Chapter 2 - MrJardina
... because they are not formed by nature. Bricks are made from clays and sediments. Bricks have been used by people for over 60 centuries. How is the way that bricks are created similar to that of how metamorphic rocks as well as sedimentary rocks are formed? ...
... because they are not formed by nature. Bricks are made from clays and sediments. Bricks have been used by people for over 60 centuries. How is the way that bricks are created similar to that of how metamorphic rocks as well as sedimentary rocks are formed? ...
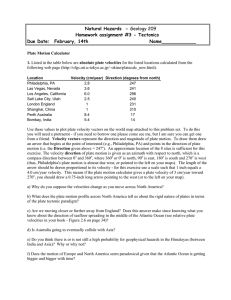
Natural Hazards - Geology 209 Homework assignment #3
... Under the proper conditions many rocks preserve a record of the orientation of the Earth's magnetic field at the time that the rock was formed. The study of this ancient fossilized magnetism is called paleomagnetism - what Professor Weil does. Paleomagnetic studies were instrumental in leading to th ...
... Under the proper conditions many rocks preserve a record of the orientation of the Earth's magnetic field at the time that the rock was formed. The study of this ancient fossilized magnetism is called paleomagnetism - what Professor Weil does. Paleomagnetic studies were instrumental in leading to th ...
Metamorphic Rocks - Lancaster City Schools
... One way that a nonfoliated rock forms is through contact with magma. During contact metamorphism, magma comes in contact with existing rock, and its thermal energy and gases interact with the surrounding rock to make new metamorphic rock. Contact metamorphism can increase crystal size. It can also f ...
... One way that a nonfoliated rock forms is through contact with magma. During contact metamorphism, magma comes in contact with existing rock, and its thermal energy and gases interact with the surrounding rock to make new metamorphic rock. Contact metamorphism can increase crystal size. It can also f ...
TCSS Earth Systems Unit 2 – Plate Tectonics Information
... Plate Tectonic Venn Diagram: This Venn Diagram should be used to compare the two ideas of continental drift and plate tectonics Plate Tectonic Activator: Reading comprehension activity discussing the formation of a mud volcano. Plate Tectonics Puzzle: Activity that will allow students to visualize t ...
... Plate Tectonic Venn Diagram: This Venn Diagram should be used to compare the two ideas of continental drift and plate tectonics Plate Tectonic Activator: Reading comprehension activity discussing the formation of a mud volcano. Plate Tectonics Puzzle: Activity that will allow students to visualize t ...
Inside the earth
... measured in centimeters per year. • Scientists use a system of satellites called the global positioning system (GPS) to measure the rate of tectonic plate movement. ...
... measured in centimeters per year. • Scientists use a system of satellites called the global positioning system (GPS) to measure the rate of tectonic plate movement. ...
Chapter 7
... measured in centimeters per year. • Scientists use a system of satellites called the global positioning system (GPS) to measure the rate of tectonic plate movement. ...
... measured in centimeters per year. • Scientists use a system of satellites called the global positioning system (GPS) to measure the rate of tectonic plate movement. ...
Rock Identification - Faculty Server Contact
... The earth is a very dynamic body and rock material is continually recycled. Plate tectonics is the description of this dynamic process. New material rising from deep in the mantle of the earth is added to the crust of the earth along mid-ocean ridge systems and crust is returned to the mantle at sub ...
... The earth is a very dynamic body and rock material is continually recycled. Plate tectonics is the description of this dynamic process. New material rising from deep in the mantle of the earth is added to the crust of the earth along mid-ocean ridge systems and crust is returned to the mantle at sub ...
AICE Env Day 5 Evidence of Plate Tectonics Stations
... underwater objects and then records the echoes of these sound waves. The mid-ocean ridges curve along the sea floor, extending into all of Earth’s oceans. Most of the mountains in the mid-ocean ridges lie hidden under hundreds of meters of water. A steep-sided valley splits the top of some mid-ocean ...
... underwater objects and then records the echoes of these sound waves. The mid-ocean ridges curve along the sea floor, extending into all of Earth’s oceans. Most of the mountains in the mid-ocean ridges lie hidden under hundreds of meters of water. A steep-sided valley splits the top of some mid-ocean ...
A Short Geological History of Lanark County
... About 550 million years ago Rodinia was torn apart by convection currents in the mantle. A new ocean, the Iapetus, was formed between the separating landmasses of ancestral North America, called Laurentia, and Europe, named Baltica. For the next 200 million years or so, much of the interior of North ...
... About 550 million years ago Rodinia was torn apart by convection currents in the mantle. A new ocean, the Iapetus, was formed between the separating landmasses of ancestral North America, called Laurentia, and Europe, named Baltica. For the next 200 million years or so, much of the interior of North ...
EU4PRT
... Mountain Building Deformation and Mountain Building Lesson 6 Measuring Earthquake Waves Seismic Waves Earthquake Magnitude & ...
... Mountain Building Deformation and Mountain Building Lesson 6 Measuring Earthquake Waves Seismic Waves Earthquake Magnitude & ...
Features on Venus generated by plate boundary processes
... differencesalone reducethe value of e(0) from 3.9 km for Earth, becausethey are smaller both in height and in latEarth to 1.75 km for Venus[Kaula and Phillips,1981]. For eral extent relative to topographicfeaturesresultingfrom oceanic plates on Earth, d _ 125 km, but the value of d for ...
... differencesalone reducethe value of e(0) from 3.9 km for Earth, becausethey are smaller both in height and in latEarth to 1.75 km for Venus[Kaula and Phillips,1981]. For eral extent relative to topographicfeaturesresultingfrom oceanic plates on Earth, d _ 125 km, but the value of d for ...
Ex. East Coast including North Carolina Piedmont
... 6. There are upwards of 4000 minerals in the world, or some such huge number. However, if you know the rock forming minerals you will be able to make most of our rocks. What are those rock-forming minerals? ...
... 6. There are upwards of 4000 minerals in the world, or some such huge number. However, if you know the rock forming minerals you will be able to make most of our rocks. What are those rock-forming minerals? ...
Every Pebble Tells a Story
... sedimentary rocks. I really don’t know what happened next except that I began to feel hot and feel increased pressure from the rock around me. Something must have been pushing on the sedimentary rock layers. The heat and pressure kept increasing until I noticed that my sand and silt particles were c ...
... sedimentary rocks. I really don’t know what happened next except that I began to feel hot and feel increased pressure from the rock around me. Something must have been pushing on the sedimentary rock layers. The heat and pressure kept increasing until I noticed that my sand and silt particles were c ...
Document
... Felsic or Sialic magma • Si-rich (> 65%) • rich in K, and Al • little Ca, Fe, and Mg. Intermediate magma • between the two extremes in Si content and other atoms. ...
... Felsic or Sialic magma • Si-rich (> 65%) • rich in K, and Al • little Ca, Fe, and Mg. Intermediate magma • between the two extremes in Si content and other atoms. ...
8th Earth Science Chapter 4 – Rocks
... _______ moves through soil and rock, it picks up materials released from ___________ during ____________. The resulting ___________ of water and dissolved materials moves through ________ spaces between sediments. _____________ occurs when minerals such as ________, calcite, and __________ are depos ...
... _______ moves through soil and rock, it picks up materials released from ___________ during ____________. The resulting ___________ of water and dissolved materials moves through ________ spaces between sediments. _____________ occurs when minerals such as ________, calcite, and __________ are depos ...
No Slide Title
... 7. What has caused the orderly division into concentric layers of the interior of the Earth? 8. List the correct sequence of the Earth's solid layers, from its surface to the interior: 9. What are the two types of crust? 10. How do the Earth's inner core and outer core differ? 11. The lithosphere is ...
... 7. What has caused the orderly division into concentric layers of the interior of the Earth? 8. List the correct sequence of the Earth's solid layers, from its surface to the interior: 9. What are the two types of crust? 10. How do the Earth's inner core and outer core differ? 11. The lithosphere is ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Somerset Independent Schools
... 3. What do we call layers of rock? Strata 4. Sedimentary rocks are normally laid down in order, one on top of another. In a sequence, the oldest is at the bottom, the youngest is at the top. This is the principle of Superposition 5. Most sedimentary rocks are laid down in flat, horizontal layers. Th ...
... 3. What do we call layers of rock? Strata 4. Sedimentary rocks are normally laid down in order, one on top of another. In a sequence, the oldest is at the bottom, the youngest is at the top. This is the principle of Superposition 5. Most sedimentary rocks are laid down in flat, horizontal layers. Th ...
Convergent Plate Boundaries
... features such as mountains supported? Earth’s continental crust and lithosphere are supported on the on the denser asthenosphere. Instead of buoyancy, the term isostatic equilibrium describes the way the lithosphere is supported on the asthenosphere. ...
... features such as mountains supported? Earth’s continental crust and lithosphere are supported on the on the denser asthenosphere. Instead of buoyancy, the term isostatic equilibrium describes the way the lithosphere is supported on the asthenosphere. ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.