Nervous System Neuron: nerve cell, functional unit of nervous
... Purpose of the refractory period is to make the stimulus reach the end because of the potassium. Parts of axon not covered by myelin the action potential jumps Nodes of Ranvier which have voltage gated channels. This is known as the refractory period. Cell begins to Reset Once refectory, +40 mV is r ...
... Purpose of the refractory period is to make the stimulus reach the end because of the potassium. Parts of axon not covered by myelin the action potential jumps Nodes of Ranvier which have voltage gated channels. This is known as the refractory period. Cell begins to Reset Once refectory, +40 mV is r ...
P215 - Basic Human Physiology
... • response of the nerve cell to the stimulus is “all or none” – Amt of depolarization always the same – differences in stimulus intensity are detected by • The number of neurons undergoing AP in response to the stimulus • The frequency of action potential generation ...
... • response of the nerve cell to the stimulus is “all or none” – Amt of depolarization always the same – differences in stimulus intensity are detected by • The number of neurons undergoing AP in response to the stimulus • The frequency of action potential generation ...
The Other Brain - lisa eportfolio
... in healing and defending the brain from disease. They are the private immune cells of the brain. NG2 Cells can transform into Oligodendrocytes and Astrocytes, as well as neurons. This newest cell discovery is leading to even more questions when it comes to distinguishing the difference between the g ...
... in healing and defending the brain from disease. They are the private immune cells of the brain. NG2 Cells can transform into Oligodendrocytes and Astrocytes, as well as neurons. This newest cell discovery is leading to even more questions when it comes to distinguishing the difference between the g ...
Cell body
... that receives contacts from other neurons. Terminal buttons (axon terminals): Button-like endings on axon branches that contain chemicals for communication between cells (i.e., neurotransmitters). ...
... that receives contacts from other neurons. Terminal buttons (axon terminals): Button-like endings on axon branches that contain chemicals for communication between cells (i.e., neurotransmitters). ...
Nervous Tissue [PPT]
... receive activating or inhibiting inputs from thousands of synaptic connections. ...
... receive activating or inhibiting inputs from thousands of synaptic connections. ...
The Nervous System
... b. the axon conducts nerve impulses away from the cell body, c. the cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles and produces neurotransmitter chemicals. 7. Explain what an impulse is 8. Know that the conduction of nerve impulses along a neuron involves movement of ions 9. Say what a neurotra ...
... b. the axon conducts nerve impulses away from the cell body, c. the cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles and produces neurotransmitter chemicals. 7. Explain what an impulse is 8. Know that the conduction of nerve impulses along a neuron involves movement of ions 9. Say what a neurotra ...
Resting membrane potential
... Consequence of demyelination in MS - Loss of axonal conduction for neurons of the CNS and in clinical disability ...
... Consequence of demyelination in MS - Loss of axonal conduction for neurons of the CNS and in clinical disability ...
Document
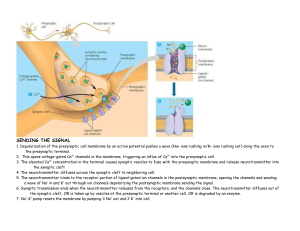
... 6. Synaptic transmission ends when the neurotransmitter releases from the receptors, and the channels close. The neurotransmitter diffuses out of the synaptic cleft, OR is taken up by vesicles at the presynaptic terminal or another cell, OR is degraded by an enzyme. 7. Na+-K+ pump resets the membran ...
... 6. Synaptic transmission ends when the neurotransmitter releases from the receptors, and the channels close. The neurotransmitter diffuses out of the synaptic cleft, OR is taken up by vesicles at the presynaptic terminal or another cell, OR is degraded by an enzyme. 7. Na+-K+ pump resets the membran ...
Action Potential Web Quest
... 5. There are about ______________ neurons in the brain as well as ______________ of support cells called _____________________. 6. There are 3 major types of glial cells. Name each of the 3 and explain their function: ...
... 5. There are about ______________ neurons in the brain as well as ______________ of support cells called _____________________. 6. There are 3 major types of glial cells. Name each of the 3 and explain their function: ...
Neuroanatomy - UCSD Cognitive Science
... Dendrites generally receive synaptic input (i.e. are postsynaptic) and axons generally send synaptic output (i.e., are presynaptic) Dynamic polarization (processes of input, integration, output) may be considered “computation.” However, DP is NOT independent of the neuroanatomy and can occur in both ...
... Dendrites generally receive synaptic input (i.e. are postsynaptic) and axons generally send synaptic output (i.e., are presynaptic) Dynamic polarization (processes of input, integration, output) may be considered “computation.” However, DP is NOT independent of the neuroanatomy and can occur in both ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... All parts of the cell are made up of protein molecules of different kinds. ...
... All parts of the cell are made up of protein molecules of different kinds. ...
Jürgen R. Schwarz
... Institute of Applied Physiology, University of Hamburg Information processing within the brain involves the generation of action potentials which are responsible for fast communication between nerve cells. Action potentials have a short duration and are generated by a transient influx of Na+ and a d ...
... Institute of Applied Physiology, University of Hamburg Information processing within the brain involves the generation of action potentials which are responsible for fast communication between nerve cells. Action potentials have a short duration and are generated by a transient influx of Na+ and a d ...
Chapter 2 quiz level - easy topic: neurons
... 2) The human brain contains somewhere between ________ and ________ neurons. A) 10 billion; 100 billion B) 10 million; 20 million C) 50 million; 100 million D) 2 trillion; 5 trillion ...
... 2) The human brain contains somewhere between ________ and ________ neurons. A) 10 billion; 100 billion B) 10 million; 20 million C) 50 million; 100 million D) 2 trillion; 5 trillion ...
The neuron Label the following terms: Soma Axon terminal Axon
... 11. Myelin Sheath (Myelin) 12. Afferent Neuron 13. Threshold 14. Neurotransmitter 15. Efferent Neurons 16. Axon Terminal 17. Stimulus 18. Refractory Period 19. Schwann 20. Nodes of Ranvier 21. Acetylc ...
... 11. Myelin Sheath (Myelin) 12. Afferent Neuron 13. Threshold 14. Neurotransmitter 15. Efferent Neurons 16. Axon Terminal 17. Stimulus 18. Refractory Period 19. Schwann 20. Nodes of Ranvier 21. Acetylc ...
BIOLOGY 3201
... 4. Which part of the autonomic nervous system helps us respond to stress? 5. Which part of the peripheral nervous system do we have conscious control over? 6. _?_ carry information from receptor cells to the CNS. 7. _?_ carry information from the CNS to effectors like muscles. 8. Modulators of the C ...
... 4. Which part of the autonomic nervous system helps us respond to stress? 5. Which part of the peripheral nervous system do we have conscious control over? 6. _?_ carry information from receptor cells to the CNS. 7. _?_ carry information from the CNS to effectors like muscles. 8. Modulators of the C ...
axon
... • Neurilamma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles Schwann cell ...
... • Neurilamma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles Schwann cell ...
Biol 203 Lab Week 10 Nervous System Histology
... • Neurilamma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles Schwann cell ...
... • Neurilamma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles Schwann cell ...
Exam 3B key
... a) hormones are lipid-soluble and readily penetrate the membranes of the target cell. b) hormones are large molecules that remain in circulation for months and can repeatedly stimulate the same cell. c) the mechanism of hormonal action involves an enzyme cascade that amplifies the response to a horm ...
... a) hormones are lipid-soluble and readily penetrate the membranes of the target cell. b) hormones are large molecules that remain in circulation for months and can repeatedly stimulate the same cell. c) the mechanism of hormonal action involves an enzyme cascade that amplifies the response to a horm ...
Neuro Physiology 1
... to the characteristics of the axon. ,Channel opening speed, ECF composition and temperature all increase conduction speed. The most important factors however in terms of conduction velocities is axon diameter and the presence of myelin. Myelin is a tight spiral wrapping of glial cells around an axon ...
... to the characteristics of the axon. ,Channel opening speed, ECF composition and temperature all increase conduction speed. The most important factors however in terms of conduction velocities is axon diameter and the presence of myelin. Myelin is a tight spiral wrapping of glial cells around an axon ...
The Nervous System
... • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: ...
... • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: ...
Node of Ranvier

The nodes of Ranvier also known as myelin sheath gaps, are the gaps (approximately 1 micrometer in length) formed between the myelin sheaths generated by different cells. A myelin sheath is a many-layered coating, largely composed of a fatty substance called myelin, that wraps around the axon of a neuron and very efficiently insulates it. At nodes of Ranvier, the axonal membrane is uninsulated and, therefore, capable of generating electrical activity.




![Nervous Tissue [PPT]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000313628_1-63044c543d97a5d91f1cbdf37558ffd7-300x300.png)