Review questions: Week 1 Nonet * cell biology Nonet * axon
... • Astrocytes – Regulate extracellular K+ – Remove excess glutamate – Regulate extracellular Na+ – Supply neurons with glutamate – Supply neurons with glutamine – Control local blood flow – Transport glucose to neurons – Transport oxygen to neurons Choose 1 or more ...
... • Astrocytes – Regulate extracellular K+ – Remove excess glutamate – Regulate extracellular Na+ – Supply neurons with glutamate – Supply neurons with glutamine – Control local blood flow – Transport glucose to neurons – Transport oxygen to neurons Choose 1 or more ...
Action Potential Webquest
... If you have time at the end of the above sections, please watch the Crashcourse video on the Nervous System: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x4PPZCLnVkA. This video will help to tie everything up that you viewed in the previous sections. We will continue this discussion as we look more at action pot ...
... If you have time at the end of the above sections, please watch the Crashcourse video on the Nervous System: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x4PPZCLnVkA. This video will help to tie everything up that you viewed in the previous sections. We will continue this discussion as we look more at action pot ...
AP Biology - Pleasantville High School
... As soon as the action potential has move on, the axon undergoes a refractory period. At this time the sodium gates are unable to open. This ensures that the action potential cannot move backwards and always moves down an axon to the axon branches B. Transmission of a Nerve Impulse Between two Differ ...
... As soon as the action potential has move on, the axon undergoes a refractory period. At this time the sodium gates are unable to open. This ensures that the action potential cannot move backwards and always moves down an axon to the axon branches B. Transmission of a Nerve Impulse Between two Differ ...
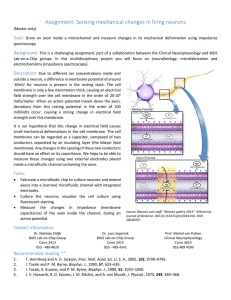
Assignment: Sensing mechanical changes in firing neurons
... membrane is only a few nanometers thick, causing an electrical field strength over the cell membrane in the order of 20∙106 Volts/meter. When an action potential travels down the axon, deviations from this resting potential in the order of 100 milliVolts occur, causing a strong change in electrical ...
... membrane is only a few nanometers thick, causing an electrical field strength over the cell membrane in the order of 20∙106 Volts/meter. When an action potential travels down the axon, deviations from this resting potential in the order of 100 milliVolts occur, causing a strong change in electrical ...
Neurons
... Voltage causes electrically charged particles, ions, to move across cell membranes. Major ions in neurons: • Sodium (Na+) • Potassium (K+) • Calcium (Ca2+) • Chloride (Cl–) Membrane potentials are measured with electrodes. • The resting potential of an axon is –60 to –70 millivolts (mV). • The insid ...
... Voltage causes electrically charged particles, ions, to move across cell membranes. Major ions in neurons: • Sodium (Na+) • Potassium (K+) • Calcium (Ca2+) • Chloride (Cl–) Membrane potentials are measured with electrodes. • The resting potential of an axon is –60 to –70 millivolts (mV). • The insid ...
Sensory function
... • The gray matter of the nervous system contains neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, unmyelinated axons, axon terminals, and neuroglia. • It appears grayish, rather than white, because the cellular organelles impart a gray color and there is little or no myelin in these areas. ...
... • The gray matter of the nervous system contains neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, unmyelinated axons, axon terminals, and neuroglia. • It appears grayish, rather than white, because the cellular organelles impart a gray color and there is little or no myelin in these areas. ...
Chapter 14
... peripheral nervous system neuron cell bodies from their surrounding interstitial fluid and regulate the continuous exchange of nutrients and waste products between peripheral neurons and their environment. Neurolemmocytes myelinate the axons in the PNS. 4. Oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheath in ...
... peripheral nervous system neuron cell bodies from their surrounding interstitial fluid and regulate the continuous exchange of nutrients and waste products between peripheral neurons and their environment. Neurolemmocytes myelinate the axons in the PNS. 4. Oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheath in ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous System – Homework – Part I
... 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contrast dendrites and axons. 4. Discuss how the following relate to each other: presynaptic cell, postsynaptic cell, synapse, neurotransmitter. 5. Describe the “resting potential” of a typical nontransmitting ne ...
... 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contrast dendrites and axons. 4. Discuss how the following relate to each other: presynaptic cell, postsynaptic cell, synapse, neurotransmitter. 5. Describe the “resting potential” of a typical nontransmitting ne ...
Neurons - Scott Melcher
... hormonal) and psychological processes. The biological psychologists may also be called, behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists, behavior geneticists, physiological psychologists, or biopsychologists. When looking at the biology of the brain and nervous system, the most basic building block i ...
... hormonal) and psychological processes. The biological psychologists may also be called, behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists, behavior geneticists, physiological psychologists, or biopsychologists. When looking at the biology of the brain and nervous system, the most basic building block i ...
NUTS AND BOLTS to get started
... • Thousands of connections where one neuron may interact (communicate) with other neurons. ...
... • Thousands of connections where one neuron may interact (communicate) with other neurons. ...
Neurons, Synapses, the Nervous System
... membrane potential to a positive value. In order to generate an action potential, a certain level of depolarization must be achieved, known as the threshold. The membrane potential is restored to its normal resting value by the inactivation of the Na+ channels and by opening voltage-gated K+ channel ...
... membrane potential to a positive value. In order to generate an action potential, a certain level of depolarization must be achieved, known as the threshold. The membrane potential is restored to its normal resting value by the inactivation of the Na+ channels and by opening voltage-gated K+ channel ...
Chapter 48: Nervous System
... o Gated ion channels: ion channels that allow neurons to change membrane potential in response to stimuli o Hyperpolarization: increase in the electrical gradient (i.e., membrane potential becomes more negative) K+ channels release potassium from inside the cell, making it more negative o Depolari ...
... o Gated ion channels: ion channels that allow neurons to change membrane potential in response to stimuli o Hyperpolarization: increase in the electrical gradient (i.e., membrane potential becomes more negative) K+ channels release potassium from inside the cell, making it more negative o Depolari ...
The Nervous System : communication
... In the normal communication process, dopamine is released by a neuron into the synapse, where it can bind to dopamine receptors on neighboring neurons. Normally, dopamine is then recycled back into the transmitting neuron by a specialized protein called the dopamine transporter. If cocaine is prese ...
... In the normal communication process, dopamine is released by a neuron into the synapse, where it can bind to dopamine receptors on neighboring neurons. Normally, dopamine is then recycled back into the transmitting neuron by a specialized protein called the dopamine transporter. If cocaine is prese ...
Ch 09 Nervous System
... In the normal communication process, dopamine is released by a neuron into the synapse, where it can bind to dopamine receptors on neighboring neurons. Normally, dopamine is then recycled back into the transmitting neuron by a specialized protein called the dopamine transporter. If cocaine is prese ...
... In the normal communication process, dopamine is released by a neuron into the synapse, where it can bind to dopamine receptors on neighboring neurons. Normally, dopamine is then recycled back into the transmitting neuron by a specialized protein called the dopamine transporter. If cocaine is prese ...
chapt12 neuron_lecture
... • Slow axonal transport or axoplasmic flow – moves cytoskeletal & new axoplasm at 10 mm/day during repair & regeneration in damaged axons ...
... • Slow axonal transport or axoplasmic flow – moves cytoskeletal & new axoplasm at 10 mm/day during repair & regeneration in damaged axons ...
I. Functions and Divisions of the Nervous System A. The nervous
... 2. The neuron cell body, also called the perikaryon or soma, is the major biosynthetic center containing the usual organelles except for centrioles. 3. Neurons have armlike processes that extend from the cell body. a. Dendrites are cell processes that are the receptive regions of the cell and provid ...
... 2. The neuron cell body, also called the perikaryon or soma, is the major biosynthetic center containing the usual organelles except for centrioles. 3. Neurons have armlike processes that extend from the cell body. a. Dendrites are cell processes that are the receptive regions of the cell and provid ...
Nervous System Introduction
... • - one Schwann cell associates with and myelinates a segment of only one axon • - Schwann cell, myelin, axon are all surrounded by a basement membrane (covers whole unit) • - help to buffer excess extracellular K+ (prevent rampant depolarization) • - myelin sheath insulation greatly speeds conducti ...
... • - one Schwann cell associates with and myelinates a segment of only one axon • - Schwann cell, myelin, axon are all surrounded by a basement membrane (covers whole unit) • - help to buffer excess extracellular K+ (prevent rampant depolarization) • - myelin sheath insulation greatly speeds conducti ...
Inside the brain
... multiple layers of fatty cell membrane that wrap around the axon. The sheath is interrupted at regular intervals (‘nodes of Ranvier’), where the channels that generate the electrical signal are located. Nodes of Ranvier: Areas of the axon without myelin. The action potential (electrical signal) jump ...
... multiple layers of fatty cell membrane that wrap around the axon. The sheath is interrupted at regular intervals (‘nodes of Ranvier’), where the channels that generate the electrical signal are located. Nodes of Ranvier: Areas of the axon without myelin. The action potential (electrical signal) jump ...
The Nervous System
... -large anions can only cross the membrane through ion channels or using carrier proteins -K+ ions are pumped into the cell and Na+ ions are pumped out -K+ ions can diffuse out of the cell more easily than Na+ because they are smaller -Gives cells a resting potential (charge) of -70 mV Transmission o ...
... -large anions can only cross the membrane through ion channels or using carrier proteins -K+ ions are pumped into the cell and Na+ ions are pumped out -K+ ions can diffuse out of the cell more easily than Na+ because they are smaller -Gives cells a resting potential (charge) of -70 mV Transmission o ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 7
... 9. The white fatty substance around the neurons that speeds up impulse transmission is called _________________________. 10. A self-propagating wave of electrical negativity that travels along the surface of the neuron membrane is called a/an _______________________. 11. Indentations between the Sch ...
... 9. The white fatty substance around the neurons that speeds up impulse transmission is called _________________________. 10. A self-propagating wave of electrical negativity that travels along the surface of the neuron membrane is called a/an _______________________. 11. Indentations between the Sch ...
S1 Table.
... Expressed in astrocytes type 1, astrocytes type 2 and oligodendrocytes, mature non-myelinating Schwann cells Rapidly transported membrane-bound protein Closely correlates with axonal regeneration and expression of class II tubulin Participates in structural remodeling and membrane formation, regulat ...
... Expressed in astrocytes type 1, astrocytes type 2 and oligodendrocytes, mature non-myelinating Schwann cells Rapidly transported membrane-bound protein Closely correlates with axonal regeneration and expression of class II tubulin Participates in structural remodeling and membrane formation, regulat ...
Node of Ranvier

The nodes of Ranvier also known as myelin sheath gaps, are the gaps (approximately 1 micrometer in length) formed between the myelin sheaths generated by different cells. A myelin sheath is a many-layered coating, largely composed of a fatty substance called myelin, that wraps around the axon of a neuron and very efficiently insulates it. At nodes of Ranvier, the axonal membrane is uninsulated and, therefore, capable of generating electrical activity.