determination of CB 1 receptor binding and agonist activity of
... control synthetic drugs, including cannabinoids. This legislation places synthetic cannabinoids into Schedule I of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 812(c)) based on structure, receptor binding, and function. There are currently at least 17 chemical classes of cannabinoid structure known with ...
... control synthetic drugs, including cannabinoids. This legislation places synthetic cannabinoids into Schedule I of the Controlled Substances Act (21 U.S.C. 812(c)) based on structure, receptor binding, and function. There are currently at least 17 chemical classes of cannabinoid structure known with ...
Receptor families2015-10-30 14:065.9 MB
... (Kinase-linked receptor) o Involved in response to hormones, growth factors. o Response occurs in minutes to hours. o They control many cellular functions as metabolism and growth. ...
... (Kinase-linked receptor) o Involved in response to hormones, growth factors. o Response occurs in minutes to hours. o They control many cellular functions as metabolism and growth. ...
Antagonists and agonists at the glycine site of the NMDA receptor for
... MK-801 is very unselective because it also interferes with the activity (firing rates) of non-nociceptive neurons in normal animals. The antihyperalgesic activity of GV196771A is not accompanied by development of tolerance, which is in line with the view that the NMDA receptor plays a pivotal role i ...
... MK-801 is very unselective because it also interferes with the activity (firing rates) of non-nociceptive neurons in normal animals. The antihyperalgesic activity of GV196771A is not accompanied by development of tolerance, which is in line with the view that the NMDA receptor plays a pivotal role i ...
Slide ()
... Touch is mediated by four types of mechano receptors in the human hand. The terminals of myelinated sensory nerves innervating the hand are surrounded by specialized structures that detect contact on the skin. The receptors differ in morphology, innervation patterns, location in the skin, receptive ...
... Touch is mediated by four types of mechano receptors in the human hand. The terminals of myelinated sensory nerves innervating the hand are surrounded by specialized structures that detect contact on the skin. The receptors differ in morphology, innervation patterns, location in the skin, receptive ...
The Science of Recovery - AAP
... Acute intoxication results in activation and deactivation of regions connected to the DA system These regions are involved in ...
... Acute intoxication results in activation and deactivation of regions connected to the DA system These regions are involved in ...
11_45_48_SG
... Action potential depolarizes the synaptic terminal membrane Ligand-gated channels open Synaptic vesicles release nerutrans into the synaptic cleft ...
... Action potential depolarizes the synaptic terminal membrane Ligand-gated channels open Synaptic vesicles release nerutrans into the synaptic cleft ...
The Eye & The Action Potential
... series of neurons that ultimately lead to the optic nerve which ultimately leads to the brain. ...
... series of neurons that ultimately lead to the optic nerve which ultimately leads to the brain. ...
CNS Autonomic NS
... The NMDA receptor complex. Activation (i.e., excitation) occurs when either glutamate (Glu) or N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) and glycine (Gly) bind to the receptor molecule. A channel within the receptor complex enables molecules to cross the cell membrane. Magnesium (Mg) blocks this channel. When Mg ...
... The NMDA receptor complex. Activation (i.e., excitation) occurs when either glutamate (Glu) or N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) and glycine (Gly) bind to the receptor molecule. A channel within the receptor complex enables molecules to cross the cell membrane. Magnesium (Mg) blocks this channel. When Mg ...
Cell signalling
... • very potent neurotoxins • bind to receptor and prevent opening of Na+ channel – e.g. cobratoxin from Indian cobra ...
... • very potent neurotoxins • bind to receptor and prevent opening of Na+ channel – e.g. cobratoxin from Indian cobra ...
Cell Communication Webquest 2014
... 15. Why does the ligand have to fit with the receptor molecule? 16. Why does signal transduction often involve a change in the shape of the receptor? 17. List three cellular responses that signal transduction can produce. View the cell communication animation at the following URL and use this to ans ...
... 15. Why does the ligand have to fit with the receptor molecule? 16. Why does signal transduction often involve a change in the shape of the receptor? 17. List three cellular responses that signal transduction can produce. View the cell communication animation at the following URL and use this to ans ...
Key Transmitters - Sinauer Associates
... Several auxilliary synaptic proteins regulate this trafficking.49 It allows rapid changes in the numbers and subunit composition of synaptic receptors during neural activity, providing the basis for many forms of synaptic plasticity (see Chapter 16). The NMDA receptors are made up of GluN1–3 subunit ...
... Several auxilliary synaptic proteins regulate this trafficking.49 It allows rapid changes in the numbers and subunit composition of synaptic receptors during neural activity, providing the basis for many forms of synaptic plasticity (see Chapter 16). The NMDA receptors are made up of GluN1–3 subunit ...
membranes and transport
... cells. Where is the cell more negative? Inside or out? Inside! This is important for propogation of signals in neurons • Export of sodium from the cell provides the driving force for several facilitated transporters, which import glucose, amino acids and other nutrients into the cell. • Creates an o ...
... cells. Where is the cell more negative? Inside or out? Inside! This is important for propogation of signals in neurons • Export of sodium from the cell provides the driving force for several facilitated transporters, which import glucose, amino acids and other nutrients into the cell. • Creates an o ...
Mechanisms of drug action
... information from the extracellular compartment and to transmit that information to the intracellular compartment. ...
... information from the extracellular compartment and to transmit that information to the intracellular compartment. ...
Cytokines
... Low molecular weight proteins (30 KDa) Bind receptors, alter gene expression Can bind the secreting cell (autocrine) Can bind another cell close by (paracrine) Few cases bind another cell far away (endocrine) Very low Kd receptors (10-10-10-12 M) Cytokines regulate immune responses ...
... Low molecular weight proteins (30 KDa) Bind receptors, alter gene expression Can bind the secreting cell (autocrine) Can bind another cell close by (paracrine) Few cases bind another cell far away (endocrine) Very low Kd receptors (10-10-10-12 M) Cytokines regulate immune responses ...
levels of the neurotransmitter GABA, which
... can block damage caused by oxidative molecules and can improve mitochondrial function. Recent research has revealed that lipoic acid can improve memory and protect against age-related cognitive dysfunction. L-phenylalanine: L-Phenylalanine is best known as an essential amino acid, but it has curious ...
... can block damage caused by oxidative molecules and can improve mitochondrial function. Recent research has revealed that lipoic acid can improve memory and protect against age-related cognitive dysfunction. L-phenylalanine: L-Phenylalanine is best known as an essential amino acid, but it has curious ...
9ReceptorTypes1
... the membrane. • Binding of ligand opens the pore. • Ions flow into or out of the cell. • Produces EPSP or IPSP (depending on the ion channel). • Rapid desensitization (loss of activity) if continuously exposed to nt. • Limits postsynaptic responding when presynaptic neurons are highly active for a p ...
... the membrane. • Binding of ligand opens the pore. • Ions flow into or out of the cell. • Produces EPSP or IPSP (depending on the ion channel). • Rapid desensitization (loss of activity) if continuously exposed to nt. • Limits postsynaptic responding when presynaptic neurons are highly active for a p ...
Flatworm nervous system as drug target
... • A truncated one, which has the glutamate-binding site but lacks the seven transmembrane domains characterizing the metabotropic glutamate receptors (Taman and Ribeiro 2011). ...
... • A truncated one, which has the glutamate-binding site but lacks the seven transmembrane domains characterizing the metabotropic glutamate receptors (Taman and Ribeiro 2011). ...
Characteristic for receptor cells
... (3) It may modulate the activity of ion channels indirectly through an enzyme cascade, which amplifies the cellular signal. ...
... (3) It may modulate the activity of ion channels indirectly through an enzyme cascade, which amplifies the cellular signal. ...
23Neurotransmitter22012-09
... • Inhibitory neurotransmitter of CNS and is also found in retina. • Formed by decarboxylation of glutamate. • The enzyme that catalyzes this reaction is ...
... • Inhibitory neurotransmitter of CNS and is also found in retina. • Formed by decarboxylation of glutamate. • The enzyme that catalyzes this reaction is ...
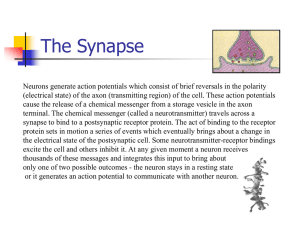
The Synapse
... (electrical state) of the axon (transmitting region) of the cell. These action potentials cause the release of a chemical messenger from a storage vesicle in the axon terminal. The chemical messenger (called a neurotransmitter) travels across a synapse to bind to a postsynaptic receptor protein. The ...
... (electrical state) of the axon (transmitting region) of the cell. These action potentials cause the release of a chemical messenger from a storage vesicle in the axon terminal. The chemical messenger (called a neurotransmitter) travels across a synapse to bind to a postsynaptic receptor protein. The ...
Drug-Receptor Interactions
... activated by alterations in membrane voltage. For example, voltage-gated sodium (Na+) channels open when the membrane is depolarized to a threshold potential and contribute to further membrane depolarization by allowing Na+ influx into the cell. Ligand-gated ion channels are activated after binding ...
... activated by alterations in membrane voltage. For example, voltage-gated sodium (Na+) channels open when the membrane is depolarized to a threshold potential and contribute to further membrane depolarization by allowing Na+ influx into the cell. Ligand-gated ion channels are activated after binding ...
PowerPoint Sunusu
... Spans the membrane once and may form dimers. These receptors also have cytosolic enzyme activity as an integral component of their ...
... Spans the membrane once and may form dimers. These receptors also have cytosolic enzyme activity as an integral component of their ...
Adrenergic receptor antagonists
... may be important to diabetic patients and to other individuals prone to hypoglycaemic attacks. The sympathetic response to hypoglycaemia produces symptoms (especially tachycardia) that warn patients of the urgent need for carbohydrate (usually in the form of a sugary drink). β-Receptor antagonists r ...
... may be important to diabetic patients and to other individuals prone to hypoglycaemic attacks. The sympathetic response to hypoglycaemia produces symptoms (especially tachycardia) that warn patients of the urgent need for carbohydrate (usually in the form of a sugary drink). β-Receptor antagonists r ...
NMDA receptor

The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and ion channel protein found in nerve cells. It is activated when glutamate and glycine (or D-serine) bind to it, and when activated it allows positively charged ions to flow through the cell membrane. The NMDA receptor is very important for controlling synaptic plasticity and memory function.The NMDAR is a specific type of ionotropic glutamate receptor. The NMDA receptor is named this because the agonist molecule N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) binds selectively to it, and not to other glutamate receptors. Activation of NMDA receptors results in the opening of an ion channel that is nonselective to cations with a reversal potential near 0 mV. A property of the NMDA receptor is its voltage-dependent activation, a result of ion channel block by extracellular Mg2+ & Zn2+ ions. This allows the flow of Na+ and small amounts of Ca2+ ions into the cell and K+ out of the cell to be voltage-dependent.Calcium flux through NMDARs is thought to be critical in synaptic plasticity, a cellular mechanism for learning and memory. The NMDA receptor is distinct in two ways: first, it is both ligand-gated and voltage-dependent; second, it requires co-activation by two ligands: glutamate and either D-serine or glycine.The activity of the NMDA receptor is affected by many psychoactive drugs such as phencyclidine (PCP), alcohol (ethanol) and dextromethorphan (DXM). The anaesthetic effects of the drugs ketamine and nitrous oxide are partially because of their effects on NMDA receptor activity.