Plate Tectonic Test Use the pictures above to answer questions 1
... ____ 20. One reason that melted material from the Earth’s mantle is rising up at location is because it isa. cooler than the surrounding material b. older than the surrounding material c. Less dense than the surrounding material ____ 21. The newest rocks are most likely found at a. Location c. L ...
... ____ 20. One reason that melted material from the Earth’s mantle is rising up at location is because it isa. cooler than the surrounding material b. older than the surrounding material c. Less dense than the surrounding material ____ 21. The newest rocks are most likely found at a. Location c. L ...
Plate Tectonics
... plates sink into the mantle due to density • Occurs near edges of oceanic plates • When subducts, forms a depression in ocean floor called a trench ...
... plates sink into the mantle due to density • Occurs near edges of oceanic plates • When subducts, forms a depression in ocean floor called a trench ...
EARTHQUAKES - NVHSEarthScienceKDudenhausen
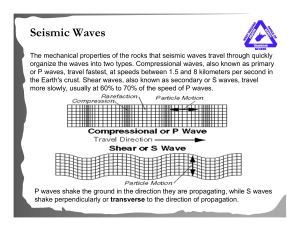
... seismic waves, surface waves and body waves (P waves and S waves) • Surface waves – seismic waves that travel along the ground, move up and down or side-to-side. Te most destructive of all earthquake waves. • P waves – push-pull waves, they compress and expand rocks in the direction the waves travel ...
... seismic waves, surface waves and body waves (P waves and S waves) • Surface waves – seismic waves that travel along the ground, move up and down or side-to-side. Te most destructive of all earthquake waves. • P waves – push-pull waves, they compress and expand rocks in the direction the waves travel ...
FS Learner Outcome Q`s Logan
... 131. _______ waves are described as primary waves; the longitudinal waves generated by an earthquake. P Waves 132. This kind of wave is the secondary transverse wave generated by an earthquake. S Wave 133. _____ waves are seismic waves that travel along the Earth’s surface causing much or the damage ...
... 131. _______ waves are described as primary waves; the longitudinal waves generated by an earthquake. P Waves 132. This kind of wave is the secondary transverse wave generated by an earthquake. S Wave 133. _____ waves are seismic waves that travel along the Earth’s surface causing much or the damage ...
Plate Tectonics and Igneous Activity
... Convergent Plate Boundaries The basic connection between plate tectonics and volcanism is that plate motions provide the mechanisms by which mantle rocks melt to generate magma When an oceanic plate sinks under another plate, it brings water and rock along with it. When that plate reaches a depth ...
... Convergent Plate Boundaries The basic connection between plate tectonics and volcanism is that plate motions provide the mechanisms by which mantle rocks melt to generate magma When an oceanic plate sinks under another plate, it brings water and rock along with it. When that plate reaches a depth ...
DR Fossil Record
... _____ 23. Fossils provide evidence that Antarctica was once located a. at the North Pole. c. at the South Pole. b. near the equator. d. where it is now. _____ 24. The continents may once have formed one landmass called Pangaea which means a. all seas. c. all Earth. b. puzzle. d. landmass. _____ 25. ...
... _____ 23. Fossils provide evidence that Antarctica was once located a. at the North Pole. c. at the South Pole. b. near the equator. d. where it is now. _____ 24. The continents may once have formed one landmass called Pangaea which means a. all seas. c. all Earth. b. puzzle. d. landmass. _____ 25. ...
No Slide Title
... erosion, and plate tectonics change the rock from one form to another Rock can be transmuted from any form to any other form’ by these processes Example: An igneous rock that is brought to the Earth’s surface is weathered and eroded. Sediment pile is buried, causing cementation into a sedimentary ro ...
... erosion, and plate tectonics change the rock from one form to another Rock can be transmuted from any form to any other form’ by these processes Example: An igneous rock that is brought to the Earth’s surface is weathered and eroded. Sediment pile is buried, causing cementation into a sedimentary ro ...
Chapter Three: The Dynamic Earth
... consists of the crust and the rigid, outermost part of the mantle Continents move on these plates Plate Boundaries is where mountain building occurs ...
... consists of the crust and the rigid, outermost part of the mantle Continents move on these plates Plate Boundaries is where mountain building occurs ...
The habitability of Earth
... had already formed 4.5 Gyr ago This implies that the Hadean Earth may have been habitable at that time Although frequent impacts may have sterilized the Hadean Earth ...
... had already formed 4.5 Gyr ago This implies that the Hadean Earth may have been habitable at that time Although frequent impacts may have sterilized the Hadean Earth ...
plate tectonics
... of the Greek root for "to build" and together the terms define how the Earth's surface is built up of moving plates. The theory of plate tectonics itself says that the Earth's lithosphere is made up individual plates that are broken down into over a dozen large and small pieces of solid rock. These ...
... of the Greek root for "to build" and together the terms define how the Earth's surface is built up of moving plates. The theory of plate tectonics itself says that the Earth's lithosphere is made up individual plates that are broken down into over a dozen large and small pieces of solid rock. These ...
Chapter 5 Fast Changes on Earth
... 2. Movements in Earth’s crust caused by a sudden shift in Earth’s plates are __B__. 3. __C__ are areas where rocks slide past one another along cracks in the Earth’s plates. 4. When land becomes so full of water that it may change into a river of mud and rock, it is called a __G__. 5. An ocean wave ...
... 2. Movements in Earth’s crust caused by a sudden shift in Earth’s plates are __B__. 3. __C__ are areas where rocks slide past one another along cracks in the Earth’s plates. 4. When land becomes so full of water that it may change into a river of mud and rock, it is called a __G__. 5. An ocean wave ...
Name Period Study Guide for 7th Grade Science Final Exam
... c. Sedimentary rock: forms from small pieces or ___________or other living material. 6. The most common intrusive igneous rock is _____________. 7. The most common extrusive igneous rock is ________________. 8. __________________ and _____________________ are two common metamorphic rocks. 9. The ___ ...
... c. Sedimentary rock: forms from small pieces or ___________or other living material. 6. The most common intrusive igneous rock is _____________. 7. The most common extrusive igneous rock is ________________. 8. __________________ and _____________________ are two common metamorphic rocks. 9. The ___ ...
Plate Tectonics
... Plate Tectonics Go through the slide show at your own pace, do more research if you need to ...
... Plate Tectonics Go through the slide show at your own pace, do more research if you need to ...
Continents Adrift: An Introduction to Continental Drift and Plate
... Magma heats the water allowing different organisms to survive there. Cracks found on the ocean floor. Rock further from the crack was older = sea floor spreading. ...
... Magma heats the water allowing different organisms to survive there. Cracks found on the ocean floor. Rock further from the crack was older = sea floor spreading. ...
Journey to the Center of Earth
... shell around Earth but is broken into many large and small slabs of rock called Tectonic Plates. Tectonic plates fit together like a jigsaw puzzle that makes up the surface of the Earth. Most large tectonic plates include both continental crust and oceanic crust. Most of the thicker continental crus ...
... shell around Earth but is broken into many large and small slabs of rock called Tectonic Plates. Tectonic plates fit together like a jigsaw puzzle that makes up the surface of the Earth. Most large tectonic plates include both continental crust and oceanic crust. Most of the thicker continental crus ...
Evidence of continental drift
... -The “plasticity” of the mantle allows the plates to glide and move along the mantle creating mountains, trenches and new land. -Heat from the core and the mantle itself causes convection currents to be create in the mantle. -The warmer magma at the bottom of the thick mantle is warmer because it is ...
... -The “plasticity” of the mantle allows the plates to glide and move along the mantle creating mountains, trenches and new land. -Heat from the core and the mantle itself causes convection currents to be create in the mantle. -The warmer magma at the bottom of the thick mantle is warmer because it is ...
Document
... •Study of the geodynamo has received considerable attention in the press •Concerns of an approaching polarity reversal •The magnetic field protects Earth’s surface from high-energy particles •Sun wind, cosmic rays from deep space •When the field switches polarity, its strength can drop to below 10% ...
... •Study of the geodynamo has received considerable attention in the press •Concerns of an approaching polarity reversal •The magnetic field protects Earth’s surface from high-energy particles •Sun wind, cosmic rays from deep space •When the field switches polarity, its strength can drop to below 10% ...
SCIENCE 6 3rd rating part 1
... Scientists have investigate the different layers of the earth through core drilling, analysis of volcanic materials and earthquake waves. Pupils describe the layers of the earth by means of an illustration. 3. Discussion/Analysis: a. What is the earth’s crust consists of? b. What is the layer be ...
... Scientists have investigate the different layers of the earth through core drilling, analysis of volcanic materials and earthquake waves. Pupils describe the layers of the earth by means of an illustration. 3. Discussion/Analysis: a. What is the earth’s crust consists of? b. What is the layer be ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.