Protein Determination - International Dairy Federation
... such as size, electrical charge or hydrophobic/hydrophilic properties and then measuring the relative amounts of each. There are several different types of chromatography methods available such as size-exclusion chromatography, ion-exchange chromatography, reverse phase chromatography and size exclu ...
... such as size, electrical charge or hydrophobic/hydrophilic properties and then measuring the relative amounts of each. There are several different types of chromatography methods available such as size-exclusion chromatography, ion-exchange chromatography, reverse phase chromatography and size exclu ...
protein - The Robinson Group – University of Nottingham
... Handouts: http://robinson.chem.nottingham.ac.uk/teaching/F14PFB ...
... Handouts: http://robinson.chem.nottingham.ac.uk/teaching/F14PFB ...
act
... for mutants with ommatidia that lack R7 cells identified three genes: sevenless (sev), bride of sevenless (Boss) and seven-in-abstentia (sina). Adult flies homozygous for mutations in any of these genes have ommatidia that lack an R7 cell and contain an additional cone cell. In the absence of R7 dif ...
... for mutants with ommatidia that lack R7 cells identified three genes: sevenless (sev), bride of sevenless (Boss) and seven-in-abstentia (sina). Adult flies homozygous for mutations in any of these genes have ommatidia that lack an R7 cell and contain an additional cone cell. In the absence of R7 dif ...
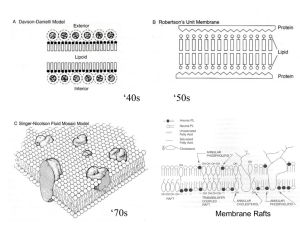
Section 3.3 The Cell Membrane
... First, the cell membrane is flexible, not rigid. As a result, the phospholipids in each layer can move from side to side and slide past each other. This makes the membrane behave like a fluid, similar to a film of oil on the surface of water. One problem……proteins embedded in the membrane do not fli ...
... First, the cell membrane is flexible, not rigid. As a result, the phospholipids in each layer can move from side to side and slide past each other. This makes the membrane behave like a fluid, similar to a film of oil on the surface of water. One problem……proteins embedded in the membrane do not fli ...
The Basics: A general review of molecular biology: DNA
... basic, 2 cysteine, 1 methione and 2 poly side chains. 2. Mix and place aa along the toober. The aa order is the primary structure of the protein (Note: No two groups will get the same order). 3. Have the students fold the toobers using the ...
... basic, 2 cysteine, 1 methione and 2 poly side chains. 2. Mix and place aa along the toober. The aa order is the primary structure of the protein (Note: No two groups will get the same order). 3. Have the students fold the toobers using the ...
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) ISSN: 2278-3008.
... agents are used in clinical practice. Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) is a pathogenic bacterial species in the genus Mycobacterium and the causative agent of most cases of tuberculosis [1]. Tuberculosis (TB), a lung infection and is one of the contagious and deadly diseases which have added to the ...
... agents are used in clinical practice. Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) is a pathogenic bacterial species in the genus Mycobacterium and the causative agent of most cases of tuberculosis [1]. Tuberculosis (TB), a lung infection and is one of the contagious and deadly diseases which have added to the ...
Receptor Cell Biology: Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
... The fundamental processes responsible for growth and development in man are exceedingly complex. The availability of cell nutrients as well as growth factors and hormones is essential for normal tissue differentiation. One of the major mechanisms responsible for delivery of these nutrient molecules/ ...
... The fundamental processes responsible for growth and development in man are exceedingly complex. The availability of cell nutrients as well as growth factors and hormones is essential for normal tissue differentiation. One of the major mechanisms responsible for delivery of these nutrient molecules/ ...
Biochemistry Ch 37 696-706 [4-20
... Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway – ubiquitin is a small and highly conserved protein; it targets intracellular proteins for degradation by covalently binding to E-amino group of lysine residues accomplished by a 3 enzyme system -target is often polyubiquitinylated, forming long ubiquitin tails -a protea ...
... Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway – ubiquitin is a small and highly conserved protein; it targets intracellular proteins for degradation by covalently binding to E-amino group of lysine residues accomplished by a 3 enzyme system -target is often polyubiquitinylated, forming long ubiquitin tails -a protea ...
Module 1: Review of General and Organic Chemistry
... glucose + ATP glucose-6-phosphate + ADP A form of hexokinase called hexokinase D has a KM for glucose of 0.1 mM; the form called glucokinase has a KM for glucose of 10 mM. Normal blood glucose level is 4-5 mM. e. Will either isozyme work near its maximal rate under normal blood glucose levels? If ...
... glucose + ATP glucose-6-phosphate + ADP A form of hexokinase called hexokinase D has a KM for glucose of 0.1 mM; the form called glucokinase has a KM for glucose of 10 mM. Normal blood glucose level is 4-5 mM. e. Will either isozyme work near its maximal rate under normal blood glucose levels? If ...
ppt
... Protein and peptide hormones • CNS mediators: neuropeptides, opioids • Hypothalamic releasing hormones and pituitary peptides • Insulin and glucagone • Growth factors: IGF, CSF, EPO • Intestinal hormones …and many others ...
... Protein and peptide hormones • CNS mediators: neuropeptides, opioids • Hypothalamic releasing hormones and pituitary peptides • Insulin and glucagone • Growth factors: IGF, CSF, EPO • Intestinal hormones …and many others ...
Prediction of protein disorder: basic concepts and practical hints
... Contains 3 receptor binding motifs: xLxxLLx (LIG_NRBOX) ...
... Contains 3 receptor binding motifs: xLxxLLx (LIG_NRBOX) ...
Clinical Neurochemistry and Neuroimaging
... agonist and causes a decrease in sympathetic tone. It is useful in the treatment of hypertension and opiate withdrawal Yohimbine is primarily an alpha2 presynaptic antagonist and causes an increase in sympathetic tone which may lead to increased arousal, panic anxiety and sexual potency. The beta ...
... agonist and causes a decrease in sympathetic tone. It is useful in the treatment of hypertension and opiate withdrawal Yohimbine is primarily an alpha2 presynaptic antagonist and causes an increase in sympathetic tone which may lead to increased arousal, panic anxiety and sexual potency. The beta ...
File S4 (DOC) - cloudfront.net
... after 50 ns simulation. A. RMSD difference. B. RMSF values of each residue. C. Hierarchy position of each residue. All the results of simulating estrogen receptor bound to DNA generated data which were remarkably different from the results obtained for the dimer unbound to DNA. However, as stated in ...
... after 50 ns simulation. A. RMSD difference. B. RMSF values of each residue. C. Hierarchy position of each residue. All the results of simulating estrogen receptor bound to DNA generated data which were remarkably different from the results obtained for the dimer unbound to DNA. However, as stated in ...
Rapid Screening of Antibodies against Membrane Proteins using a
... fluorescent or radioactive labels. However, biosensors have not been widely used for antibody screening against membrane protein targets, such as GPCRs and ion channels, because of the inherent difficulties of manipulating membrane proteins within microfluidic devices. Integral Molecular‘s Lipoparti ...
... fluorescent or radioactive labels. However, biosensors have not been widely used for antibody screening against membrane protein targets, such as GPCRs and ion channels, because of the inherent difficulties of manipulating membrane proteins within microfluidic devices. Integral Molecular‘s Lipoparti ...
1. Given the molecule: a. What type of molecule is this? b. Give the
... shown to the right. Would you expect the pKa of pyruvate’s carboxyl group to differ from that of the molecule above? If yes, which pKa would be lower and why? If no, why wouldn’t they differ? (Explain in 40 words or fewer.) ...
... shown to the right. Would you expect the pKa of pyruvate’s carboxyl group to differ from that of the molecule above? If yes, which pKa would be lower and why? If no, why wouldn’t they differ? (Explain in 40 words or fewer.) ...
Biomolecules and Nanotechnology
... Figure 1. Biomolecular machines are comparable in size and complexity to the engineeringinspired nanomachines currently being proposed, but the forms and characteristics of the two are entirely different. Opposite are two solutions to atom-level synthesis. Model nanomanipulators (top right) build th ...
... Figure 1. Biomolecular machines are comparable in size and complexity to the engineeringinspired nanomachines currently being proposed, but the forms and characteristics of the two are entirely different. Opposite are two solutions to atom-level synthesis. Model nanomanipulators (top right) build th ...
Unknown function, JCSG
... As part of its mission to increase structural coverage of protein families, JCSG is targeting proteins from the large CATH homologous superfamily 3.40.630.10 of zinc peptidases, which belong to the phosphorylase/hydrolase-like fold in SCOP and are comprised of proteins from several Pfam families (th ...
... As part of its mission to increase structural coverage of protein families, JCSG is targeting proteins from the large CATH homologous superfamily 3.40.630.10 of zinc peptidases, which belong to the phosphorylase/hydrolase-like fold in SCOP and are comprised of proteins from several Pfam families (th ...
Document
... http://bioportal.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/index.htm http://cbm.msoe.edu/teachRes/index.html ...
... http://bioportal.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/index.htm http://cbm.msoe.edu/teachRes/index.html ...
Protein Folding - USD Home Pages
... hydrophobic parts hate the water, and instead they’d like to find another hydrophobic place to be. The exposed hydrophobic parts of a protein join together with exposed hydrophobic parts of other proteins, ...
... hydrophobic parts hate the water, and instead they’d like to find another hydrophobic place to be. The exposed hydrophobic parts of a protein join together with exposed hydrophobic parts of other proteins, ...
gelbank
... Proteome Analysis requires the isolation of the complete proteome, separation of complex protein mixtures into discrete protein components measurement of relative abundance and identification of each protein Component. The most widely used separation method is: 2-dimensional gel electrophoresis ...
... Proteome Analysis requires the isolation of the complete proteome, separation of complex protein mixtures into discrete protein components measurement of relative abundance and identification of each protein Component. The most widely used separation method is: 2-dimensional gel electrophoresis ...
BICH 303 Exam #1 Fall 2005 1. Amphiphilic or amphipathic
... E. favors the binding of Bohr protons. 25. The trigger for the conformational change in quaternary structure of hemoglobin is: A. oxygen binding to the distal histidine B. oxygen binding to the Fe(II) C. oxygen binding to the proximal histidine D. the loss of Bohr protons E. the loss of 2,3- bispho ...
... E. favors the binding of Bohr protons. 25. The trigger for the conformational change in quaternary structure of hemoglobin is: A. oxygen binding to the distal histidine B. oxygen binding to the Fe(II) C. oxygen binding to the proximal histidine D. the loss of Bohr protons E. the loss of 2,3- bispho ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).