The Earth
... •Sunlight not reflected by clouds reaches the Earths surface (about 50%) •The heated earth re-radiates this light in the form of infrared radiation •Infrared light is partially blocked by the Earth’s carbon dioxide (and water vapor) •So, only part of the IR light goes into space, part goes back to e ...
... •Sunlight not reflected by clouds reaches the Earths surface (about 50%) •The heated earth re-radiates this light in the form of infrared radiation •Infrared light is partially blocked by the Earth’s carbon dioxide (and water vapor) •So, only part of the IR light goes into space, part goes back to e ...
2nd_nine_weeks_exam_review_answers
... 42. What does it mean if the same sequence of rocks is observed over a large area? a large deposit of rock formed over a large area 43. In a series of undisturbed rock layers where shale lies between sandstone below and limestone above, what is the oldest rock layer? The youngest? Oldest – sandstone ...
... 42. What does it mean if the same sequence of rocks is observed over a large area? a large deposit of rock formed over a large area 43. In a series of undisturbed rock layers where shale lies between sandstone below and limestone above, what is the oldest rock layer? The youngest? Oldest – sandstone ...
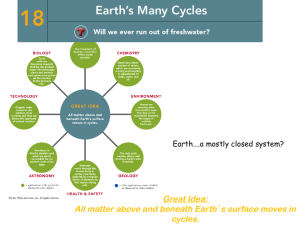
Great Idea: All matter above and beneath Earth`s surface moves in
... The biosphere is the net sum of all of the ecosystems on Earth. It is often referred to as the Earth’s life zone. In the most broad sense of the word, in biophysiology, biosphere is the global ecological system integrating all living beings and their relationships, including their interaction with ...
... The biosphere is the net sum of all of the ecosystems on Earth. It is often referred to as the Earth’s life zone. In the most broad sense of the word, in biophysiology, biosphere is the global ecological system integrating all living beings and their relationships, including their interaction with ...
Chapter 3 - Igneous Rocks
... Correlation: Using relative dating techniques to date a sequence of sedimentary strata and structures. Relative dating problem, e.g. #21 from Ch. 18 Absolute Dating with Radioactivity Radioactivity – an unstable element decays, by gaining or losing nuclear particles, and becomes another, more ...
... Correlation: Using relative dating techniques to date a sequence of sedimentary strata and structures. Relative dating problem, e.g. #21 from Ch. 18 Absolute Dating with Radioactivity Radioactivity – an unstable element decays, by gaining or losing nuclear particles, and becomes another, more ...
Hutton, Kelvin, and the great Earth debates.
... • Metals (especially Fe and Ni) sank to the center • Molten rock rose to produce a primitive crust • Chemical segregation established the three basic divisions of Earth’s interior: core, mantle, and ...
... • Metals (especially Fe and Ni) sank to the center • Molten rock rose to produce a primitive crust • Chemical segregation established the three basic divisions of Earth’s interior: core, mantle, and ...
Rock Cycle Study Guide Key
... 7. Give an example of metamorphic rock marble. How does it form? Heat and pressure causing change in composition and appearance. ...
... 7. Give an example of metamorphic rock marble. How does it form? Heat and pressure causing change in composition and appearance. ...
File
... In the 1960’s Princeton professor H.H. Hess came up with the concept of convection cells – moving mantle patterns that pushed magma up for form ocean ridges. ...
... In the 1960’s Princeton professor H.H. Hess came up with the concept of convection cells – moving mantle patterns that pushed magma up for form ocean ridges. ...
Lecture 17
... Magmas have higher concentrations of some elements that most other rocks and depending on the cooling processes affecting the magma, very high concentrations of certain elements can occur. Basic transport – diamonds are carried to the surface/near surface by exotic ultramafic volcanic rocks from a s ...
... Magmas have higher concentrations of some elements that most other rocks and depending on the cooling processes affecting the magma, very high concentrations of certain elements can occur. Basic transport – diamonds are carried to the surface/near surface by exotic ultramafic volcanic rocks from a s ...
Plate Tectonics Timeline
... portions moved thousands of miles apart over long periods of geologic time, a phenomenon he called "continental displacement" (now known as continental drift). Until the 1950s and ’60s, however, his idea was rejected by most geologists because he could not describe the driving forces behind continen ...
... portions moved thousands of miles apart over long periods of geologic time, a phenomenon he called "continental displacement" (now known as continental drift). Until the 1950s and ’60s, however, his idea was rejected by most geologists because he could not describe the driving forces behind continen ...
File
... densities of the materials that it is made of. One property of density is that it determines the way materials in a mixture are sorted. ...
... densities of the materials that it is made of. One property of density is that it determines the way materials in a mixture are sorted. ...
Foundation 1 - Discovering Astronomy
... chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) • Slowly replenishes itself as it is created from sunlight and lightning • Earth’s protective ozone layer had to form before early life could move from the oceans onto dry land ...
... chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) • Slowly replenishes itself as it is created from sunlight and lightning • Earth’s protective ozone layer had to form before early life could move from the oceans onto dry land ...
Natural Causes of Climate Change
... b) wobble (precession) → from the north pole pointing toward or away from the sun in a 23,000 year cycle. c) tilt (obliquity) → from 22° to 24.5° at a 41,000 year cycle. Eccentricity is the major forcing factor for the timing of ice ages. ...
... b) wobble (precession) → from the north pole pointing toward or away from the sun in a 23,000 year cycle. c) tilt (obliquity) → from 22° to 24.5° at a 41,000 year cycle. Eccentricity is the major forcing factor for the timing of ice ages. ...
Unit Vocab
... above the inner core Inner Core: solid center made of heavy metals; hottest layer Hydrosphere: all the water on Earth Page 1 of 2 ...
... above the inner core Inner Core: solid center made of heavy metals; hottest layer Hydrosphere: all the water on Earth Page 1 of 2 ...
The geological time scale divides Earth`s history into units from its
... Objectives • Explain the several different methods used by scientist to determine absolute age. • Describe how objects are dated by the use of selected radioactive elements. • Explain how annual tree rings and glacial varves are used to date geological events. ...
... Objectives • Explain the several different methods used by scientist to determine absolute age. • Describe how objects are dated by the use of selected radioactive elements. • Explain how annual tree rings and glacial varves are used to date geological events. ...
Dimensions of the Earth
... The Earth is composed of a series of spheres. Each sphere has a different composition of materials and is held together by gravity. The spheres of Earth are arranged from least dense (atmosphere) to most dense (geosphere) depending on how close they are found to the Earth’s center. ...
... The Earth is composed of a series of spheres. Each sphere has a different composition of materials and is held together by gravity. The spheres of Earth are arranged from least dense (atmosphere) to most dense (geosphere) depending on how close they are found to the Earth’s center. ...
Long and Short-term Changes in Climate
... Why do Interglacial and Ice Ages happen? Serbian engineer and astronomer Milutin Milankovitch theorized that the ice age cycles occur because the earth’s orbit around the sun changes in 3 main ways: ● Eccentricity: shape of orbit (more or less ...
... Why do Interglacial and Ice Ages happen? Serbian engineer and astronomer Milutin Milankovitch theorized that the ice age cycles occur because the earth’s orbit around the sun changes in 3 main ways: ● Eccentricity: shape of orbit (more or less ...
"Plate Tectonics" Extra Credit Assignment
... 2. The inner core is made mostly of ____________ and is found __________ miles to _____________miles below the surface and is about ____________ in diameter. 3. What is the Earth’s only liquid layer? ____________________________ 4. Is the crust the thickest under the ocean or under the continents? _ ...
... 2. The inner core is made mostly of ____________ and is found __________ miles to _____________miles below the surface and is about ____________ in diameter. 3. What is the Earth’s only liquid layer? ____________________________ 4. Is the crust the thickest under the ocean or under the continents? _ ...
Week 27 CCA Review
... Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation states that the gravity between 2 objects depends on the mass of the objects and the distance between them. The greater the mass, the stronger the gravitational force. The closer the distance, the stronger the gravitational force. The planets closest to the sun ...
... Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation states that the gravity between 2 objects depends on the mass of the objects and the distance between them. The greater the mass, the stronger the gravitational force. The closer the distance, the stronger the gravitational force. The planets closest to the sun ...
part – i (mcq) (compulsory)
... (b) the Theory of Evolution is proven by the succession of fossils observed in rocks (c) the fossil record of life proves that life has succeeded on Earth (d) it is unlikely that life could have succeeded on other planets (e) None of these ...
... (b) the Theory of Evolution is proven by the succession of fossils observed in rocks (c) the fossil record of life proves that life has succeeded on Earth (d) it is unlikely that life could have succeeded on other planets (e) None of these ...
Chapter 2 & Latin America
... The total amount of water always remains the same, but it is in constant motion. Water Cycle: the catalyst => The SUN ...
... The total amount of water always remains the same, but it is in constant motion. Water Cycle: the catalyst => The SUN ...
“HOW DO WE KNOW WHAT IS INSIDE THE EARTH” The deepest
... followed by S-waves, or shearing waves. P-waves travel through both solids and liquids, but are slower in liquids. Swaves travel only through solids. With this information, scientists can observe the seismic waves and infer solid and liquid layers within the Earth. Volcanic activity transports mater ...
... followed by S-waves, or shearing waves. P-waves travel through both solids and liquids, but are slower in liquids. Swaves travel only through solids. With this information, scientists can observe the seismic waves and infer solid and liquid layers within the Earth. Volcanic activity transports mater ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.