Earth Interior quest
... 3. What makes up the “Lithosphere” and the “Asthenosphere”? 4. What portion of the Earth is partially melted? 5. In fraction form write out how much each layer encompasses. Example: the crust is 70km/6250km. Now determine what percent of the whole each layer is equal to. 6. Is the “Rigid Mantle” a p ...
... 3. What makes up the “Lithosphere” and the “Asthenosphere”? 4. What portion of the Earth is partially melted? 5. In fraction form write out how much each layer encompasses. Example: the crust is 70km/6250km. Now determine what percent of the whole each layer is equal to. 6. Is the “Rigid Mantle” a p ...
sample 7 - msaldrichscience
... up with the contraction theory. Suess stated that as the earth cooled from a molten state, the more dense materials contracted and sank toward the center, and the least dense materials “floated” and cooled to form the crust. Suess claimed that certain parts of the seafloor and continents could rise ...
... up with the contraction theory. Suess stated that as the earth cooled from a molten state, the more dense materials contracted and sank toward the center, and the least dense materials “floated” and cooled to form the crust. Suess claimed that certain parts of the seafloor and continents could rise ...
File
... Convection currents in action! At left, two animal cookies represent two of the Earth's tectonic plates. At right, the two plates have moved apart, much like what happens at a divergent margin. The chocolate pudding represents the Earth's mantle. The heat source beneath the pot created convection c ...
... Convection currents in action! At left, two animal cookies represent two of the Earth's tectonic plates. At right, the two plates have moved apart, much like what happens at a divergent margin. The chocolate pudding represents the Earth's mantle. The heat source beneath the pot created convection c ...
FS Learner Outcome Q`s Logan
... form the apparent exchange of ions between ion compounds. Double Displacement 90. What kind of reaction is A + B = AB Synthesis 91. What kind of reaction is AB = A + B Decomposition 92. What kind of reaction is AB + C = AC + B Single Displacement 93. What kind of reaction is AB + CD = AD + CB Double ...
... form the apparent exchange of ions between ion compounds. Double Displacement 90. What kind of reaction is A + B = AB Synthesis 91. What kind of reaction is AB = A + B Decomposition 92. What kind of reaction is AB + C = AC + B Single Displacement 93. What kind of reaction is AB + CD = AD + CB Double ...
How are metamorphic rocks classified?
... Rocks may be flattened or bent or atoms may be exchanged to form new minerals. ...
... Rocks may be flattened or bent or atoms may be exchanged to form new minerals. ...
The Structure of the Earth
... The outer layer of Earth is called the _______________. It is made up of tectonic _____________. Just underneath the crust is the ________________ and right in the middle is the _____________. Colliding plates produce ______________ and ________________ at the plate ________________. ...
... The outer layer of Earth is called the _______________. It is made up of tectonic _____________. Just underneath the crust is the ________________ and right in the middle is the _____________. Colliding plates produce ______________ and ________________ at the plate ________________. ...
Science Framework
... float on a layer of liquid rock called the mantle. At the center of the earth is a metal core which is broken into two parts, the inner and A Look Inside the Earth ...
... float on a layer of liquid rock called the mantle. At the center of the earth is a metal core which is broken into two parts, the inner and A Look Inside the Earth ...
The Earth`s Layers and Plate Tectonics Study Guide #1 Unit 3
... states: that the continents have moved and are still moving today. ...
... states: that the continents have moved and are still moving today. ...
What are Earth`s physical layers?
... mantle made of solid rock that moves very slowly. • The asthenosphere is located below the lithosphere and is often described as “plastic like” • Tectonic plates move on top of the asthenosphere. ...
... mantle made of solid rock that moves very slowly. • The asthenosphere is located below the lithosphere and is often described as “plastic like” • Tectonic plates move on top of the asthenosphere. ...
The Layers of the Earth PPT
... * The Earth’s crust is like the skin of an apple. It is very thin compared to the other three layers. *The crust makes up 1% of the Earth. * The crust of the Earth is broken into many pieces ...
... * The Earth’s crust is like the skin of an apple. It is very thin compared to the other three layers. *The crust makes up 1% of the Earth. * The crust of the Earth is broken into many pieces ...
Earth and Space Science (Volcanoes)
... Earth and Space Science (Volcanoes) Grade 8 Science Grade 8 Science Start Date: November 18, 2013 End Date : November 29, 2013 OH_Academic_Content_Standards - Science (2011) - Grade 8 Strand ESS Earth and Space Science Topic ESS.1 This topic focuses on the physical features of Earth and how they fo ...
... Earth and Space Science (Volcanoes) Grade 8 Science Grade 8 Science Start Date: November 18, 2013 End Date : November 29, 2013 OH_Academic_Content_Standards - Science (2011) - Grade 8 Strand ESS Earth and Space Science Topic ESS.1 This topic focuses on the physical features of Earth and how they fo ...
EarthTestReview_Coelho
... crust – we can not dig as far as the mantle) 2. Hydroelectric (hydro=water) – energy generated from the force of water in rivers, dams, & ...
... crust – we can not dig as far as the mantle) 2. Hydroelectric (hydro=water) – energy generated from the force of water in rivers, dams, & ...
Science Exam Review - June - Gr7
... Where on earth would you find new rock and old rock? Explain. Why is the inner core of the Earth solid even though it is so hot? What clues are the clues that tell us that continental drift has been occurring for millions of years? Explain how energy is generated from geothermal water reservoirs. Ho ...
... Where on earth would you find new rock and old rock? Explain. Why is the inner core of the Earth solid even though it is so hot? What clues are the clues that tell us that continental drift has been occurring for millions of years? Explain how energy is generated from geothermal water reservoirs. Ho ...
UNIT C - apel slice
... Volcanoes and Earthquakes On the morning of May 18, 1980, the volcano Mount St. Helens, in the state of Washington, erupted. A volcano is a mountain that forms as lava flows through a crack onto Earth's surface. This major eruption threw ash 19 kilometers (12 miles) into the air. The lava, ash, rock ...
... Volcanoes and Earthquakes On the morning of May 18, 1980, the volcano Mount St. Helens, in the state of Washington, erupted. A volcano is a mountain that forms as lava flows through a crack onto Earth's surface. This major eruption threw ash 19 kilometers (12 miles) into the air. The lava, ash, rock ...
Earth`s Layers
... •Is the outermost layer on the earth. (EGG SHELL) •Thickness varies. Under mountains it can be as thick as 60 km and less than 5 km under the ocean. •It is the least dense of all the layers. (lightest layer) •It is made up of silicon and oxygen. ...
... •Is the outermost layer on the earth. (EGG SHELL) •Thickness varies. Under mountains it can be as thick as 60 km and less than 5 km under the ocean. •It is the least dense of all the layers. (lightest layer) •It is made up of silicon and oxygen. ...
the proof-----seafloor spreading
... chains underwater) and destroyed at deepsea trenches. •This is proof that the plates are moving along on a “conveyor belt” so Wegner’s idea on continent drift was correct. ...
... chains underwater) and destroyed at deepsea trenches. •This is proof that the plates are moving along on a “conveyor belt” so Wegner’s idea on continent drift was correct. ...
Our AMAZING Planet
... •These circulations are called CONVECTION CURRENTS •Continents are in the CRUST so the movement below them makes the continents move too •This is called CONTINENTAL DRIFT. ...
... •These circulations are called CONVECTION CURRENTS •Continents are in the CRUST so the movement below them makes the continents move too •This is called CONTINENTAL DRIFT. ...
9.2 – Sea Floor Spreading
... poles moveup to 50 miles (80 km) per day. (average of 25 miles per year) •In the last 150 years, the pole has wandered a total of about 685 miles •The last time the poles switched was 780,000 years ago, and it's happened about 400 times in 330 million years ...
... poles moveup to 50 miles (80 km) per day. (average of 25 miles per year) •In the last 150 years, the pole has wandered a total of about 685 miles •The last time the poles switched was 780,000 years ago, and it's happened about 400 times in 330 million years ...
File - Brighten Academy Middle School
... The theory that states that the continents move over time as a result of sea floor spreading and subduction of plates. ...
... The theory that states that the continents move over time as a result of sea floor spreading and subduction of plates. ...
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAPER Earth`s Layers Key Concepts
... A. the inner core B. the outer core C. the crust D. the mantle 2. Earth has five layers based on physical properties: the inner core, the outer core, the mesosphere, the asthenosphere, and the lithosphere. Which of these layers do the tectonic plates move on top of? A. outer core B. lithosphere C. m ...
... A. the inner core B. the outer core C. the crust D. the mantle 2. Earth has five layers based on physical properties: the inner core, the outer core, the mesosphere, the asthenosphere, and the lithosphere. Which of these layers do the tectonic plates move on top of? A. outer core B. lithosphere C. m ...
1. What is rock? 2. The layer of solid rock that surrounds Earth`s
... 18. Other types of rock are changed to metamorphic rock by ??? and ???? beneath Earth’s surface. 19. As metamorphic rock forms, chemical changes may change the ???? in the rock. 20. Is the following sentence true or false? Only sedimentary rock can become metamorphic rock. 21. The metamorphic rock g ...
... 18. Other types of rock are changed to metamorphic rock by ??? and ???? beneath Earth’s surface. 19. As metamorphic rock forms, chemical changes may change the ???? in the rock. 20. Is the following sentence true or false? Only sedimentary rock can become metamorphic rock. 21. The metamorphic rock g ...
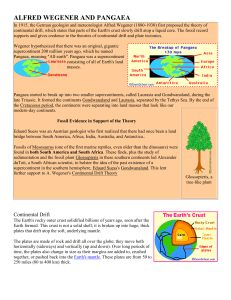
ALFRED WEGENER AND PANGAEA In 1915, the German geologist
... Earth formed. This crust is not a solid shell; it is broken up into huge, thick plates that drift atop the soft, underlying mantle. The plates are made of rock and drift all over the globe; they move both horizontally (sideways) and vertically (up and down). Over long periods of time, the plates als ...
... Earth formed. This crust is not a solid shell; it is broken up into huge, thick plates that drift atop the soft, underlying mantle. The plates are made of rock and drift all over the globe; they move both horizontally (sideways) and vertically (up and down). Over long periods of time, the plates als ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.