As Powerpoint Slide
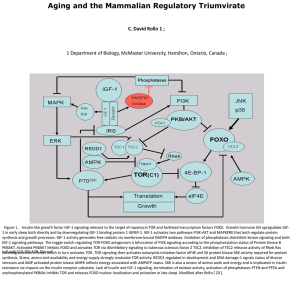
... 1 Department of Biology, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada ; ...
... 1 Department of Biology, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada ; ...
TDS - BD Biosciences
... β-Arrestins were discovered due to their ability to modulate interactions between the phosphorylated β2-Adrenergic receptors and G proteins. This modulation results in diminished β2-Adrenergic receptor function, also known as desensitization. Because arrestins are found at the synaptic terminals, th ...
... β-Arrestins were discovered due to their ability to modulate interactions between the phosphorylated β2-Adrenergic receptors and G proteins. This modulation results in diminished β2-Adrenergic receptor function, also known as desensitization. Because arrestins are found at the synaptic terminals, th ...
Protein kinases
... • Many signal molecules trigger formation of cAMP • Other components of cAMP pathways are G proteins, G protein-coupled receptors, and protein kinases • cAMP usually activates protein kinase A, which phosphorylates various other proteins • Further regulation of cell metabolism is provided by G-prot ...
... • Many signal molecules trigger formation of cAMP • Other components of cAMP pathways are G proteins, G protein-coupled receptors, and protein kinases • cAMP usually activates protein kinase A, which phosphorylates various other proteins • Further regulation of cell metabolism is provided by G-prot ...
Publication JournalArticle (Originalarbeit in einer wissenschaftlichen
... Steroid/*genetics/metabolism; Thyroid Hormone/*genetics/metabolism; Tissue Distribution; Trans-Activation (Genetics) Orphan nuclear receptors belong to the nuclear receptor superfamily of liganded transcription factors, whose ligands either do not exist or remain to be identified. We report here the ...
... Steroid/*genetics/metabolism; Thyroid Hormone/*genetics/metabolism; Tissue Distribution; Trans-Activation (Genetics) Orphan nuclear receptors belong to the nuclear receptor superfamily of liganded transcription factors, whose ligands either do not exist or remain to be identified. We report here the ...
last year`s final exam
... 18) What microtubule motor helps move secretory vesicles toward the cell membrane? 19) What happens in the E site of ribosomes? 20) Where does phosphatidylserine get synthesized? 21) What happens if phosphatidylserine is on the outside of a cell? 22) What is meant by, “The ribosome is a ribozyme”? 2 ...
... 18) What microtubule motor helps move secretory vesicles toward the cell membrane? 19) What happens in the E site of ribosomes? 20) Where does phosphatidylserine get synthesized? 21) What happens if phosphatidylserine is on the outside of a cell? 22) What is meant by, “The ribosome is a ribozyme”? 2 ...
Catecholamines (dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine)
... anti-psychotic (D2 antagonist), addictive drugs (DA transporter) ...
... anti-psychotic (D2 antagonist), addictive drugs (DA transporter) ...
Cell Signaling
... located on the cytoplasm side. How GDP becomes GTP. • The activated G-protein activates a membrane-bound enzyme which ...
... located on the cytoplasm side. How GDP becomes GTP. • The activated G-protein activates a membrane-bound enzyme which ...
Ligand Binding - Stroud
... • teasing out source of unexpected kinetics and how to work around _____________________________________________________________________________ P11) Neal SE, Eccleston JF, Hall A, Webb MR. Kinetic Analysis of the hydrolysis of GTP by p21N-ras. J. Biol. Chem. 1988;263:19718-22. • Ras GTPase activity ...
... • teasing out source of unexpected kinetics and how to work around _____________________________________________________________________________ P11) Neal SE, Eccleston JF, Hall A, Webb MR. Kinetic Analysis of the hydrolysis of GTP by p21N-ras. J. Biol. Chem. 1988;263:19718-22. • Ras GTPase activity ...
Self Test Quiz-1 Given below are some questions related to protein
... Self Test Quiz-1 Given below are some questions related to protein and enzymes in general. Each statement is followed by 4 choices. Choose a single correct answer for each question. 1. How many different types of amino acid are used to make proteins? a. 4 b. 20 c. 23 d. 38 2. Amino acids contain car ...
... Self Test Quiz-1 Given below are some questions related to protein and enzymes in general. Each statement is followed by 4 choices. Choose a single correct answer for each question. 1. How many different types of amino acid are used to make proteins? a. 4 b. 20 c. 23 d. 38 2. Amino acids contain car ...
Neuro Objectives 17
... intrinsic GTPases and the G-proteins bind back to their receptors. cAMP formation: when G-proteins bind adenylate cyclase, it forms cAMP from ATP which activates enzymes including PKA. cAMP is terminated by phosphodiesterase. o Positive coupling: noradrenergic beta-adrenergic receptor, dopamine D1 ...
... intrinsic GTPases and the G-proteins bind back to their receptors. cAMP formation: when G-proteins bind adenylate cyclase, it forms cAMP from ATP which activates enzymes including PKA. cAMP is terminated by phosphodiesterase. o Positive coupling: noradrenergic beta-adrenergic receptor, dopamine D1 ...
Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS)
... specify the direction for destination for initial transfer to the ER: with a signal sequence at N-terminus; consisting of 5-10 hydrophobic aa Go forward Golgi: most proteins Return to ER (ER residents): with a specific sequence of 4 aa at C-terminus Go to mitochondria: positively charged amino ...
... specify the direction for destination for initial transfer to the ER: with a signal sequence at N-terminus; consisting of 5-10 hydrophobic aa Go forward Golgi: most proteins Return to ER (ER residents): with a specific sequence of 4 aa at C-terminus Go to mitochondria: positively charged amino ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Each question in this section is
... Each question in this section is worth 3 points. For full credit, choose only one of the possible answers. Alternatively, you may choose two answers and if one of them is correct you will receive 1.5 points for that question. 1) Indicate what would happen to the Ras pathway if you expressed an alter ...
... Each question in this section is worth 3 points. For full credit, choose only one of the possible answers. Alternatively, you may choose two answers and if one of them is correct you will receive 1.5 points for that question. 1) Indicate what would happen to the Ras pathway if you expressed an alter ...
2. Intro to Proteins
... • Have similarities in amino acid sequence and 3-D structure • Have similar functions such as breakdown proteins but do it differently ...
... • Have similarities in amino acid sequence and 3-D structure • Have similar functions such as breakdown proteins but do it differently ...
Signal Receptors 4 types
... • Don’t get bogged down in all details in this chapter. Use the KISS principle. • Know - 3 stages of cell signaling. • Know - At least one example of a receptor and how it works (in detail). ...
... • Don’t get bogged down in all details in this chapter. Use the KISS principle. • Know - 3 stages of cell signaling. • Know - At least one example of a receptor and how it works (in detail). ...
Review For Final I - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... • multiply each exam score by 0.4 • add the three numbers together • subtract this sum from the average you want to get • divide the difference by 40 for the percent score you need ...
... • multiply each exam score by 0.4 • add the three numbers together • subtract this sum from the average you want to get • divide the difference by 40 for the percent score you need ...
doc IntracellularTraffic (3
... Arf). Importin-β interacts with nuclear pore (through FG-Nucleoporins) to mediate import. Mechanism is as: 1. Importin-α/β heterodimer recognizes an NLS in the cytosol and complexes as cargo- α- β 2. The complex transiently contacts pore during import, which allows the complex to proceed into the nu ...
... Arf). Importin-β interacts with nuclear pore (through FG-Nucleoporins) to mediate import. Mechanism is as: 1. Importin-α/β heterodimer recognizes an NLS in the cytosol and complexes as cargo- α- β 2. The complex transiently contacts pore during import, which allows the complex to proceed into the nu ...
Chapter 8 Questions
... 8. Explain why the presence of dissolved particles on one side of a membrane results in diffusion of water across the membrane. 9. List two ways that a cell can move a substance against its concentration gradient. 10. Based on what you have learned about homeostasis and osmosis, why should humans av ...
... 8. Explain why the presence of dissolved particles on one side of a membrane results in diffusion of water across the membrane. 9. List two ways that a cell can move a substance against its concentration gradient. 10. Based on what you have learned about homeostasis and osmosis, why should humans av ...
CELL SIGNALING How do cells receive and respond to signals from
... (PEPTIDE HORMONES AND GROWTH FACTORS) ...
... (PEPTIDE HORMONES AND GROWTH FACTORS) ...
Proteins File
... Muscle proteins (able to contract, use energy to do work). Transport proteins. Cell membrane proteins. ...
... Muscle proteins (able to contract, use energy to do work). Transport proteins. Cell membrane proteins. ...
Winning the war against disease: an industry perspective (PPT 2.4
... Claude Benchimol SVP, R&D UCSD Workshop December 9, 2005 ...
... Claude Benchimol SVP, R&D UCSD Workshop December 9, 2005 ...
Lecture # 15: The Endocrine System 2
... and thyroid glands. Epinephrine, norepinephrine, melatonin, and thyroid hormone are mono-amines. Aminoacid ...
... and thyroid glands. Epinephrine, norepinephrine, melatonin, and thyroid hormone are mono-amines. Aminoacid ...
Slide
... From: Effect of Connective Tissue Growth Factor on Protein Kinase Expression and Activity in Human Corneal Fibroblasts Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci.. 2012;53(13):8076-8085. doi:10.1167/iovs.12-10790 ...
... From: Effect of Connective Tissue Growth Factor on Protein Kinase Expression and Activity in Human Corneal Fibroblasts Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci.. 2012;53(13):8076-8085. doi:10.1167/iovs.12-10790 ...
Leukaemia Section t(4;12)(p16;p13) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... lympthoma with a t(4;12)(p16;p13) chromosomal translocation. ...
... lympthoma with a t(4;12)(p16;p13) chromosomal translocation. ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).























