Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics
... along Earth’s mid-ocean ridges, slowly moves outward across ocean basins, and finally sinks back into the mantle beneath deep-ocean trenches. Sea-floor spreading new oceanic lithosphere is formed and the ocean floor gets wider ...
... along Earth’s mid-ocean ridges, slowly moves outward across ocean basins, and finally sinks back into the mantle beneath deep-ocean trenches. Sea-floor spreading new oceanic lithosphere is formed and the ocean floor gets wider ...
7 Grade Earth Science Movie Maker Requirements:
... 7th Grade Earth Science Movie Maker Requirements: Learning Target: I will be able to create & develop a Movie with Live Movie Maker by utilizing the knowledge I have been practicing over the last two weeks. I will explore and compile facts about an Earth Science topic that I am starting to study in ...
... 7th Grade Earth Science Movie Maker Requirements: Learning Target: I will be able to create & develop a Movie with Live Movie Maker by utilizing the knowledge I have been practicing over the last two weeks. I will explore and compile facts about an Earth Science topic that I am starting to study in ...
Movements of Earth`s Major Plates PPT
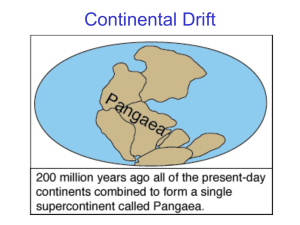
... You try it! Make Pangaea with the pieces of continents at your group. ...
... You try it! Make Pangaea with the pieces of continents at your group. ...
How plate tectonics clicked
... did, including several British geophysicists led by P. M. S. Blackett and Keith Runcorn. In an effort to understand “More than the origins of Earth’s two dozen magnetic field, they discovered that magscientists netic minerals pointed did the key in different directions work that at different times i ...
... did, including several British geophysicists led by P. M. S. Blackett and Keith Runcorn. In an effort to understand “More than the origins of Earth’s two dozen magnetic field, they discovered that magscientists netic minerals pointed did the key in different directions work that at different times i ...
seismic tomography
... type of material they travel through. Waves travel faster through cold, stiff materials, like a plate subducting into ...
... type of material they travel through. Waves travel faster through cold, stiff materials, like a plate subducting into ...
Plate Tectonics
... It was not until the 1960s that the theory of continental drift became accepted by the scientific community. Some continents fit together almost perfectly, e.g. South America and Africa. Similar fossils can be found on different continents. This shows these regions were once very close or joined tog ...
... It was not until the 1960s that the theory of continental drift became accepted by the scientific community. Some continents fit together almost perfectly, e.g. South America and Africa. Similar fossils can be found on different continents. This shows these regions were once very close or joined tog ...
Ch 12.1
... Wegener also realized that other evidence also supported his theory. There were matching geologic features and rocks on different continents. There were matching fossils, like Mesosaurus, on different continents. There was evidence of different climates, (eg. Such as glaciers) on warm contin ...
... Wegener also realized that other evidence also supported his theory. There were matching geologic features and rocks on different continents. There were matching fossils, like Mesosaurus, on different continents. There was evidence of different climates, (eg. Such as glaciers) on warm contin ...
Study Guide Answer Key for Plate Tectonics
... 3. If we could travel from the crust to the inner core, how would temperature change? Temperature would increase (as would density and pressure) 4. Why is the inner core of the Earth solid? The pressure of all the surrounding layers keep the atoms held so tightly together that they form a solid 5. W ...
... 3. If we could travel from the crust to the inner core, how would temperature change? Temperature would increase (as would density and pressure) 4. Why is the inner core of the Earth solid? The pressure of all the surrounding layers keep the atoms held so tightly together that they form a solid 5. W ...
Objectives - cloudfront.net
... • Seismic waves that travel through Earth’s interior are called_______________ _______________. There are two kinds of body waves: _______________ and _______________. P-waves or _______________ _______________, are an example of longitudinal waves. Rocks move back and forth in the same direction th ...
... • Seismic waves that travel through Earth’s interior are called_______________ _______________. There are two kinds of body waves: _______________ and _______________. P-waves or _______________ _______________, are an example of longitudinal waves. Rocks move back and forth in the same direction th ...
chapter1
... sets geology apart The geologic time scale is the calendar that geologists use to date past events in Earth’s history. Fig. 1.17, p. 24 ...
... sets geology apart The geologic time scale is the calendar that geologists use to date past events in Earth’s history. Fig. 1.17, p. 24 ...
Chapter 1: Introduction
... Earth as a system The Earth system is also powered by the Earth’s interior • Heat remaining from the formation and heat that is continuously generated by radioactive decay powers the internal processes that produce volcanoes, earthquakes, and mountains ...
... Earth as a system The Earth system is also powered by the Earth’s interior • Heat remaining from the formation and heat that is continuously generated by radioactive decay powers the internal processes that produce volcanoes, earthquakes, and mountains ...
Don`t Break Your Plate
... When mantle rock near the Earth’s core heats up it becomes less dense and rises while the cooler rock near the surface sinks—mantle convection Moves plates a few centimeters each year http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/visual izations/es0804/es0804page01.cfm?chapter_no=visuali ...
... When mantle rock near the Earth’s core heats up it becomes less dense and rises while the cooler rock near the surface sinks—mantle convection Moves plates a few centimeters each year http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/visual izations/es0804/es0804page01.cfm?chapter_no=visuali ...
Grade 8 Chapter 2 : Notes
... is called the Coriolis effect. Clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and Counter clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere ...
... is called the Coriolis effect. Clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and Counter clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere ...
Chapter 2 - TeacherWeb
... is called the Coriolis effect. Clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and Counter clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere ...
... is called the Coriolis effect. Clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and Counter clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere ...
Geologic Time
... • The zone of the Earth below the crust and above the core • Divided into the upper mantle and the lower mantle, with a transition zone between ...
... • The zone of the Earth below the crust and above the core • Divided into the upper mantle and the lower mantle, with a transition zone between ...
Atmospheric Heating
... You have learned that plate tectonics is the theory that ::.lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that move around :: top of the asthenosphere. What causes the motion of tecto:-: plates? Remember that the solid rock of the asthenosph=:= flows very slowly. This movement occurs because of chan.: ...
... You have learned that plate tectonics is the theory that ::.lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that move around :: top of the asthenosphere. What causes the motion of tecto:-: plates? Remember that the solid rock of the asthenosph=:= flows very slowly. This movement occurs because of chan.: ...
Digest #: 3535 TITLE WHAT IS EARTH SCIENCE?
... single, hot, dense, chaotic mass; our solar system formed from a nebular cloud of dust and gas about 4.6 billion years ago (See Instructional Goal #3 and #5) ...
... single, hot, dense, chaotic mass; our solar system formed from a nebular cloud of dust and gas about 4.6 billion years ago (See Instructional Goal #3 and #5) ...
Document
... if you choose to type your answers, be aware that cutting & pasting from the Internet (or other’s work) is PLAGARISM, and will be counted as cheating! Note: LEDC = less economically developed country, MEDC = more economically developed country 1. Define lithosphere. 2. Describe the internal structur ...
... if you choose to type your answers, be aware that cutting & pasting from the Internet (or other’s work) is PLAGARISM, and will be counted as cheating! Note: LEDC = less economically developed country, MEDC = more economically developed country 1. Define lithosphere. 2. Describe the internal structur ...
EQ I - Facts, Rebound, & Seismograph
... directly above the focus EQ happen along faults which are long cracks in the earth’s crust ...
... directly above the focus EQ happen along faults which are long cracks in the earth’s crust ...
Heat Flow in Brief,
... moves in this broad cyclic flow, indicated by the arrows in the figure. This zone, where rock is soft enough to flow, is called the asthenosphere. Occasionally, however, masses of hotter-than-normal rock rise independently of the broad flow, like bubbles through a flowing stream. These masses of v ...
... moves in this broad cyclic flow, indicated by the arrows in the figure. This zone, where rock is soft enough to flow, is called the asthenosphere. Occasionally, however, masses of hotter-than-normal rock rise independently of the broad flow, like bubbles through a flowing stream. These masses of v ...
TAKS Review - Greenslime
... Rotation causes _?_. Seasons are caused by _?_. Spring tides occur in what moon phases? List the components of the universe from smallest to largest. 5. Name two things about stars that we can get from a Hertzsprung-Russel Diagram. ...
... Rotation causes _?_. Seasons are caused by _?_. Spring tides occur in what moon phases? List the components of the universe from smallest to largest. 5. Name two things about stars that we can get from a Hertzsprung-Russel Diagram. ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.