The Nervous System
... • All cells have a membrane potential, a difference in charge between inside and outside. Developed 2 weeks post conception, maintained through life. • The resting potential of an unstimulated nerve cell is about -70mV; negative inside the cell. • The resting membrane potential is maintained by the ...
... • All cells have a membrane potential, a difference in charge between inside and outside. Developed 2 weeks post conception, maintained through life. • The resting potential of an unstimulated nerve cell is about -70mV; negative inside the cell. • The resting membrane potential is maintained by the ...
Basis of Membrane Potential Action Potential Movie
... – Pulse of electric charge is conducted along the axon at speeds up to 100 meters per second – Membrane potential changes from -60 to +50 ...
... – Pulse of electric charge is conducted along the axon at speeds up to 100 meters per second – Membrane potential changes from -60 to +50 ...
Nervous System I
... Unmyelinated axons generate action potentials across the length of the entire axon. ...
... Unmyelinated axons generate action potentials across the length of the entire axon. ...
Slide 1
... Neurons carry a negative electrical charge relative to the extra cellular fluid bathing them The plasma membrane is a semi permeable because certain ions can cross at certain times but there is not a free exchange The opening and closing of specific ion channels can be controlled by chemical signals ...
... Neurons carry a negative electrical charge relative to the extra cellular fluid bathing them The plasma membrane is a semi permeable because certain ions can cross at certain times but there is not a free exchange The opening and closing of specific ion channels can be controlled by chemical signals ...
Bioenergetics - Eastern Michigan University
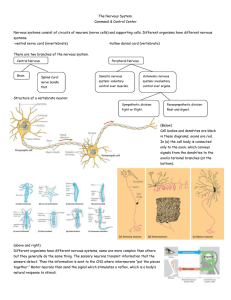
... Relationship between motor and sensory fibers of the PNS and the CNS ...
... Relationship between motor and sensory fibers of the PNS and the CNS ...
“The Physiology of Excitable Cells”
... chloride ions interacting through the intermolecular potential. Here we apply a potential difference across the channel such that inside is positive with respect to outside. The motion of each ion during each discrete time step is determined by, first, the net electrical force acting on it; secondly ...
... chloride ions interacting through the intermolecular potential. Here we apply a potential difference across the channel such that inside is positive with respect to outside. The motion of each ion during each discrete time step is determined by, first, the net electrical force acting on it; secondly ...
Nervous System
... 1. A cell membrane is usually polarized as a result of an unequal distribution of ions. 2. Distribution of ions. a) The distribution of ions is due to the presence of pores and channels in the membranes which allow passage of some ions, but not others. K+ pass more easily through cell membranes than ...
... 1. A cell membrane is usually polarized as a result of an unequal distribution of ions. 2. Distribution of ions. a) The distribution of ions is due to the presence of pores and channels in the membranes which allow passage of some ions, but not others. K+ pass more easily through cell membranes than ...
Nervous System and Senses - Avon Community School Corporation
... negative charge diminishes Potassium channels open and potassium moves out of the axon, repolarizing the membrane ...
... negative charge diminishes Potassium channels open and potassium moves out of the axon, repolarizing the membrane ...
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling
... between the inside and outside of the cell membrane. Resting Potential- the membrane potential of a resting neuron is -60 to -80 mV. Formed by a high concentration of K+ ions inside the cell, and high Na+ ions outside the cell. ...
... between the inside and outside of the cell membrane. Resting Potential- the membrane potential of a resting neuron is -60 to -80 mV. Formed by a high concentration of K+ ions inside the cell, and high Na+ ions outside the cell. ...
Essentials of Anatony and Physiology, 5e (Martini
... The brain and spinal cord comprise which branch of the nervous system? Neurons responsible for integrating sensory information and coordinating motor activity are called… Neurons that monitor the internal and external environment and relay information to the brain and spinal cord are… The division o ...
... The brain and spinal cord comprise which branch of the nervous system? Neurons responsible for integrating sensory information and coordinating motor activity are called… Neurons that monitor the internal and external environment and relay information to the brain and spinal cord are… The division o ...
The Nervous System
... Stimulation causes the membrane of a neuron to open the Na+ ion channels allowing Na+ ions to rush into the cell This causes the local area of the neuron to become positively charged (depolarized) Depolarization causes the Na+ ion channels to close and the K+ channels to open Diffusion of K+ ions ou ...
... Stimulation causes the membrane of a neuron to open the Na+ ion channels allowing Na+ ions to rush into the cell This causes the local area of the neuron to become positively charged (depolarized) Depolarization causes the Na+ ion channels to close and the K+ channels to open Diffusion of K+ ions ou ...
Lecture Outline ()
... – fewer than 25 per m2 in myelin-covered regions – up to 12,000 per m2 in nodes of Ranvier ...
... – fewer than 25 per m2 in myelin-covered regions – up to 12,000 per m2 in nodes of Ranvier ...
PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION BSc Counselling Psychology
... 67. Areas that include large number of cell bodies are called __________________. a. White matter c. Ganglia b. Gray matter d. Nerve 68. When the action potential reaches the axon ending, it causes tiny bubbles of chemicals called ____________________ to release their contents into the synaptic gap. ...
... 67. Areas that include large number of cell bodies are called __________________. a. White matter c. Ganglia b. Gray matter d. Nerve 68. When the action potential reaches the axon ending, it causes tiny bubbles of chemicals called ____________________ to release their contents into the synaptic gap. ...
So it is the number of action potentials per second
... migrate throughout the developing embryo ...
... migrate throughout the developing embryo ...
Notes – Neurons and the nervous system
... This depolarization then causes the next set of sodium channels to open, thus depolarizing the next part of the axon, and this continues like a domino effect. Axons also have channels that pump sodium back out of the cell, to restore the negative resting potential so that it becomes ready again ...
... This depolarization then causes the next set of sodium channels to open, thus depolarizing the next part of the axon, and this continues like a domino effect. Axons also have channels that pump sodium back out of the cell, to restore the negative resting potential so that it becomes ready again ...
Chapter Outline
... – fewer than 25 per m2 in myelin-covered regions – up to 12,000 per m2 in nodes of Ranvier ...
... – fewer than 25 per m2 in myelin-covered regions – up to 12,000 per m2 in nodes of Ranvier ...
The Nervous System : communication
... hundreds of synaptic connections and work together to perform a common function ...
... hundreds of synaptic connections and work together to perform a common function ...
Nervous
... The nervous system also has cells that are essential for the structure of the nervous system called supporting cells or Glia. Some of these are: Astrocyte: glial cell that provides structural and metabolic support for neurons. Blood-brain barrier: a specialized capillary arrangement in the brain th ...
... The nervous system also has cells that are essential for the structure of the nervous system called supporting cells or Glia. Some of these are: Astrocyte: glial cell that provides structural and metabolic support for neurons. Blood-brain barrier: a specialized capillary arrangement in the brain th ...
Nervous System - Phoenix Union High School District
... c) ependymal- (epithelial-like) provide a barrier between brain and cerebrospinal fluid. ...
... c) ependymal- (epithelial-like) provide a barrier between brain and cerebrospinal fluid. ...
BioH Nervous System PPT 2013
... Impulses always travel from dendrites, through the cell body to the axon terminal ...
... Impulses always travel from dendrites, through the cell body to the axon terminal ...
Node of Ranvier

The nodes of Ranvier also known as myelin sheath gaps, are the gaps (approximately 1 micrometer in length) formed between the myelin sheaths generated by different cells. A myelin sheath is a many-layered coating, largely composed of a fatty substance called myelin, that wraps around the axon of a neuron and very efficiently insulates it. At nodes of Ranvier, the axonal membrane is uninsulated and, therefore, capable of generating electrical activity.