Central nervous system
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. path of action potential 1. After an action potential arrives at an axon terminal, ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. path of action potential 1. After an action potential arrives at an axon terminal, ...
test1 - Scioly.org
... _____18. The inner ear structure that resembles a shell and houses multiple receptors is known as the ____. a. hammer b. cochlea c. vestibule d. semicircular canals _____19. The structure that contains the hearing receptors is known as the ____. a. cochlea b. organ of Corti c. vestibule d. stirrup ...
... _____18. The inner ear structure that resembles a shell and houses multiple receptors is known as the ____. a. hammer b. cochlea c. vestibule d. semicircular canals _____19. The structure that contains the hearing receptors is known as the ____. a. cochlea b. organ of Corti c. vestibule d. stirrup ...
Chapter 23 take home test File
... b) Dendrites receive electrical impulses from other neurons. Axons send electrical impulses to other neurons. c) Dendrites tend to be thinner then axons. d) A neuron might have more than one dendrite. There is never more than one axon per neuron. e) Bundles of dendrites from several cells are called ...
... b) Dendrites receive electrical impulses from other neurons. Axons send electrical impulses to other neurons. c) Dendrites tend to be thinner then axons. d) A neuron might have more than one dendrite. There is never more than one axon per neuron. e) Bundles of dendrites from several cells are called ...
Chapter 13 The nervous system Expanding on neurons
... • Meninges – 3 protective membranes that wrap around CNS • Cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) – space between meninges is filled with this fluid that cushions and protects the CNS ...
... • Meninges – 3 protective membranes that wrap around CNS • Cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) – space between meninges is filled with this fluid that cushions and protects the CNS ...
Membranes
... After proteins have been synthesized by ribosomes they are transported to the rough endoplasmic reticulum where they can be modified. Vesicles carrying the protein then bud off the rough endoplasmic reticulum and are transported to the Golgi apparatus to be further modified. After this the vesicles ...
... After proteins have been synthesized by ribosomes they are transported to the rough endoplasmic reticulum where they can be modified. Vesicles carrying the protein then bud off the rough endoplasmic reticulum and are transported to the Golgi apparatus to be further modified. After this the vesicles ...
nervous system notes
... Drugs - many affect transmission of impulses across synapse by increasing/decreasing the production of the neurotransmitter or by affecting the rate of breakdown of the neurotransmitter. Ectasy affects nerve cells that produce serotonin. It causes the nerve cells to release all the stored serotoni ...
... Drugs - many affect transmission of impulses across synapse by increasing/decreasing the production of the neurotransmitter or by affecting the rate of breakdown of the neurotransmitter. Ectasy affects nerve cells that produce serotonin. It causes the nerve cells to release all the stored serotoni ...
Lecture 3
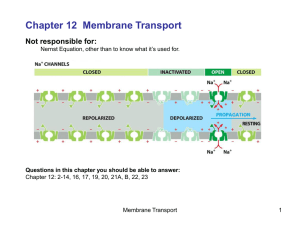
... membrane potential becomes more positive more sodium channels open Even more sodium ions enter the cells membrane potential even more positive and so on == Positive feedback loop == explosion == gun powder ...
... membrane potential becomes more positive more sodium channels open Even more sodium ions enter the cells membrane potential even more positive and so on == Positive feedback loop == explosion == gun powder ...
Postsynaptic Potential
... • In glia, glutamate is converted to glutamine by glutamine synthetase • Released from the glia, • taken up by the nerve terminal, • converted back to glutamate by the ...
... • In glia, glutamate is converted to glutamine by glutamine synthetase • Released from the glia, • taken up by the nerve terminal, • converted back to glutamate by the ...
CH 8 Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Chuck was not seriously injured, but when he was revived, he could not remember how many balls and strikes the batter had. This was because A. sensory memory had not been converted to short-term memory. B. short-term memory had not been converted to sensory memory. C. he lost both sensory and short- ...
... Chuck was not seriously injured, but when he was revived, he could not remember how many balls and strikes the batter had. This was because A. sensory memory had not been converted to short-term memory. B. short-term memory had not been converted to sensory memory. C. he lost both sensory and short- ...
Regulation of ion channels
... • Local depolarization of membrane spreads to adjacent region (purple) opening voltage-gated Na+ channels • This causes further depolarization of membrane and opening of additional voltage-gated Na+ channels • Na+ channels in the region of the membrane (green) where the action potential originated r ...
... • Local depolarization of membrane spreads to adjacent region (purple) opening voltage-gated Na+ channels • This causes further depolarization of membrane and opening of additional voltage-gated Na+ channels • Na+ channels in the region of the membrane (green) where the action potential originated r ...
Zika virus persists in the central nervous system
... lymph nodes and colorectal tissue of infected rhesus monkeys for weeks after the virus has been More information: Malika Aid et al, Zika Virus cleared from blood, urine and mucosal secretions, Persistence in the Central Nervous System and according to a study published online in Cell. The Lymph Node ...
... lymph nodes and colorectal tissue of infected rhesus monkeys for weeks after the virus has been More information: Malika Aid et al, Zika Virus cleared from blood, urine and mucosal secretions, Persistence in the Central Nervous System and according to a study published online in Cell. The Lymph Node ...
Nervous System - Serrano High School AP Biology
... If there is sufficient stimulus (above the threshold), then the neuron changes. 1) At any dendrite that receives a stimulus, the sodium pump stops briefly, less than a millisecond. 2) The Na+ rushes into the negatively charged interior, and the threshold is met (-55 mV). 3) All the Na+ channels of a ...
... If there is sufficient stimulus (above the threshold), then the neuron changes. 1) At any dendrite that receives a stimulus, the sodium pump stops briefly, less than a millisecond. 2) The Na+ rushes into the negatively charged interior, and the threshold is met (-55 mV). 3) All the Na+ channels of a ...
The Lymphatic System - leavingcertbiology.net
... along the lymphatic pathways where they filter the lymph before it is returned to the blood • Lymph nodes are not present in the central nervous system • There are three superficial regions on each side of the body where lymph nodes tend to cluster: – Groin – Armpit – Neck ...
... along the lymphatic pathways where they filter the lymph before it is returned to the blood • Lymph nodes are not present in the central nervous system • There are three superficial regions on each side of the body where lymph nodes tend to cluster: – Groin – Armpit – Neck ...
chapter 50, part 1 the nervous system a basic neuron
... 2. Myelin is composed of 80% lipid and 20% protein. 3. Myelin is made of special cells called Schwann Cells that forms an insulated sheath, or wrapping around the axon. 4. There are SMALL NODES or GAPS called the Nodes of Ranvier between adjacent myelin sheath cells along the axon. (Figure 50-8) ...
... 2. Myelin is composed of 80% lipid and 20% protein. 3. Myelin is made of special cells called Schwann Cells that forms an insulated sheath, or wrapping around the axon. 4. There are SMALL NODES or GAPS called the Nodes of Ranvier between adjacent myelin sheath cells along the axon. (Figure 50-8) ...
Nerve Impulse Transmission
... the next one. • This gap is called the synapse or synaptic cleft. • The nerve impulse needs to cross this gap and it does so by the release of special chemicals called neurotransmitters. ...
... the next one. • This gap is called the synapse or synaptic cleft. • The nerve impulse needs to cross this gap and it does so by the release of special chemicals called neurotransmitters. ...
MicroRNA ablation affects Bergmann glial morphology and disrupts
... Keywords: hGFAP, miR-9, Dicer, Cre-flox, Bergmann glia. Abstract: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles during development of the central nervous system (CNS). Several reports indicate that tissue development and cellular differentiation in the developing forebrains are disrupted in the absence of ...
... Keywords: hGFAP, miR-9, Dicer, Cre-flox, Bergmann glia. Abstract: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles during development of the central nervous system (CNS). Several reports indicate that tissue development and cellular differentiation in the developing forebrains are disrupted in the absence of ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... spines are found on dendrites and these spines contain a spine apparatus which seems to function like a capacitor, charging and then discharging when its current load is exceeded. Immediately behind the postsynaptic membrane is an elaborate complex of interlinked proteins called the postsynaptic den ...
... spines are found on dendrites and these spines contain a spine apparatus which seems to function like a capacitor, charging and then discharging when its current load is exceeded. Immediately behind the postsynaptic membrane is an elaborate complex of interlinked proteins called the postsynaptic den ...
peripheral nervous system
... The axon: It is a slender process. It may transfer the nerve impulses from the beginning part (axon hillock) to the end (axon terminal). Because the axoplasm does not contain RNA and ribosome, proteins synthesis cannot take place in the axon. All axonal proteins, therefore, must come from the cell b ...
... The axon: It is a slender process. It may transfer the nerve impulses from the beginning part (axon hillock) to the end (axon terminal). Because the axoplasm does not contain RNA and ribosome, proteins synthesis cannot take place in the axon. All axonal proteins, therefore, must come from the cell b ...
primary motor Cortex
... approximately 300 times greater than normal. This efflux of (+) charges causes the membrane to repolarize back toward the resting membrane potential. Sodium channels open more rapidly than K+ channels because they are more voltage sensitive and a small depolarization is sufficient to open them. Larg ...
... approximately 300 times greater than normal. This efflux of (+) charges causes the membrane to repolarize back toward the resting membrane potential. Sodium channels open more rapidly than K+ channels because they are more voltage sensitive and a small depolarization is sufficient to open them. Larg ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... Neurons communicate with each other through an electrochemical process. Neurons contain some very specialized structures (for example, synapses) and chemicals (for example, neurotransmitters) that enable one cell to communicate with another. ...
... Neurons communicate with each other through an electrochemical process. Neurons contain some very specialized structures (for example, synapses) and chemicals (for example, neurotransmitters) that enable one cell to communicate with another. ...
FIGURE LEGNEDS FIGURE 24.1 A dorsal root ganglion cell is a
... FIGURE 24.1 A dorsal root ganglion cell is a pseudo-unipolar neuron with an axon that divides at a T-junction into a peripheral branch and a central branch. At the tip of the peripheral branch are receptor proteins that, through opening of cation channels, produce a depolarization called a generator ...
... FIGURE 24.1 A dorsal root ganglion cell is a pseudo-unipolar neuron with an axon that divides at a T-junction into a peripheral branch and a central branch. At the tip of the peripheral branch are receptor proteins that, through opening of cation channels, produce a depolarization called a generator ...
Node of Ranvier

The nodes of Ranvier also known as myelin sheath gaps, are the gaps (approximately 1 micrometer in length) formed between the myelin sheaths generated by different cells. A myelin sheath is a many-layered coating, largely composed of a fatty substance called myelin, that wraps around the axon of a neuron and very efficiently insulates it. At nodes of Ranvier, the axonal membrane is uninsulated and, therefore, capable of generating electrical activity.