Name________________________ Midterm #1 Biology 3330, Fall
... b) What 3 criteria must be satisfied to prove that a chemical is a neurotransmitter? ...
... b) What 3 criteria must be satisfied to prove that a chemical is a neurotransmitter? ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... Neurons communicate with each other through an electrochemical process. Neurons contain some very specialized structures (i.e., synapses) and chemicals (i.e, neurotransmitters) that enable one cell to communicate with another. ...
... Neurons communicate with each other through an electrochemical process. Neurons contain some very specialized structures (i.e., synapses) and chemicals (i.e, neurotransmitters) that enable one cell to communicate with another. ...
Structural and functional study of potassium channel inhibitor HsTX1
... least 10 000 membrane proteins encoded in the human genome. Ion channels are integral membrane proteins that allow movement of ions across membranes down their electro- chemical gradients. These channel proteins form water-filled, gated pores that are often highly selective for specific ions (such a ...
... least 10 000 membrane proteins encoded in the human genome. Ion channels are integral membrane proteins that allow movement of ions across membranes down their electro- chemical gradients. These channel proteins form water-filled, gated pores that are often highly selective for specific ions (such a ...
ANATOMY OF A NEURON
... The All-or-None Law: A single neuron is either fires or does not fire. If fires, it always fires at full speed and intensity. ...
... The All-or-None Law: A single neuron is either fires or does not fire. If fires, it always fires at full speed and intensity. ...
File: Chap011, Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
... Schwann cells differ from oligodendrocytes in which of the following ways? A) Schwann cells form myelin; oligodendrocytes do not. B) Oligodendrocytes are only found in the PNS; Schwann cells are only found in the CNS. C) Schwann cells form sheaths around several axons, while oligodendrocytes form sh ...
... Schwann cells differ from oligodendrocytes in which of the following ways? A) Schwann cells form myelin; oligodendrocytes do not. B) Oligodendrocytes are only found in the PNS; Schwann cells are only found in the CNS. C) Schwann cells form sheaths around several axons, while oligodendrocytes form sh ...
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
... Schwann cells differ from oligodendrocytes in which of the following ways? A) Schwann cells form myelin; oligodendrocytes do not. B) Oligodendrocytes are only found in the PNS; Schwann cells are only found in the CNS. C) Schwann cells form sheaths around several axons, while oligodendrocytes form sh ...
... Schwann cells differ from oligodendrocytes in which of the following ways? A) Schwann cells form myelin; oligodendrocytes do not. B) Oligodendrocytes are only found in the PNS; Schwann cells are only found in the CNS. C) Schwann cells form sheaths around several axons, while oligodendrocytes form sh ...
The Central Nervous System
... SPPA 2050 Speech Anatomy and Physiology (Figure 2.7) will change their permeability depending upon the membrane potential. If there is a change in the membrane potential, these channels may open (or close). For example, a NT may attach to a receptor site and open a Na+ channel. Given the electroche ...
... SPPA 2050 Speech Anatomy and Physiology (Figure 2.7) will change their permeability depending upon the membrane potential. If there is a change in the membrane potential, these channels may open (or close). For example, a NT may attach to a receptor site and open a Na+ channel. Given the electroche ...
Unit 1 – Nervous and Endocrine System
... - Describe the general structure and function of a neuron and myelin sheath, explaining the formation and transmission of an action potential, including all-or-none response and intensity of response; - Describe, using an example, the organization of neurons into nerves and the composition and funct ...
... - Describe the general structure and function of a neuron and myelin sheath, explaining the formation and transmission of an action potential, including all-or-none response and intensity of response; - Describe, using an example, the organization of neurons into nerves and the composition and funct ...
Biology and Behavior note frame
... a. The state of a neuron when it is at _______________ and capable of _______________ an action potential b. The neuron is set and _______________ _______________ _______________ 4. All-or-None Principle a. The principle stating that ___________________________________________ ______________________ ...
... a. The state of a neuron when it is at _______________ and capable of _______________ an action potential b. The neuron is set and _______________ _______________ _______________ 4. All-or-None Principle a. The principle stating that ___________________________________________ ______________________ ...
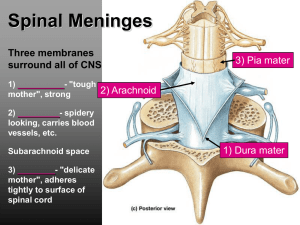
Ch 14: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... Posterior gray horn contains somatic and visceral sensory nuclei Anterior gray horns deal with somatic motor control Lateral gray horns contain visceral motor neurons Gray commissures contain axons that cross from one side to the other ...
... Posterior gray horn contains somatic and visceral sensory nuclei Anterior gray horns deal with somatic motor control Lateral gray horns contain visceral motor neurons Gray commissures contain axons that cross from one side to the other ...
Robert Jones
... Autoradiography with 125I-alpha-bungarotoxin (Bgt) and 3H-methyllycaconitine were used to map the general distribution of alpha7 nAChR within the rat PFC. AlexaFluor 488-conjugated Bgt in conjunction with other neuronal markers provided further analysis of regions of interest at higher magnificatio ...
... Autoradiography with 125I-alpha-bungarotoxin (Bgt) and 3H-methyllycaconitine were used to map the general distribution of alpha7 nAChR within the rat PFC. AlexaFluor 488-conjugated Bgt in conjunction with other neuronal markers provided further analysis of regions of interest at higher magnificatio ...
nervous system
... 3. The enteric division consists of networks of neurons in the digestive tract, pancreas, and gallbladder that control secretion and peristalsis. ...
... 3. The enteric division consists of networks of neurons in the digestive tract, pancreas, and gallbladder that control secretion and peristalsis. ...
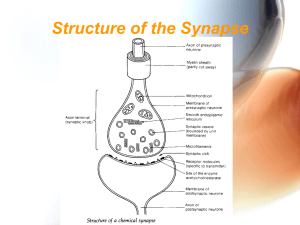
Structure of the Synapse
... parasympathetic nervous system (relaxing responses) - cholinergic synapses • Noradrenaline - involved in the sympathetic nervous system ('fight or flight' responses) - adrenergic synapses ...
... parasympathetic nervous system (relaxing responses) - cholinergic synapses • Noradrenaline - involved in the sympathetic nervous system ('fight or flight' responses) - adrenergic synapses ...
The Neuron Doctrine, Redux
... was Cajal who envisioned the neuron as ways than original envisaged: Intercellular communication by gap junctions, slow electrical potentials, action an individual functional unit, polarized potentials initiated in dendrites, neuromodulatory effects, extrasynaptic release of neurotransmitters, and s ...
... was Cajal who envisioned the neuron as ways than original envisaged: Intercellular communication by gap junctions, slow electrical potentials, action an individual functional unit, polarized potentials initiated in dendrites, neuromodulatory effects, extrasynaptic release of neurotransmitters, and s ...
histology of the central nervous system
... Occasionally the neuron like in the amacrine cells of the retina does not contain axon, but this is quite uncommon. Axon is usually thinner and much longer than the dendrites of the same cell. The part of the axon between the hillock and the beginning of the myelin sheath is called the initial segme ...
... Occasionally the neuron like in the amacrine cells of the retina does not contain axon, but this is quite uncommon. Axon is usually thinner and much longer than the dendrites of the same cell. The part of the axon between the hillock and the beginning of the myelin sheath is called the initial segme ...
D. What Causes Multiple Sclerosis?
... MS is thought to be an auto-immune disease that affects the central nervous system (CNS). The CNS consists of the brain, spinal cord, and the optic nerves. Surrounding and protecting the nerve fibers of the CNS is a fatty tissue called myelin, which helps nerve fibers conduct electrical impulses. Mu ...
... MS is thought to be an auto-immune disease that affects the central nervous system (CNS). The CNS consists of the brain, spinal cord, and the optic nerves. Surrounding and protecting the nerve fibers of the CNS is a fatty tissue called myelin, which helps nerve fibers conduct electrical impulses. Mu ...
Nervous system
... Characters of AP conduction on a nerve fiber The anatomic and physiological integrity Not easy to fatigue Conduct in a non-decremental fashion ...
... Characters of AP conduction on a nerve fiber The anatomic and physiological integrity Not easy to fatigue Conduct in a non-decremental fashion ...
13_QuizShowQuestions
... Which of the following statements regarding “reverberation” in neural circuits is false? a. Complex examples of reverberation may be involved in the maintenance of consciousness, muscular coordination, and normal breathing patterns. b. Reverberation circuits use negative feedback to function, in whi ...
... Which of the following statements regarding “reverberation” in neural circuits is false? a. Complex examples of reverberation may be involved in the maintenance of consciousness, muscular coordination, and normal breathing patterns. b. Reverberation circuits use negative feedback to function, in whi ...
Ennio Pannese Fine Structure of Neurons, Nerve Processes, and
... the continuity of research. Having arrived at the end of my research career, I have made every effort to complete this new edition in the hope that it encourages young researchers to further advance our knowledge on the cytology of the nervous system. It is a pleasure to express my sincere thanks to ...
... the continuity of research. Having arrived at the end of my research career, I have made every effort to complete this new edition in the hope that it encourages young researchers to further advance our knowledge on the cytology of the nervous system. It is a pleasure to express my sincere thanks to ...
Self Assessment Chapter 11 - CM
... • Sensory functions – gather information about internal and external environments of body; input is gathered by sensory or afferent division of PNS; further divided into somatic and visceral divisions; Sensory input from both divisions is carried from sensory receptors to spinal cord and/or brain by ...
... • Sensory functions – gather information about internal and external environments of body; input is gathered by sensory or afferent division of PNS; further divided into somatic and visceral divisions; Sensory input from both divisions is carried from sensory receptors to spinal cord and/or brain by ...
The Nervous System
... Nervous Tissue: Neurons • Myelin sheath—whitish, fatty material covering axons • Schwann cells—produce myelin sheaths in jelly roll-like fashion around axons (PNS) • Nodes of Ranvier—gaps in myelin sheath along the axon • Oligodendrocytes—produce myelin sheaths around axons of the CNS ...
... Nervous Tissue: Neurons • Myelin sheath—whitish, fatty material covering axons • Schwann cells—produce myelin sheaths in jelly roll-like fashion around axons (PNS) • Nodes of Ranvier—gaps in myelin sheath along the axon • Oligodendrocytes—produce myelin sheaths around axons of the CNS ...
General classification of peripheral nervous system
... The autonomic nervous system consists of sensory neurons and motor neurons that run between the central nervous system (especially the hypothalamus and medulla oblongata) and various internal organs such as the(heart, lungs, viscera and glands). The contraction of both smooth muscle and cardiac musc ...
... The autonomic nervous system consists of sensory neurons and motor neurons that run between the central nervous system (especially the hypothalamus and medulla oblongata) and various internal organs such as the(heart, lungs, viscera and glands). The contraction of both smooth muscle and cardiac musc ...
An Introduction to the Nervous System
... An Introduction to the Nervous System • Organs of the Nervous System – Brain and spinal cord – Sensory receptors of sense organs (eyes, ears, etc.) – Nerves connect nervous system with other ...
... An Introduction to the Nervous System • Organs of the Nervous System – Brain and spinal cord – Sensory receptors of sense organs (eyes, ears, etc.) – Nerves connect nervous system with other ...
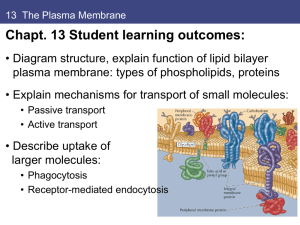
ppt
... • Carrier proteins bind molecules on one side; undergo conformational change to allow molecule to pass through membrane to other side. • Channel proteins form open pores through membrane; allow free diffusion of molecule of appropriate size and charge. ...
... • Carrier proteins bind molecules on one side; undergo conformational change to allow molecule to pass through membrane to other side. • Channel proteins form open pores through membrane; allow free diffusion of molecule of appropriate size and charge. ...
Node of Ranvier

The nodes of Ranvier also known as myelin sheath gaps, are the gaps (approximately 1 micrometer in length) formed between the myelin sheaths generated by different cells. A myelin sheath is a many-layered coating, largely composed of a fatty substance called myelin, that wraps around the axon of a neuron and very efficiently insulates it. At nodes of Ranvier, the axonal membrane is uninsulated and, therefore, capable of generating electrical activity.