Chapter 15
... • When the waves reach the outer core, the P-waves slow down and the S-waves stop. • S-waves can’t travel through liquids, and P-waves move easiest through solids. • **The change in velocity is evidence that the outer core is liquid • After passing through the outer core, the P-waves increase in vel ...
... • When the waves reach the outer core, the P-waves slow down and the S-waves stop. • S-waves can’t travel through liquids, and P-waves move easiest through solids. • **The change in velocity is evidence that the outer core is liquid • After passing through the outer core, the P-waves increase in vel ...
FAQs
... (15) What are roles played by human being in changing the earth’s surface Ans. Humans have cut down forests and have destroyed pasture to bring more and more agricultural level. As a result the disturbances in the ecological balance of nature and environment has taken place. Constructions of roads, ...
... (15) What are roles played by human being in changing the earth’s surface Ans. Humans have cut down forests and have destroyed pasture to bring more and more agricultural level. As a result the disturbances in the ecological balance of nature and environment has taken place. Constructions of roads, ...
for true or “F” - University of South Alabama
... 3. (T F) After a theory has survived much scientific scrutiny, it may be elevated to hypothesis status. 4. (T F) Convergent plate tectonic boundaries are located where plates move toward one another. 5. (T F) Transform plate boundaries only affect oceanic lithosphere. 6. (T F) A dike is a concordant ...
... 3. (T F) After a theory has survived much scientific scrutiny, it may be elevated to hypothesis status. 4. (T F) Convergent plate tectonic boundaries are located where plates move toward one another. 5. (T F) Transform plate boundaries only affect oceanic lithosphere. 6. (T F) A dike is a concordant ...
what is an earthquake?
... SWBAT: define problems that may be caused by a catastrophic event resulting from plate movements and design possible devices or solutions to minimize the effects of that event on Earth’s surface and/or human structures. ...
... SWBAT: define problems that may be caused by a catastrophic event resulting from plate movements and design possible devices or solutions to minimize the effects of that event on Earth’s surface and/or human structures. ...
How Do Stress Forces Affect Rock?
... carrying the energy released during an earthquake – They move like ripples on a pond – They carry the energy of an earthquake away from the focus, through Earth’s interior, and across the surface – The energy is greatest the the ...
... carrying the energy released during an earthquake – They move like ripples on a pond – They carry the energy of an earthquake away from the focus, through Earth’s interior, and across the surface – The energy is greatest the the ...
Table of Contents - Carson
... Patterns of Earth Activity and Plate Tectonics Volcanoes and earthquakes may occur unexpectedly, but not without a pattern. Many volcanoes erupt in an area that encircles the Pacific Ocean, often called “The Ring of Fire.” Similarly, a string of mountains in the midAtlantic Ocean that stretches nort ...
... Patterns of Earth Activity and Plate Tectonics Volcanoes and earthquakes may occur unexpectedly, but not without a pattern. Many volcanoes erupt in an area that encircles the Pacific Ocean, often called “The Ring of Fire.” Similarly, a string of mountains in the midAtlantic Ocean that stretches nort ...
SEA FLOOR SPREADING Mid
... The force responsible for driving or moving the plates is _____________________. convection currents Convection Currents occur within the mantle of the earth when hot magma rises and cool magma sinks ...
... The force responsible for driving or moving the plates is _____________________. convection currents Convection Currents occur within the mantle of the earth when hot magma rises and cool magma sinks ...
Homework #4 - Leslie Looney
... Question 3: (5 points) Where did the majority of the large amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the second major atmosphere to form on the early Earth end up on the Earth? 1. As nitrogen oxides and carbon, after chemical reactions with the majority component of the atmosphere, the nitrogen molecules. ...
... Question 3: (5 points) Where did the majority of the large amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the second major atmosphere to form on the early Earth end up on the Earth? 1. As nitrogen oxides and carbon, after chemical reactions with the majority component of the atmosphere, the nitrogen molecules. ...
Steven Taylor Eportfolio Volcanoes Part II Askja Volcano in Iceland
... Todra Volcanic Field (in Niger, Africa) Cinder cone type volcano This volcano must be a hotspot, because it is seriously in the middle of the African plate. There is an unusually heated spot of magma which is fed by the hot mantle of the earth, where this magma creates pockets and rises up due to it ...
... Todra Volcanic Field (in Niger, Africa) Cinder cone type volcano This volcano must be a hotspot, because it is seriously in the middle of the African plate. There is an unusually heated spot of magma which is fed by the hot mantle of the earth, where this magma creates pockets and rises up due to it ...
Chapter 8
... – Familiar but outdated – Based on height of largest P or S wave – Increase of 1 = ten fold increase • Ex: M 5.0 is ten times greater than M4.0 ...
... – Familiar but outdated – Based on height of largest P or S wave – Increase of 1 = ten fold increase • Ex: M 5.0 is ten times greater than M4.0 ...
Continents on the Move - westerville.k12.oh.us
... In 1910, a young German scientist named Alfred Wegener became curious about why the coasts of several continents matched so well, like the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. He formed a hypothesis that Earth’s continents had moved! Wegener’s hypothesis was that all the continents had once been joined togeth ...
... In 1910, a young German scientist named Alfred Wegener became curious about why the coasts of several continents matched so well, like the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. He formed a hypothesis that Earth’s continents had moved! Wegener’s hypothesis was that all the continents had once been joined togeth ...
Lesson 4 Earthquakes Notes
... Tsunamis usually occur after underwater earthquakes that are great than 6.5 on the Richter ...
... Tsunamis usually occur after underwater earthquakes that are great than 6.5 on the Richter ...
Plate Tectonics Webquest
... Go to the following site: http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html On the top of the screen are different tabs, click on each section as listed below. To move through the section, click the next button. Section: Earth’s Structure 1. What do scientists study to learn about the eart ...
... Go to the following site: http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html On the top of the screen are different tabs, click on each section as listed below. To move through the section, click the next button. Section: Earth’s Structure 1. What do scientists study to learn about the eart ...
The History of Life
... – Cenozoic Era ( Earth’s most recent period: 65 million years ago-present) ...
... – Cenozoic Era ( Earth’s most recent period: 65 million years ago-present) ...
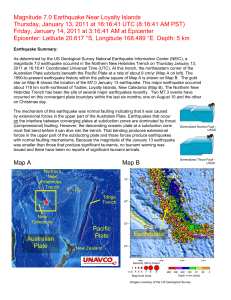
Earthquake Summary Sheet
... 1. earthquake: the release of tension (energy) built up from the movement of plates along plate boundaries 2. fault: a break along the rocks where earthquakes occur 3. focus: place inside the Earth where the earthquake starts 4. epicenter: place on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus 5. sei ...
... 1. earthquake: the release of tension (energy) built up from the movement of plates along plate boundaries 2. fault: a break along the rocks where earthquakes occur 3. focus: place inside the Earth where the earthquake starts 4. epicenter: place on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus 5. sei ...
Seafloor Spreading - Paramus Public Schools
... fills gap in ridge 2. When hardens adds new ocean floor 3. As spreading occurs, more magma is forced upward and the crust moves away from ridge 4. Crust is destroyed by subduction at trenches ...
... fills gap in ridge 2. When hardens adds new ocean floor 3. As spreading occurs, more magma is forced upward and the crust moves away from ridge 4. Crust is destroyed by subduction at trenches ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.