NIH Public Access
... after the peripheral lesion, while others take place more gradually [6]. It is likely that lesioninduced auditory cortical plasticity involves similar short-term and longer-term changes. 2.3 Possible perceptual consequences of lesion-induced auditory cortical plasticity ...
... after the peripheral lesion, while others take place more gradually [6]. It is likely that lesioninduced auditory cortical plasticity involves similar short-term and longer-term changes. 2.3 Possible perceptual consequences of lesion-induced auditory cortical plasticity ...
Diagnosis of auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder p y p Ryan
... • Medical genetics evaluation is for children with hearing loss – Identification of related medical conditions – Exploring etiologies associated with progressive hearing loss ...
... • Medical genetics evaluation is for children with hearing loss – Identification of related medical conditions – Exploring etiologies associated with progressive hearing loss ...
Sensory systems: II. Auditory
... useful when wavelengths are less than the I.D. (~.2 m; frequency greater than ~ 1,700 Hz). Differences in time of arrival at the two ears Is unambiguous only when wavelengths are greater than 1/2 the I.D. (~.1 m; frequency less than about 3,400 Hz). ...
... useful when wavelengths are less than the I.D. (~.2 m; frequency greater than ~ 1,700 Hz). Differences in time of arrival at the two ears Is unambiguous only when wavelengths are greater than 1/2 the I.D. (~.1 m; frequency less than about 3,400 Hz). ...
Types and Causes of Peripheral Hearing Loss
... Wax blockage in ear canal; middle ear infections (otitis media), glue ear (otitis media with effusion OME), perforated eardrum; no or malformed ear canal (atresia/stenosis of canal). Middle ear problems such as otitis media, partly due to Eustachian Tube dysfunction/abnormality, may often occur in c ...
... Wax blockage in ear canal; middle ear infections (otitis media), glue ear (otitis media with effusion OME), perforated eardrum; no or malformed ear canal (atresia/stenosis of canal). Middle ear problems such as otitis media, partly due to Eustachian Tube dysfunction/abnormality, may often occur in c ...
Unique Needs of the Elderly Hearing Impaired Patient
... • An auditory processing disorder is a deficit in the processing of information in the auditory modality. It may be related to difficulty in listening, speech understanding, language development, and learning. These problems can be exacerbated in unfavorable acoustic environments. • What does a peri ...
... • An auditory processing disorder is a deficit in the processing of information in the auditory modality. It may be related to difficulty in listening, speech understanding, language development, and learning. These problems can be exacerbated in unfavorable acoustic environments. • What does a peri ...
Overview of Behavioral and Clinical Research at the Boys Town
... Goal: To better understand: (1) the inter-relationships of the acoustic functioning of the external, middle and inner ear in children and adults, and (2) the impact of this functioning on the processes of hearing in both normal-hearing and hearing-impaired listeners. ...
... Goal: To better understand: (1) the inter-relationships of the acoustic functioning of the external, middle and inner ear in children and adults, and (2) the impact of this functioning on the processes of hearing in both normal-hearing and hearing-impaired listeners. ...
Spatial Hearing
... The cues to direction include binaural cues and monaural spectral cues. These cues appear to be first encoded in the brainstem and then combined in midbrain and cortex. ITDs are encoded in the MSO, ILDs in the LSO. The Superior Colliculus is the only structure in the mammalian brain that contains a ...
... The cues to direction include binaural cues and monaural spectral cues. These cues appear to be first encoded in the brainstem and then combined in midbrain and cortex. ITDs are encoded in the MSO, ILDs in the LSO. The Superior Colliculus is the only structure in the mammalian brain that contains a ...
Este
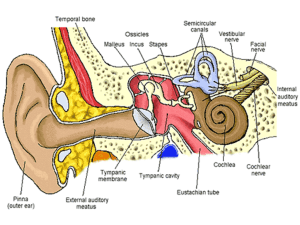
... tympanic membrane, receives sound waves and transmits them through the auditory canal to produce vibrations on the tympanic membrane. ...
... tympanic membrane, receives sound waves and transmits them through the auditory canal to produce vibrations on the tympanic membrane. ...
File
... 4. State 5 types of receptors in the skin and their function. 5. What’s the 2 factors which affect the sensitivity of the skin? 6. What’s function of the sweat glands in the skin? 7. What is mucus? 8. How can a common cold decrease our sense of ...
... 4. State 5 types of receptors in the skin and their function. 5. What’s the 2 factors which affect the sensitivity of the skin? 6. What’s function of the sweat glands in the skin? 7. What is mucus? 8. How can a common cold decrease our sense of ...
Guideline 9C_Auditory Evoked Potentials
... The importance of obtaining formal audiometric testing in patients undergoing BAEP examination is emphasized by the consideration that the proper application of two of five criteria of BAEP abnormality (Nos. 1 and 5) requires knowledge of the patient’s audiogram. There are at present insufficient da ...
... The importance of obtaining formal audiometric testing in patients undergoing BAEP examination is emphasized by the consideration that the proper application of two of five criteria of BAEP abnormality (Nos. 1 and 5) requires knowledge of the patient’s audiogram. There are at present insufficient da ...
The physiology of hearing impairment 1
... Sensorineural - damage to, degeneration of, or decreased gain of hair cells (IHC, OHC), degeneration of auditory nerve fibers (SGN, AN), or central auditory neurons and circuits. ...
... Sensorineural - damage to, degeneration of, or decreased gain of hair cells (IHC, OHC), degeneration of auditory nerve fibers (SGN, AN), or central auditory neurons and circuits. ...