Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre
... Hearing loss is mainly caused by damage to inner ear auditory hair cells – cells that detect sound, or auditory neurons – cells that connect the hair cells to the brain. Humans do not regenerate these cells, thus leading to permanent hearing loss. The goal of our group is to understand how these cel ...
... Hearing loss is mainly caused by damage to inner ear auditory hair cells – cells that detect sound, or auditory neurons – cells that connect the hair cells to the brain. Humans do not regenerate these cells, thus leading to permanent hearing loss. The goal of our group is to understand how these cel ...
Hair Cells
... the cochlea (at the level of the cortex?): “periodicity pitch” • Pitch perception significantly influenced by the fundamental frequency • Pitch can be processed at the level of the cochlea (by analyzing different “peak waves” on the basilar membrane) • However, what happens if you: – take out the fu ...
... the cochlea (at the level of the cortex?): “periodicity pitch” • Pitch perception significantly influenced by the fundamental frequency • Pitch can be processed at the level of the cochlea (by analyzing different “peak waves” on the basilar membrane) • However, what happens if you: – take out the fu ...
Psychoacoustic and physiological reflections of hearing loss: C315/A6
... – conductive hearing loss – a problem in the conduction of sound from air to the inner ear ...
... – conductive hearing loss – a problem in the conduction of sound from air to the inner ear ...
Auditory Neuroscience Core Course (NS599
... score for each module will be weighted according to the number of lectures in that module. Course Material: Course materials (syllabus, readings, lecture figures, etc.) will be available on Blackboard: https://blackboard.usc.edu. Be sure to check this site frequently. Many important announcements wi ...
... score for each module will be weighted according to the number of lectures in that module. Course Material: Course materials (syllabus, readings, lecture figures, etc.) will be available on Blackboard: https://blackboard.usc.edu. Be sure to check this site frequently. Many important announcements wi ...
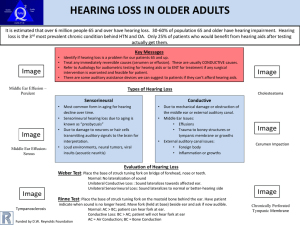
HEARING LOSS in Older Adults
... Treat any immediately reversible causes (cerumen or effusion). These are usually CONDUCTIVE causes. Refer to Audiology for audiometric testing for hearing aids or to ENT for treatment if any surgical intervention is warranted and feasible for patient. There are some auditory assistance devices we ca ...
... Treat any immediately reversible causes (cerumen or effusion). These are usually CONDUCTIVE causes. Refer to Audiology for audiometric testing for hearing aids or to ENT for treatment if any surgical intervention is warranted and feasible for patient. There are some auditory assistance devices we ca ...
Auditory Processing Disorders Related to Traumatic
... ¾ Describe the auditory brain structures that could be damaged in Traumatic Brain Injury. ¾ Describe the relationship between damage to auditory brain structures and various types of auditory processing dysfunction. ¾ Discuss the types of behavioral and electrophysiological testing that might be use ...
... ¾ Describe the auditory brain structures that could be damaged in Traumatic Brain Injury. ¾ Describe the relationship between damage to auditory brain structures and various types of auditory processing dysfunction. ¾ Discuss the types of behavioral and electrophysiological testing that might be use ...
Introduction to Audiology Study Guide Ch. 1 Audiology
... Central Auditory Processing Disorders Malingering Factitious disorder – how can we tell? Listening devices include Types of hearing aids Basic components of a hearing aid (be able to label) What should be in an SLPs listening kit? Candidates for Bone Anchored Implant Electrode array Speech processor ...
... Central Auditory Processing Disorders Malingering Factitious disorder – how can we tell? Listening devices include Types of hearing aids Basic components of a hearing aid (be able to label) What should be in an SLPs listening kit? Candidates for Bone Anchored Implant Electrode array Speech processor ...
Hearing and the environment
... Experiment by Warren et al. Tones were presented interrupted by gaps of silence or by noise. In the silence condition, listeners perceived that the sound stopped during the gaps. In the noise condition, the perception was that the sound continued behind the noise. ...
... Experiment by Warren et al. Tones were presented interrupted by gaps of silence or by noise. In the silence condition, listeners perceived that the sound stopped during the gaps. In the noise condition, the perception was that the sound continued behind the noise. ...
Histologic Analysis of Chronos in an
... 7. Roberts MT, Trussell LO. Molecular layer inhibitory interneurons provide feedforward and lateral inhibition in the dorsal cochlear nucleus. J Neurophysiol. 2010. 104, 2462-2473. 8. Zhang S, Oertel D. Giant cells of the dorsal cochlear nucleus of mice: intracellular recordings in slices. J Neuroph ...
... 7. Roberts MT, Trussell LO. Molecular layer inhibitory interneurons provide feedforward and lateral inhibition in the dorsal cochlear nucleus. J Neurophysiol. 2010. 104, 2462-2473. 8. Zhang S, Oertel D. Giant cells of the dorsal cochlear nucleus of mice: intracellular recordings in slices. J Neuroph ...
Auditory evoked potentials - Brainvolts
... latencies can have distinctive patterns that alert skilled clinicians to neural damage (e.g., eighth nerve tumors). Another major use of ABR is intraoperative monitoring. During neurosurgery, monitoring of ABR enables an immediate indication of whether any of the structures involved in the auditory ...
... latencies can have distinctive patterns that alert skilled clinicians to neural damage (e.g., eighth nerve tumors). Another major use of ABR is intraoperative monitoring. During neurosurgery, monitoring of ABR enables an immediate indication of whether any of the structures involved in the auditory ...
Human Body Project Auditory System
... corti to shear against the hair cells. This creates an electrochemical signal then it sends the sounds to the auditory nerve to the brain where the sound is recognized. ...
... corti to shear against the hair cells. This creates an electrochemical signal then it sends the sounds to the auditory nerve to the brain where the sound is recognized. ...
Click ABR with SmartEP - Intelligent Hearing Systems
... What is ABR? Auditory Brainstem Responses are potential differences generated when a person’s ear is stimulated with any kind of sound. The potential difference originates in the VIII cranial nerve and the auditory brainstem system. These potential differences can be evoked using controlled stimulation ...
... What is ABR? Auditory Brainstem Responses are potential differences generated when a person’s ear is stimulated with any kind of sound. The potential difference originates in the VIII cranial nerve and the auditory brainstem system. These potential differences can be evoked using controlled stimulation ...
Auditory System - PROFESSOR AC BROWN
... 3. Columns are frequency-specific (cochlear map) 4. Although some frequency discrimination is possible even with bilateral injury to A1, discrimination of complex sounds, such as speech, requires the auditory cortex C. Auditory Cortex Projections 1. A1 projects to adjacent areas such as A2 (secondar ...
... 3. Columns are frequency-specific (cochlear map) 4. Although some frequency discrimination is possible even with bilateral injury to A1, discrimination of complex sounds, such as speech, requires the auditory cortex C. Auditory Cortex Projections 1. A1 projects to adjacent areas such as A2 (secondar ...