Relative and Absolute Dating 2013
... When magma/lava cools, radioactive elements are incorporated into the minerals Examples: -- Potassium 40 -- Uranium 235 ...
... When magma/lava cools, radioactive elements are incorporated into the minerals Examples: -- Potassium 40 -- Uranium 235 ...
Layer of the Earth
... Activating Prior Knowledge: In the space below, bullet facts that you already know about the layers of Earth! ...
... Activating Prior Knowledge: In the space below, bullet facts that you already know about the layers of Earth! ...
Earth`s Interior Worksheet A Journey to the Center of the Earth (p. 9
... 6. Name the two types of Earth’s crust. 7. Why do you think the ocean crust contains rocks that are more dense than the rocks found on land? Mantle (p. 10 - 11) 8. What does the layer of mantle consist of? 9. What makes up the lithosphere? 10. Right below the lithosphere is a layer of mantle that is ...
... 6. Name the two types of Earth’s crust. 7. Why do you think the ocean crust contains rocks that are more dense than the rocks found on land? Mantle (p. 10 - 11) 8. What does the layer of mantle consist of? 9. What makes up the lithosphere? 10. Right below the lithosphere is a layer of mantle that is ...
Geol 201 - American University of Beirut
... This course is designed to provide the basic principles, and fundamental concepts of the various aspects of geological sciences. Emphasis will be on the internal structure of the Earth, properties of minerals, mineral groups, formation and behaviour of earth materials, description, classification, a ...
... This course is designed to provide the basic principles, and fundamental concepts of the various aspects of geological sciences. Emphasis will be on the internal structure of the Earth, properties of minerals, mineral groups, formation and behaviour of earth materials, description, classification, a ...
Chapter 1 Introducing Earth Study Guide
... How do convection currents help to transfer heat through the inside of the earth? ...
... How do convection currents help to transfer heat through the inside of the earth? ...
Inside the Earth
... • 2 types of crust – Oceanic (very dense, made of basalt) – Continental (less dense, made of granite) ...
... • 2 types of crust – Oceanic (very dense, made of basalt) – Continental (less dense, made of granite) ...
chapter1
... at sufficiently high pressures some of the hydrogen reacts to form helium - light is emitted the chemical elements are formed within the interiors of stars ...
... at sufficiently high pressures some of the hydrogen reacts to form helium - light is emitted the chemical elements are formed within the interiors of stars ...
Chapter 2 Concept Review
... the lithosphere; made of mantle rock that flows very slowly, which allows tectonic plates to move on top of it. ...
... the lithosphere; made of mantle rock that flows very slowly, which allows tectonic plates to move on top of it. ...
final_examgq - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... 10. [True or False] Seismic P-waves can’t travel through the liquid outer core of the Earth but Swaves can. This results in a P-wave shadow on the side of the Earth opposite an earthquake. 11. To reach its dew point temperature, a packet of unsaturated air must usually be [heated / cooled ]. 12. Whi ...
... 10. [True or False] Seismic P-waves can’t travel through the liquid outer core of the Earth but Swaves can. This results in a P-wave shadow on the side of the Earth opposite an earthquake. 11. To reach its dew point temperature, a packet of unsaturated air must usually be [heated / cooled ]. 12. Whi ...
Our Changing World
... • Earth has existed much longer than people have been writing about it • Rocks provide the best record of Earth’s history • Most rocks form in layers as bits of gravel, sand, and mud pressed together • These are known as sedimentary rocks • These preserve a rough record of the past ...
... • Earth has existed much longer than people have been writing about it • Rocks provide the best record of Earth’s history • Most rocks form in layers as bits of gravel, sand, and mud pressed together • These are known as sedimentary rocks • These preserve a rough record of the past ...
The History of Life
... nuclei that break down, or decay, over time, giving off radiation. Because every radioactive isotope has a characteristic decay rate, scientists use the rate of decay as a type of clock. The decay rate of a radioactive isotope is ...
... nuclei that break down, or decay, over time, giving off radiation. Because every radioactive isotope has a characteristic decay rate, scientists use the rate of decay as a type of clock. The decay rate of a radioactive isotope is ...
The Geosphere
... the different parts of the Earth • Geosphere – consists of all the rock, soils and sediments on the Earth • Atmosphere – consists of the air that surrounds the Earth • Hydrosphere – consists of all water, fresh or ...
... the different parts of the Earth • Geosphere – consists of all the rock, soils and sediments on the Earth • Atmosphere – consists of the air that surrounds the Earth • Hydrosphere – consists of all water, fresh or ...
Important Steps in the Development of Geology…
... published a book “Theory of the Earth with Proof and Illustrations”, and this became the foundation of modern geology. Hutton proposed his theory of uniformitarianism, stating that: The earth was very old, and not formed by catastrophes alone. The earth was a great internal heat machine (hence t ...
... published a book “Theory of the Earth with Proof and Illustrations”, and this became the foundation of modern geology. Hutton proposed his theory of uniformitarianism, stating that: The earth was very old, and not formed by catastrophes alone. The earth was a great internal heat machine (hence t ...
The Geosphere
... the different parts of the Earth • Geosphere – consists of all the rock, soils and sediments on the Earth • Atmosphere – consists of the air that surrounds the Earth • Hydrosphere – consists of all water, fresh or ...
... the different parts of the Earth • Geosphere – consists of all the rock, soils and sediments on the Earth • Atmosphere – consists of the air that surrounds the Earth • Hydrosphere – consists of all water, fresh or ...
Earth`s Interior (Geosphere)
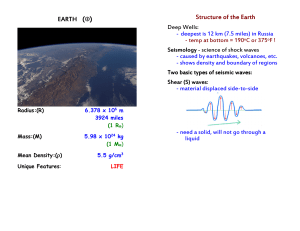
... structure of the earth? Because of how seismic waves from earthquakes travel through the earth we understand that the earth is made of different layers. ...
... structure of the earth? Because of how seismic waves from earthquakes travel through the earth we understand that the earth is made of different layers. ...
Faith and Science: The Age of the Earth from
... remnants of primitive life forms in rocks that were formed 3.6 Billion years ago. ...
... remnants of primitive life forms in rocks that were formed 3.6 Billion years ago. ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... Figure 1-3. Variation in P and S wave velocities with depth. Compositional subdivisions of the Earth are on the left, rheological subdivisions on the right. After Kearey and Vine (1990), Global Tectonics. © Blackwell Scientific. Oxford. ...
... Figure 1-3. Variation in P and S wave velocities with depth. Compositional subdivisions of the Earth are on the left, rheological subdivisions on the right. After Kearey and Vine (1990), Global Tectonics. © Blackwell Scientific. Oxford. ...
01 - Middletown Public Schools
... 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical composition. _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 5. What three elements make up most of the Earth’s crust? ______________________ ...
... 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical composition. _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 5. What three elements make up most of the Earth’s crust? ______________________ ...
File
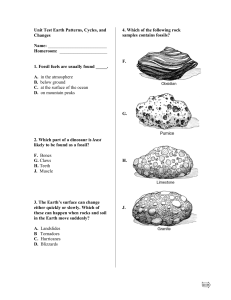
... ________________1. A great depression occupied by the ocean on the surface of the lithosphere. ________________ 2. a rigid layer of the Earth's crust that is believed to drift slowly. ________________ 3. The movement, formation, or re-formation of continents described by the theory of plate tectonic ...
... ________________1. A great depression occupied by the ocean on the surface of the lithosphere. ________________ 2. a rigid layer of the Earth's crust that is believed to drift slowly. ________________ 3. The movement, formation, or re-formation of continents described by the theory of plate tectonic ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.