair termination scheme uses a pull−down resistor, RE, located at each driver pin to return the output transistor bias current near the driver, and an impedance matching parallel resistor, RT, located at the receiver ...
Negative-Sequence Impedance Directional Element
... There are five settings required for the negative-sequence impedance directional element in the SEL-321 Relay. These settings consist of a forward and reverse negative-sequence impedance threshold (Z2F and Z2R), a forward and reverse negative-sequence current threshold (50QF and 50QR), and a positiv ...
... There are five settings required for the negative-sequence impedance directional element in the SEL-321 Relay. These settings consist of a forward and reverse negative-sequence impedance threshold (Z2F and Z2R), a forward and reverse negative-sequence current threshold (50QF and 50QR), and a positiv ...
Nominal impedance
Nominal impedance in electrical engineering and audio engineering refers to the approximate designed impedance of an electrical circuit or device. The term is applied in a number of different fields, most often being encountered in respect of:The nominal value of the characteristic impedance of a cable or other form of transmission line.The nominal value of the input, output or image impedance of a port of a network, especially a network intended for use with a transmission line, such as filters, equalisers and amplifiers.The nominal value of the input impedance of a radio frequency antennaThe actual impedance may vary quite considerably from the nominal figure with changes in frequency. In the case of cables and other transmission lines, there is also variation along the length of the cable, if it is not properly terminated. It is usual practice to speak of nominal impedance as if it were a constant resistance, that is, it is invariant with frequency and has a zero reactive component, despite this often being far from the case. Depending on the field of application, nominal impedance is implicitly referring to a specific point on the frequency response of the circuit under consideration. This may be at low-frequency, mid-band or some other point and specific applications are discussed in the sections below.In most applications, there are a number of values of nominal impedance that are recognised as being standard. The nominal impedance of a component or circuit is often assigned one of these standard values, regardless of whether the measured impedance exactly corresponds to it. The item is assigned the nearest standard value.