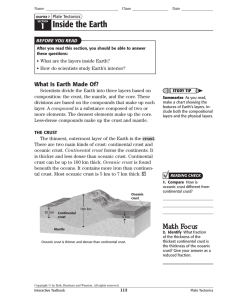
Name - OnCourse
... 1. Use the graham cracker, broken into two pieces for this part. Fit the two pieces together side to side on top of the wax paper. 2. Place one hand on each of the graham cracker pieces and push them together by applying steady, moderate pressure. At the same time, also push one of the pieces away f ...
... 1. Use the graham cracker, broken into two pieces for this part. Fit the two pieces together side to side on top of the wax paper. 2. Place one hand on each of the graham cracker pieces and push them together by applying steady, moderate pressure. At the same time, also push one of the pieces away f ...
Pangea - Mrs. LeFevre`s Class
... Earth Science Pangaea Millions of years ago the Earth looked much different than it looks today. All seven continents1 (North America, South America, Asia, Africa, Europe, Australia, and Antarctica) were one gigantic continent which scientists call Pangaea (pan-gee-uh). The name Pangaea is derived f ...
... Earth Science Pangaea Millions of years ago the Earth looked much different than it looks today. All seven continents1 (North America, South America, Asia, Africa, Europe, Australia, and Antarctica) were one gigantic continent which scientists call Pangaea (pan-gee-uh). The name Pangaea is derived f ...
Chapter 2 Lecture Powerpoint Handout
... • The rates of movement changes over time • North American plate along the San Andreas fault about 3.5 cm (1.4 in.) per year • When rough edges along the plate move quickly, an earthquake may be produced • Often slow creeping movement • The direction of movement changes too (see Figure 2.4a) • Wilso ...
... • The rates of movement changes over time • North American plate along the San Andreas fault about 3.5 cm (1.4 in.) per year • When rough edges along the plate move quickly, an earthquake may be produced • Often slow creeping movement • The direction of movement changes too (see Figure 2.4a) • Wilso ...
mid-oceanic ridges
... upwelling of magma from the core-mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. A volcano is an opening, or rupture, in a planet's surface or crust, which allows hot magma, volcanic ash and gases to escape from below the surface ...
... upwelling of magma from the core-mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. A volcano is an opening, or rupture, in a planet's surface or crust, which allows hot magma, volcanic ash and gases to escape from below the surface ...
Plate Tectonics
... Geologists use seismic waves to study Earth’s interior. Radioactive substances heat the interior of Earth. The crust is thickest under high mountains. The mantle is solid. Movements in the outer core create Earth’s magnetic field. ...
... Geologists use seismic waves to study Earth’s interior. Radioactive substances heat the interior of Earth. The crust is thickest under high mountains. The mantle is solid. Movements in the outer core create Earth’s magnetic field. ...
How do we know if a rock is intrusive or extrusive?
... – Intrusive Rocks – are typically coarse grained – Extrusive Rocks – are typically fine grained • Pyroclastic Rocks – are typically made of volcanic glass and/or pieces of pre-existing rocks ...
... – Intrusive Rocks – are typically coarse grained – Extrusive Rocks – are typically fine grained • Pyroclastic Rocks – are typically made of volcanic glass and/or pieces of pre-existing rocks ...
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics
... How do scientists know things about the deepest parts of the Earth? No one has ever been to these places. Scientists have never even drilled through the crust, which is only a thin layer on the surface of the Earth. So how do we know so much about the mantle and the core? Much of what scientists kno ...
... How do scientists know things about the deepest parts of the Earth? No one has ever been to these places. Scientists have never even drilled through the crust, which is only a thin layer on the surface of the Earth. So how do we know so much about the mantle and the core? Much of what scientists kno ...
Document
... Zqmd - Quartz monzodiorite: The rocks within the map areas designated as quartz monzodiorite appear similar to the typical diorite. Rare pinkish alkali feldspar is present in some samples (specifically on the south side of Blackwood Mountain). Whole rock chemical analyses from 9 rock samples of Blan ...
... Zqmd - Quartz monzodiorite: The rocks within the map areas designated as quartz monzodiorite appear similar to the typical diorite. Rare pinkish alkali feldspar is present in some samples (specifically on the south side of Blackwood Mountain). Whole rock chemical analyses from 9 rock samples of Blan ...
Complete Earth.s struct
... kilometres long. They cut through the abyssal plains. They can be so high that they emerge from the water and create islands, as is the case of Iceland. • Ridges have a fissure down their middle, called a rift. Rift ...
... kilometres long. They cut through the abyssal plains. They can be so high that they emerge from the water and create islands, as is the case of Iceland. • Ridges have a fissure down their middle, called a rift. Rift ...
Rock Reading
... The composition of magma is also important in determining which minerals will crystallize. Hence, terms such as “mafic” or “felsic” are typically used to describe magmas. In summary, Bowen’s Reaction Series provide a relationship between composition of magmas, temperature and resulting rocks. For ex ...
... The composition of magma is also important in determining which minerals will crystallize. Hence, terms such as “mafic” or “felsic” are typically used to describe magmas. In summary, Bowen’s Reaction Series provide a relationship between composition of magmas, temperature and resulting rocks. For ex ...
Porphyritic Fine
... Complete the following table by identifying which of the characteristics in the left-hand column are present in volcanic and/or plutonic igneous rocks by stating yes or no for the appropriate number. One characteristic has been completed as an example. ...
... Complete the following table by identifying which of the characteristics in the left-hand column are present in volcanic and/or plutonic igneous rocks by stating yes or no for the appropriate number. One characteristic has been completed as an example. ...
Writing and Bell Ringer 2-14-11
... How are clastic rocks and organic rocks similar? How are they different? 1. Why are the oldest parts of the ocean floor no older than about 200 million years old? 2. How do magnetic stripes form on the ocean floor? Why are these stripes ...
... How are clastic rocks and organic rocks similar? How are they different? 1. Why are the oldest parts of the ocean floor no older than about 200 million years old? 2. How do magnetic stripes form on the ocean floor? Why are these stripes ...
earthquakes our restless planet
... impending earthquake. What could explain this ? While no one can say with certainty how, or even if, animals can sense an impending earthquake, it is common knowledge that many animals have keener senses than humans and some have abilities which we do not. For example, catfish are believed to be sen ...
... impending earthquake. What could explain this ? While no one can say with certainty how, or even if, animals can sense an impending earthquake, it is common knowledge that many animals have keener senses than humans and some have abilities which we do not. For example, catfish are believed to be sen ...
plate tectonics
... Explain the theory of Plate Tectonics. COMPARE AND CONTRAST DIVERGENT, CONVERGENT AND TRANSFORM BOUNDARIES. ***very important. Describe what geologic features form at each of the three CONVERGENT boundary types (oceanic-oceanic, oceaniccontinental, continental-continental). For each boundary type, g ...
... Explain the theory of Plate Tectonics. COMPARE AND CONTRAST DIVERGENT, CONVERGENT AND TRANSFORM BOUNDARIES. ***very important. Describe what geologic features form at each of the three CONVERGENT boundary types (oceanic-oceanic, oceaniccontinental, continental-continental). For each boundary type, g ...
Volcanoes, Nature`s Incredible Fireworks
... 1. Read the Big Ideas and Key Understandings and the Synopsis. Please do not read this to the students. This is a description for teachers, about the big ideas and key understanding that students should take away after completing this task. Big Ideas and Key Understandings The earth is made up of ma ...
... 1. Read the Big Ideas and Key Understandings and the Synopsis. Please do not read this to the students. This is a description for teachers, about the big ideas and key understanding that students should take away after completing this task. Big Ideas and Key Understandings The earth is made up of ma ...
The Theory of Plate Tectonics
... 5. What does the word tectonics mean? _______________________________ 6. What causes the plates to move? _______________________________________________ 7. What is a plate boundary? _____________________________________________________ 8. What is a fault? ____________________________________________ ...
... 5. What does the word tectonics mean? _______________________________ 6. What causes the plates to move? _______________________________________________ 7. What is a plate boundary? _____________________________________________________ 8. What is a fault? ____________________________________________ ...
Plate Tectonics
... broken into several large sections known It is theorized that these plates are dynamic and move continually. The interaction between plates produces changes on Earth’s surface such as, volcanoes, mountains, and earthquakes. ...
... broken into several large sections known It is theorized that these plates are dynamic and move continually. The interaction between plates produces changes on Earth’s surface such as, volcanoes, mountains, and earthquakes. ...
Earthquakes
... • At the present there is no known way to prevent quakes. However, the amount of destruction caused can be lessened but quake resistant structures and proper ...
... • At the present there is no known way to prevent quakes. However, the amount of destruction caused can be lessened but quake resistant structures and proper ...
The Geological Journey of Charles Darwin
... Charles Darwin was a modern naturalist عالم طبيعة معاصرwith a passion شغفfor Geology, even if most people would think of him as a biologist عالم أحياء. He believed in the words of Alexander von Humboldt: “It is by isolating facts that travellers عزل الحقائقhave given birth to so many fal ...
... Charles Darwin was a modern naturalist عالم طبيعة معاصرwith a passion شغفfor Geology, even if most people would think of him as a biologist عالم أحياء. He believed in the words of Alexander von Humboldt: “It is by isolating facts that travellers عزل الحقائقhave given birth to so many fal ...
1 Plate Tectonics Review w
... The Geology Paradigm – Plate Tectonics Sir Francis Bacon 1620 Benjamin Franklin 1782 The crust of the earth must be a shell floating on a fluid interior. Thus the surface of the globe would be broken … by … movements of the fluids…. Continents fit together Surprise: Mid-Ocean Ridges ...
... The Geology Paradigm – Plate Tectonics Sir Francis Bacon 1620 Benjamin Franklin 1782 The crust of the earth must be a shell floating on a fluid interior. Thus the surface of the globe would be broken … by … movements of the fluids…. Continents fit together Surprise: Mid-Ocean Ridges ...
Presentation
... Thorium Provinces • Placer deposits with monazite are known from many areas around the world, e.g.: • East and West coast of Australia, inland deposits in New South Wales and Victoria. „Parent“ rocks regarded as sources have a wide range in composition (mainly magmatic and metamorphic) and age (Arc ...
... Thorium Provinces • Placer deposits with monazite are known from many areas around the world, e.g.: • East and West coast of Australia, inland deposits in New South Wales and Victoria. „Parent“ rocks regarded as sources have a wide range in composition (mainly magmatic and metamorphic) and age (Arc ...
Name
... Indicator 19: Describe how objects in the Solar System are in regular and predictable motions that explain such phenomena as days, years, seasons, eclipses, tides and moon cycles. Indicator 20: Explain that the gravitational force is the dominant force determining motions in the Solar system and in ...
... Indicator 19: Describe how objects in the Solar System are in regular and predictable motions that explain such phenomena as days, years, seasons, eclipses, tides and moon cycles. Indicator 20: Explain that the gravitational force is the dominant force determining motions in the Solar system and in ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.