Foundation 1 - Discovering Astronomy
... • Earth’s protective ozone layer had to form before early life could move from the oceans onto dry land ...
... • Earth’s protective ozone layer had to form before early life could move from the oceans onto dry land ...
Science Study Guide - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... Lith- rigid layer of Earth’s surface including crust and upper mantle. Asthn-flowing layer (hot rock) beneath lithosphere (contains convection currents). 9. What is a seismic wave? Energy released by an earthquake that travels through the earth 10. What is a seismograph? Tool used to measure the amo ...
... Lith- rigid layer of Earth’s surface including crust and upper mantle. Asthn-flowing layer (hot rock) beneath lithosphere (contains convection currents). 9. What is a seismic wave? Energy released by an earthquake that travels through the earth 10. What is a seismograph? Tool used to measure the amo ...
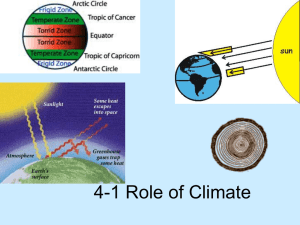
4-1 Role of Climate
... that trap sun light from escaping into space. C. Solar energy penetrates the atmosphere and is converted to heat energy and then some radiates back to space, but most stays trapped. ...
... that trap sun light from escaping into space. C. Solar energy penetrates the atmosphere and is converted to heat energy and then some radiates back to space, but most stays trapped. ...
Decision One: Concept Map and Learning Unit
... 3. How have wind and ice changed the shape of earth’s surface? 4. What forces cause earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountains? What is a fault? What effect do plate tectonics have on changes in earth’s surface? 5. How can technology help control land and water forces? Decision 3: What is the performance ...
... 3. How have wind and ice changed the shape of earth’s surface? 4. What forces cause earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountains? What is a fault? What effect do plate tectonics have on changes in earth’s surface? 5. How can technology help control land and water forces? Decision 3: What is the performance ...
Ch - saddlespace.org
... 4. Earthquake energy travels in WAVES P-Wave or Primary, travels fastest through all the Earth in a push and pull, back and forth motion. These waves are usually not felt (6-10km/sec). Can travel thru any material. (solid, liquid or gas) S-Waves or Secondary waves travel at right angles to their dir ...
... 4. Earthquake energy travels in WAVES P-Wave or Primary, travels fastest through all the Earth in a push and pull, back and forth motion. These waves are usually not felt (6-10km/sec). Can travel thru any material. (solid, liquid or gas) S-Waves or Secondary waves travel at right angles to their dir ...
Mid-Ocean Ridges
... Where does this picture come from? Direct Observations: • Exposures on Surface • Up from 50 km (30 miles) depth ...
... Where does this picture come from? Direct Observations: • Exposures on Surface • Up from 50 km (30 miles) depth ...
Constructive and Destructive Forces Study Guide
... II. Earth’s layers: The crust and mantle are divided into sections called plates, which “float” on the softer rock of the __mantle_________. These plate movements cause many changes in Earth’s surface. A. Crust – surface layer of the Earth. It is solid rock. B. Mantle – made up of two layers – a sol ...
... II. Earth’s layers: The crust and mantle are divided into sections called plates, which “float” on the softer rock of the __mantle_________. These plate movements cause many changes in Earth’s surface. A. Crust – surface layer of the Earth. It is solid rock. B. Mantle – made up of two layers – a sol ...
General Geology
... the rocks and minerals which compose it, the processes which are constantly changing it, the concepts of relative and absolute time, the risks associated with geologic hazards, and the role of geology in shaping man’s environment. The course presents the tools, methods and approach employed by pract ...
... the rocks and minerals which compose it, the processes which are constantly changing it, the concepts of relative and absolute time, the risks associated with geologic hazards, and the role of geology in shaping man’s environment. The course presents the tools, methods and approach employed by pract ...
Plate Tectonics 1. Continental Drift
... - Continental drift was a hypothesis proposed by Alfred Wegner (German Scientist) in 1912 -Said all continents were once one large land mass and began to separate 200 MYA to the world we see today -He called this supercontinent Pangea -Evidence for hypothesis 1) Similar coastlines, continents are sh ...
... - Continental drift was a hypothesis proposed by Alfred Wegner (German Scientist) in 1912 -Said all continents were once one large land mass and began to separate 200 MYA to the world we see today -He called this supercontinent Pangea -Evidence for hypothesis 1) Similar coastlines, continents are sh ...
Convection Currents - Effingham County Schools
... • The crust is the upper part of the rigid lithosphere and has a different composition under land than it does on the ocean floor. ...
... • The crust is the upper part of the rigid lithosphere and has a different composition under land than it does on the ocean floor. ...
Earth*s Structure
... 11. According to plate tectonics theory Earth’s outer layer, the __________________, is broken into several large __________________, which hold the continents and the oceans, and are in constant motion. 12. Plate tectonics theory explains how ____________________________________, __________________ ...
... 11. According to plate tectonics theory Earth’s outer layer, the __________________, is broken into several large __________________, which hold the continents and the oceans, and are in constant motion. 12. Plate tectonics theory explains how ____________________________________, __________________ ...
Document
... Seas, Gulfs, and Bays-Large bodies of salt water partially enclosed by land. The Gulf of Mexico is nearly encircled by the coast of the US and Mexico. These are the three types of ...
... Seas, Gulfs, and Bays-Large bodies of salt water partially enclosed by land. The Gulf of Mexico is nearly encircled by the coast of the US and Mexico. These are the three types of ...
Molnar, P. (2011), Jack Oliver (1923-2011), Nature, 470, 176.
... waves, at their seismographs. These waves travel through the interior of Earth. Longperiod waves that ripple over the surface of the planet offered a ‘place’ where few had gone before. Oliver was the first to recognize many of the peculiarities of the waveforms that computers now analyse and simulat ...
... waves, at their seismographs. These waves travel through the interior of Earth. Longperiod waves that ripple over the surface of the planet offered a ‘place’ where few had gone before. Oliver was the first to recognize many of the peculiarities of the waveforms that computers now analyse and simulat ...
Planet Earth Test Review
... 9. The Andes Mountains are located in Chile. The San Andreas Fault is in California. 10. According to the idea or the “theory of plate tectonics,” the surface of the earth is divided into large sections called what? Tectonic Plates ...
... 9. The Andes Mountains are located in Chile. The San Andreas Fault is in California. 10. According to the idea or the “theory of plate tectonics,” the surface of the earth is divided into large sections called what? Tectonic Plates ...
Earthquakes "I can..." Review
... travel through the interior of the Earth and the way they travel can show an image of the interior. For example S waves do not travel through liquid ...
... travel through the interior of the Earth and the way they travel can show an image of the interior. For example S waves do not travel through liquid ...
File - Brighten Academy Middle School
... Earth's Interior for 600 If you were to send a probe from the surface to the center of the Earth, what differences in temperature and pressure would it measure? ...
... Earth's Interior for 600 If you were to send a probe from the surface to the center of the Earth, what differences in temperature and pressure would it measure? ...
3202 INTRODUCTION
... • refers to the movement of the more than 20 plates (9 major) due to convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries. • The continents drift at a rate of 2 inches a year. • Started 200 million years ago • Pangea (land) & Panthalasa (sea) ...
... • refers to the movement of the more than 20 plates (9 major) due to convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries. • The continents drift at a rate of 2 inches a year. • Started 200 million years ago • Pangea (land) & Panthalasa (sea) ...
AWegener_DavidH
... •The crust and the rigid part of the mantle make the lithosphere. •The lithosphere is broken into plates . ...
... •The crust and the rigid part of the mantle make the lithosphere. •The lithosphere is broken into plates . ...
Page 420 - ClassZone
... similar things happen even without water. Wind can carry sand grains that batter at rocks and form new features. Even on a planet without air, rock breaks down from being heated in the daylight and cooled at night. The material is pulled downhill by gravity. A small object sometimes hits a planet’s ...
... similar things happen even without water. Wind can carry sand grains that batter at rocks and form new features. Even on a planet without air, rock breaks down from being heated in the daylight and cooled at night. The material is pulled downhill by gravity. A small object sometimes hits a planet’s ...
lava
... 3. Made up of loose materials, like rocks, seabed. 4. Has mountains, ocean floor, volcanoes, and continents. ...
... 3. Made up of loose materials, like rocks, seabed. 4. Has mountains, ocean floor, volcanoes, and continents. ...
Earthquake Study Guide Key
... 6. What do the locations of earthquakes and volcanoes have in common? Earthquakes and volcanoes both tend to occur along plate boundaries. The most common area for earthquakes and volcanoes worldwide is the Ring of Fire (The Circum-Pacific Belt). The Ring of Fire is a nearly continuous chain of volc ...
... 6. What do the locations of earthquakes and volcanoes have in common? Earthquakes and volcanoes both tend to occur along plate boundaries. The most common area for earthquakes and volcanoes worldwide is the Ring of Fire (The Circum-Pacific Belt). The Ring of Fire is a nearly continuous chain of volc ...
Plate Tectonics Test Review
... How does temperature and pressure relate to the layers of the earth? • As you go deeper into the earth, the pressure and the temperature both increase ...
... How does temperature and pressure relate to the layers of the earth? • As you go deeper into the earth, the pressure and the temperature both increase ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.