To demonstrate how Young Fold Mountains are
... To demonstrate how Young Fold Mountains are formed: Fig. 1: You will need – atta dough, a tennis or cricket ball, cloth of two different colors (folded thickly, as shown). The atta dough represents the molten magma, the colored cloth pieces represent the ‘crust’ of the earth consisting of the ‘SIAL’ ...
... To demonstrate how Young Fold Mountains are formed: Fig. 1: You will need – atta dough, a tennis or cricket ball, cloth of two different colors (folded thickly, as shown). The atta dough represents the molten magma, the colored cloth pieces represent the ‘crust’ of the earth consisting of the ‘SIAL’ ...
what`s inside the earth?
... makes the point: "Oil, water, lava: these are just a few of the things that come from deep within the earth." Next, we see students examining a large globe. As useful as globes are, they are unable to tell us what's inside our planet. Since nobody has ever been to the center of the earth, how do we ...
... makes the point: "Oil, water, lava: these are just a few of the things that come from deep within the earth." Next, we see students examining a large globe. As useful as globes are, they are unable to tell us what's inside our planet. Since nobody has ever been to the center of the earth, how do we ...
Convergent Boundaries
... of how the earth’s surface is formed e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. Review: 1. List the geologic event(s) that can occur at each plate boundary. (What happens or is formed here?) • ____ & ____ @ Divergent Boundaries • _ ...
... of how the earth’s surface is formed e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. Review: 1. List the geologic event(s) that can occur at each plate boundary. (What happens or is formed here?) • ____ & ____ @ Divergent Boundaries • _ ...
Micropaleontology in Petroleum Exploration
... bottom of the hole. However, in studies of rock units exposed at the surface of the Earth and in some cases from well bores, these FADs are extremely useful biostratigraphic events. Lastly from (fig.2), one can recognize that the range of the three fossils overlap for only a relatively short period ...
... bottom of the hole. However, in studies of rock units exposed at the surface of the Earth and in some cases from well bores, these FADs are extremely useful biostratigraphic events. Lastly from (fig.2), one can recognize that the range of the three fossils overlap for only a relatively short period ...
Plate tectonics - Geological Society of India
... Most earthquakes occur along the edge of lithospheric plates. The earth's outer layer is made up of several brittle or rigid pieces or blocks, called the lithospheric plates. These plates may largely be made up of oceanic or continental crust or a combination of both. These plates comprise the entir ...
... Most earthquakes occur along the edge of lithospheric plates. The earth's outer layer is made up of several brittle or rigid pieces or blocks, called the lithospheric plates. These plates may largely be made up of oceanic or continental crust or a combination of both. These plates comprise the entir ...
Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... How do volcanoes form? Rising magma eventually can lead to an eruption, where magma, solids, and gas are spewed out to form cone-shaped mountains called volcanoes. Lava is when magma flows onto Earth’s surface through a vent, or opening. Lava and other volcanic materials can be expelled through a v ...
... How do volcanoes form? Rising magma eventually can lead to an eruption, where magma, solids, and gas are spewed out to form cone-shaped mountains called volcanoes. Lava is when magma flows onto Earth’s surface through a vent, or opening. Lava and other volcanic materials can be expelled through a v ...
Section 3 Deforming Earth`s Crust
... Compare how the three types of faults form. Recognizing Faults Some faults are only a few meters long. Other faults are several hundred kilometers long. So, how can you recognize a fault when you see one? Movement along faults causes rock layers to become offset. Therefore, layers of different kinds ...
... Compare how the three types of faults form. Recognizing Faults Some faults are only a few meters long. Other faults are several hundred kilometers long. So, how can you recognize a fault when you see one? Movement along faults causes rock layers to become offset. Therefore, layers of different kinds ...
Geology 13/14 (RTF 44kB)
... GL3301 Sedimentary Petrology: from sediment to rock TBA 5 credits This module deals with how sediment is produced at the Earth’s surface and then becomes rock and how the information preserved in these sedimentary rocks can be related to the physical, chemical and biological processes that occurred ...
... GL3301 Sedimentary Petrology: from sediment to rock TBA 5 credits This module deals with how sediment is produced at the Earth’s surface and then becomes rock and how the information preserved in these sedimentary rocks can be related to the physical, chemical and biological processes that occurred ...
science - Alpine School District
... Fossils are evidence of living organisms from the past and are usually preserved in sedimentary rocks. A fossil may be an impression left in sediments, the preserved remains of an organism, or a trace mark showing that an organism once existed. Fossils are usually made from the hard parts of an orga ...
... Fossils are evidence of living organisms from the past and are usually preserved in sedimentary rocks. A fossil may be an impression left in sediments, the preserved remains of an organism, or a trace mark showing that an organism once existed. Fossils are usually made from the hard parts of an orga ...
Click here for the "Slip... Slide... Collide
... Background: Learn about how each type of plate shifts and which features form at boundaries 1. _________________ plate boundaries occur where plates are drawing apart from each other. 2. _________________ plate boundaries occur when adjacent plates move towards each other. 3. In some places, plates ...
... Background: Learn about how each type of plate shifts and which features form at boundaries 1. _________________ plate boundaries occur where plates are drawing apart from each other. 2. _________________ plate boundaries occur when adjacent plates move towards each other. 3. In some places, plates ...
Meaning and Effects 2014-2015 Mechanical or Physical Weathering
... Q.2. (a).Define:i. Weathering- Weathering is the process that consists of disintegration and decomposition of rocks on the surface of the Earth due to atmospheric conditions. ii.Erosion:- Erosion is wearing and carrying away of eroded materials on the surface of the Earth by the agents like running ...
... Q.2. (a).Define:i. Weathering- Weathering is the process that consists of disintegration and decomposition of rocks on the surface of the Earth due to atmospheric conditions. ii.Erosion:- Erosion is wearing and carrying away of eroded materials on the surface of the Earth by the agents like running ...
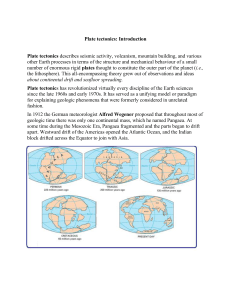
What evidence did Alfred Wagner use to support his theory of
... How old are the rocks off the east coast of North America relative to the rocks right along the mid Atlantic ridge, why do you think this is the case? The age of rocks increases as they move away from the ridge. The youngest rocks are closest to the ridge. ...
... How old are the rocks off the east coast of North America relative to the rocks right along the mid Atlantic ridge, why do you think this is the case? The age of rocks increases as they move away from the ridge. The youngest rocks are closest to the ridge. ...
Earthquakes
... SUBDUCTION ZONE - An elongated region of the Earth's crust where one tectonic plate moves below another resulting in volcanoes and earthquakes. REVERSE FAULT - A type of fault along which the plane of movement slants toward the uplifted side. TRANSFORM FAULT BOUNDARY - A boundary between tectonic pl ...
... SUBDUCTION ZONE - An elongated region of the Earth's crust where one tectonic plate moves below another resulting in volcanoes and earthquakes. REVERSE FAULT - A type of fault along which the plane of movement slants toward the uplifted side. TRANSFORM FAULT BOUNDARY - A boundary between tectonic pl ...
10.2 Dir. Reading Plate Tectonics
... Section: The Theory of Plate Tectonics 1. The theory that explains why and how continents move is called _________________________________________________________________. 2. By what time period was there evidence supporting continental drift, which led to the development of plate tectonics? _______ ...
... Section: The Theory of Plate Tectonics 1. The theory that explains why and how continents move is called _________________________________________________________________. 2. By what time period was there evidence supporting continental drift, which led to the development of plate tectonics? _______ ...
Volcanic Activity
... inside of the planet makes its way through to the planet's surface. One way is "material spewing from the top of a mountain", but there are other forms as well. The first question this raises is: what exactly is this "material from the inside"? On our planet, it's magma, fluid molten rock. This mate ...
... inside of the planet makes its way through to the planet's surface. One way is "material spewing from the top of a mountain", but there are other forms as well. The first question this raises is: what exactly is this "material from the inside"? On our planet, it's magma, fluid molten rock. This mate ...
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Part 1 Multiple Choice
... 24. Which of the following was the biggest problem with Wegener's Theory of Continental Drift? a. He could not explain the mechanism for movement of the continents b. Too many scientists already came up with the same theory c. All of his evidence turned out to be fake 25. Which two mountain ranges a ...
... 24. Which of the following was the biggest problem with Wegener's Theory of Continental Drift? a. He could not explain the mechanism for movement of the continents b. Too many scientists already came up with the same theory c. All of his evidence turned out to be fake 25. Which two mountain ranges a ...
Sample - Chapter 02 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... suggesting that the Earth was already a large, coherent mass at that time. Approaching this question another way, The Earth must be older than the 4.37-billion-year-old zircon grains collected from sandstone in Australia. In sum, our planet has existed for about 4.5 billion years. The recognition of ...
... suggesting that the Earth was already a large, coherent mass at that time. Approaching this question another way, The Earth must be older than the 4.37-billion-year-old zircon grains collected from sandstone in Australia. In sum, our planet has existed for about 4.5 billion years. The recognition of ...
An Introduction to the Seafloor and Plate Tectonics
... on land (840 meters), yet it is only a tiny fraction of the total Earth’s volume on a planetary scale (0.13% of the Earth’s volume). Although the rest of the Earth is composed of rock, it is not homogeneous. Instead, it consists of distinctive layer at different depths, each characterized by specifi ...
... on land (840 meters), yet it is only a tiny fraction of the total Earth’s volume on a planetary scale (0.13% of the Earth’s volume). Although the rest of the Earth is composed of rock, it is not homogeneous. Instead, it consists of distinctive layer at different depths, each characterized by specifi ...
Earth Science SOL Expanded Test Blueprint Summary Table Blue
... Earth and life can be inferred by studying rocks and fossils. Key concepts include a) traces and remains of ancient, often extinct, life are preserved by various means in many sedimentary rocks; b) superposition, cross-cutting relationships, index fossils, and radioactive decay are methods of dating ...
... Earth and life can be inferred by studying rocks and fossils. Key concepts include a) traces and remains of ancient, often extinct, life are preserved by various means in many sedimentary rocks; b) superposition, cross-cutting relationships, index fossils, and radioactive decay are methods of dating ...
Spring Study Guide
... 1. Explain the difference between revolution & rotation and how it relates to the Earth, Moon and Sun. 2. What causes the cycles of the seasons? a. What does the Earth’s tilt influence? b. Explain when the Northern Hemisphere would have summer/winter c. Explain when the Southern Hemisphere would hav ...
... 1. Explain the difference between revolution & rotation and how it relates to the Earth, Moon and Sun. 2. What causes the cycles of the seasons? a. What does the Earth’s tilt influence? b. Explain when the Northern Hemisphere would have summer/winter c. Explain when the Southern Hemisphere would hav ...
Ocean - abyss of time planet earth
... to be associated with much higher numbers of foreshocks but lower numbers of aftershocks in comparison to continental counterparts. Moreover, changes in ocean tides appear to have triggered seismicity in the vicinity of submarine volcanoes. New knowledge obtained from studying the way the rocky shel ...
... to be associated with much higher numbers of foreshocks but lower numbers of aftershocks in comparison to continental counterparts. Moreover, changes in ocean tides appear to have triggered seismicity in the vicinity of submarine volcanoes. New knowledge obtained from studying the way the rocky shel ...
Age of the Earth

The age of the Earth is 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years (4.54 × 109 years ± 1%). This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples.Following the development of radiometric age dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Comparing the mass and luminosity of the Sun to those of other stars, it appears that the Solar System cannot be much older than those rocks. Calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions – the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System – are 4.567 billion years old, giving an age for the solar system and an upper limit for the age of Earth.It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon after the formation of the calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions and the meteorites. Because the exact amount of time this accretion process took is not yet known, and the predictions from different accretion models range from a few millions up to about 100 million years, the exact age of Earth is difficult to determine. It is also difficult to determine the exact age of the oldest rocks on Earth, exposed at the surface, as they are aggregates of minerals of possibly different ages.