ChanTest: Ion Channel Cell lines validated on
... information, all are conducted on non-human mammalian preparations (e.g. rabbit, dog, or guinea pig). ChanTest now offers a human cardiomyocyte assay that detects drug effects on cardiac action potential parameters. Drug effects are assessed in ventricular-type cardiomyocytes derived from human embr ...
... information, all are conducted on non-human mammalian preparations (e.g. rabbit, dog, or guinea pig). ChanTest now offers a human cardiomyocyte assay that detects drug effects on cardiac action potential parameters. Drug effects are assessed in ventricular-type cardiomyocytes derived from human embr ...
III Sensory - Washington State University
... This is another very ancient sensory system, with roots in the earliest animals… • Turning a mechanical stimulus into an electrical signal is something that is happening when a Paramecium moves through the debris of pond water, bumping into this and that, backing up and taking another direction. • ...
... This is another very ancient sensory system, with roots in the earliest animals… • Turning a mechanical stimulus into an electrical signal is something that is happening when a Paramecium moves through the debris of pond water, bumping into this and that, backing up and taking another direction. • ...
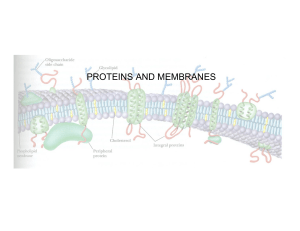
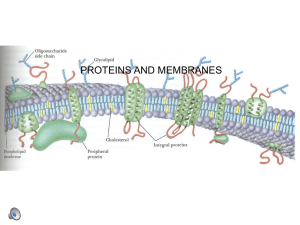
PROTEINS AND MEMBRANES
... applied heat stimuli to 186 healthy women, they found that those with the rare version were more likely to have lower pain thresholds. It was as if the normal subjects had taken an ibuprofen, but the subjects with the rare SNP hadn't. ...
... applied heat stimuli to 186 healthy women, they found that those with the rare version were more likely to have lower pain thresholds. It was as if the normal subjects had taken an ibuprofen, but the subjects with the rare SNP hadn't. ...
Summary
... applied heat stimuli to 186 healthy women, they found that those with the rare version were more likely to have lower pain thresholds. It was as if the normal subjects had taken an ibuprofen, but the subjects with the rare SNP hadn't. ...
... applied heat stimuli to 186 healthy women, they found that those with the rare version were more likely to have lower pain thresholds. It was as if the normal subjects had taken an ibuprofen, but the subjects with the rare SNP hadn't. ...
Biol 155 Human Physiology - University of British Columbia
... These individual potentials are sub-threshold. If the transmitter opens an anion influx, the resulting hyperpolarization is called an Inhibitory Post Synaptic Potential (IPSP All these potentials are additive. ...
... These individual potentials are sub-threshold. If the transmitter opens an anion influx, the resulting hyperpolarization is called an Inhibitory Post Synaptic Potential (IPSP All these potentials are additive. ...
Host cell ion channels as new anti-viral targets
... Ion channels are pore-forming proteins that allow passage of selected ions across cell membranes. They perform a broad range of critical functions that control all aspects of cellular life, ranging from cell signaling, membrane potential regulation, ionic homeostasis and cell volume regulation. Work ...
... Ion channels are pore-forming proteins that allow passage of selected ions across cell membranes. They perform a broad range of critical functions that control all aspects of cellular life, ranging from cell signaling, membrane potential regulation, ionic homeostasis and cell volume regulation. Work ...
chapter 8 neuronal physiology A
... Factors that influence the membrane potential • Concentration gradient of ions across the membrane • Membrane permeability to ions (channels) • If these change, the membrane potential changes ...
... Factors that influence the membrane potential • Concentration gradient of ions across the membrane • Membrane permeability to ions (channels) • If these change, the membrane potential changes ...
Review For Final I - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... Distribution of phospholipids and glycolipids in the lipid bilayer of human red blood cells ...
... Distribution of phospholipids and glycolipids in the lipid bilayer of human red blood cells ...
Review Questions: 1. A tissue is a A. structure contained within a cell
... 6. Hyperventilation causes the loss of large amounts of carbon dioxide from the body, decreasing the amount of hydrogen ions in solution. As a result, A. the pH of body fluids will rise. B. the pH of body fluids will fall. C. the pH of body fluids will become neutral. D. the pH of body fluids will ...
... 6. Hyperventilation causes the loss of large amounts of carbon dioxide from the body, decreasing the amount of hydrogen ions in solution. As a result, A. the pH of body fluids will rise. B. the pH of body fluids will fall. C. the pH of body fluids will become neutral. D. the pH of body fluids will ...
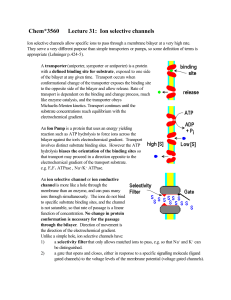
Chem*3560 Lecture 31: Ion selective channels
... radius. If the ion is too large, it clearly won't fit, e.g. K+ (radius 1.33 Å) in a Na+ (radius 0.95 Å) specific channel. However, the smaller Na+ can also be excluded by a K+ selective channel, because it fails to line up with all ligands at an appropriate distance. The energy of interaction with m ...
... radius. If the ion is too large, it clearly won't fit, e.g. K+ (radius 1.33 Å) in a Na+ (radius 0.95 Å) specific channel. However, the smaller Na+ can also be excluded by a K+ selective channel, because it fails to line up with all ligands at an appropriate distance. The energy of interaction with m ...
Patch Clamp Technique
... Patch Clamp Technique is a laboratory technique in electrophysiology that allows the study of single or multiple ion channels in cells. This discovery made it possible to record the currents of single ion channels for the first time, proving their involvement in fundamental cell processes such as ac ...
... Patch Clamp Technique is a laboratory technique in electrophysiology that allows the study of single or multiple ion channels in cells. This discovery made it possible to record the currents of single ion channels for the first time, proving their involvement in fundamental cell processes such as ac ...
Atomic basis for binding of a novel epilepsy drug
... Atomic basis for binding of a novel epilepsy drug Epilepsy is a highly common neurological disorder, affecting about 1% of the worldwide population. The disease is often caused by mutations in genes encoding for membrane proteins called ion channels. Retigabine, is a first-in-class drug targeting vo ...
... Atomic basis for binding of a novel epilepsy drug Epilepsy is a highly common neurological disorder, affecting about 1% of the worldwide population. The disease is often caused by mutations in genes encoding for membrane proteins called ion channels. Retigabine, is a first-in-class drug targeting vo ...
Cell and Molecular Biology 5/e
... Osmotic Balance and Stabilize Cell Volume Sources of Intracellular Osmolarity: large number of counterions (inorganic ions of opposite charge) that are attracted to large macromolecules (most are charged). small metabolites (high concentration of small organic molecules, sugars, amino acids, nucleot ...
... Osmotic Balance and Stabilize Cell Volume Sources of Intracellular Osmolarity: large number of counterions (inorganic ions of opposite charge) that are attracted to large macromolecules (most are charged). small metabolites (high concentration of small organic molecules, sugars, amino acids, nucleot ...
Jürgen R. Schwarz
... Information processing within the brain involves the generation of action potentials which are responsible for fast communication between nerve cells. Action potentials have a short duration and are generated by a transient influx of Na+ and a delayed outflow of K+ through voltage-gated ion channels ...
... Information processing within the brain involves the generation of action potentials which are responsible for fast communication between nerve cells. Action potentials have a short duration and are generated by a transient influx of Na+ and a delayed outflow of K+ through voltage-gated ion channels ...
Nervous System Class Overview Questions
... 3. What is it about neurons (nerve cells) that make their properties different from those of other cells? In other words, what enables nerve cells to produce action potentials? 4. How is the an AP started and propagated? ...
... 3. What is it about neurons (nerve cells) that make their properties different from those of other cells? In other words, what enables nerve cells to produce action potentials? 4. How is the an AP started and propagated? ...
Slide ()
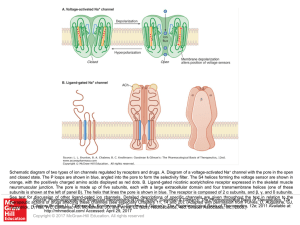
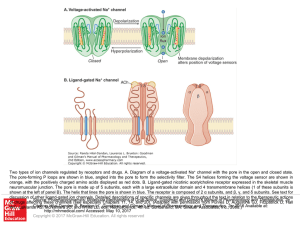
... Schematic diagram of two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are ...
... Schematic diagram of two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are ...
Review sheet exam 2
... 1 ) Explain in detail how a neuron fires an action potential. Include ion channels, membrane pumps, ion movements, and membrane potentials. 2) Explain in detail how one neuron signals another across a synapse. Include ion channels, membrane pumps, ion movements, and membrane potentials. 3) Draw a di ...
... 1 ) Explain in detail how a neuron fires an action potential. Include ion channels, membrane pumps, ion movements, and membrane potentials. 2) Explain in detail how one neuron signals another across a synapse. Include ion channels, membrane pumps, ion movements, and membrane potentials. 3) Draw a di ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
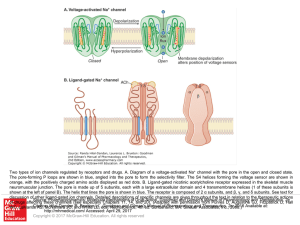
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
Slide ()
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
ion channel activity found in cytoplasmic droplets of n…
... analyzing action potentials as well as the characteristics of ion channels [1]. Patch clamp technique employs a microelectrode to seal an area of a chosen membrane to create a high resistance (usually larger than 1 GΩ) contact. Thus any electrical current passing through the sealed area can be easil ...
... analyzing action potentials as well as the characteristics of ion channels [1]. Patch clamp technique employs a microelectrode to seal an area of a chosen membrane to create a high resistance (usually larger than 1 GΩ) contact. Thus any electrical current passing through the sealed area can be easil ...
Association of voltage-dependent calcium channels with docked
... order to begin or complete a response. Any such cell is able to secrete low amounts of product continuously without external stimulus. However, in the case of certain neuronal and endocrine secretions, voltage gated calcium channels need to be activated for regulated secretion to occur. Using rat in ...
... order to begin or complete a response. Any such cell is able to secrete low amounts of product continuously without external stimulus. However, in the case of certain neuronal and endocrine secretions, voltage gated calcium channels need to be activated for regulated secretion to occur. Using rat in ...
6-2_RegulationOfIonChannel_BódisV
... through channels down thir electrochemical gradient and this process do not need energy, it is passiv transport.The channel has two state:opened or closed. Ions flow through the channel or not.This fact is proved by the patch clamp technique.The patch clamp technique is a laboratory technique in ele ...
... through channels down thir electrochemical gradient and this process do not need energy, it is passiv transport.The channel has two state:opened or closed. Ions flow through the channel or not.This fact is proved by the patch clamp technique.The patch clamp technique is a laboratory technique in ele ...
Mechanosensitive channels

Mechanosensitive channels or mechanosensitive ion channels are membrane proteins capable of responding to mechanical stress over a wide dynamic range of external mechanical stimuli. They are found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The channels vary in selectivity for the permeating ions from nonselective between anions and cations in bacteria, to cation selective allowing passage Ca2+, K+ and Na+ in eukaryotes, and highly selective K+ channels in bacteria and eukaryotes.All organisms, and apparently all cell types, sense and respond to mechanical stimuli. MSCs function as mechanotransducers capable of generating both electrical and ion flux signals as a response to external or internal stimuli. Under extreme turgor in bacteria, non selective MSCs such as MSCL and MSCS serve as safety valves to prevent lysis. In specialized cells of the higher organisms, other types of MSCs are probably the basis of the senses of hearing and touch and sense the stress needed for muscular coordination. However, none of these channels have been cloned. MSCs also allow plants to distinguish up from down by sensing the force of gravity. MSCs are not pressure-sensitive, but sensitive to local stress, most likely tension in the surrounding lipid bilayer.