intro plate tec
... At a constructive plate boundary, two plates move apart. As the two plates move apart, magma rises up to fill the gap. This causes volcanoes at this type of boundary. However, since the magma can escape easily at the surface the volcano does not erupt with much force. Earthquakes are also found at c ...
... At a constructive plate boundary, two plates move apart. As the two plates move apart, magma rises up to fill the gap. This causes volcanoes at this type of boundary. However, since the magma can escape easily at the surface the volcano does not erupt with much force. Earthquakes are also found at c ...
FREE Sample Here
... each pair to separate, one going left and the other to the right upon reaching the front of the room. When they reach the front of the room, they are to hold their arms up if the instructor's arms are up, or leave them down if the instructor's arms are down. In this way, the plates grow at the fro ...
... each pair to separate, one going left and the other to the right upon reaching the front of the room. When they reach the front of the room, they are to hold their arms up if the instructor's arms are up, or leave them down if the instructor's arms are down. In this way, the plates grow at the fro ...
plate tectonics and california geology - FOG
... live along its path are familiar with its associated earthquake hazards. The Loma Prieta earthquake in 1989 was one of the most recent large earthquakes. The magnitude-6.9 earthquake caused significant shaking and damage from Santa Cruz to San Francisco as it released built up stress related to the ...
... live along its path are familiar with its associated earthquake hazards. The Loma Prieta earthquake in 1989 was one of the most recent large earthquakes. The magnitude-6.9 earthquake caused significant shaking and damage from Santa Cruz to San Francisco as it released built up stress related to the ...
Statement: True/False: Information Learned: Important Picture
... How far does the Pacific plate move in one year? (Use a ruler to draw this distance). ...
... How far does the Pacific plate move in one year? (Use a ruler to draw this distance). ...
7.3
... Convection in the mantle is related to plate tectonic activity. The warmth for convection comes from radioactive elements inside Earth, such as uranium, thorium, and potassium. When materials such as solid rock are heated, they expand and become less dense. Heated mantle material rises and comes in ...
... Convection in the mantle is related to plate tectonic activity. The warmth for convection comes from radioactive elements inside Earth, such as uranium, thorium, and potassium. When materials such as solid rock are heated, they expand and become less dense. Heated mantle material rises and comes in ...
A free plate surface and weak oceanic crust
... Berg, 2008]. However in recent Earth history, plate tectonics is certainly characterized by single-sided subduction as observed nowadays by seismic tomography [King, 2001; Wortel and Spakman, 2000; Zhao, 2004]. [13] The use of numerical models (like the ones presented here) is central in the study o ...
... Berg, 2008]. However in recent Earth history, plate tectonics is certainly characterized by single-sided subduction as observed nowadays by seismic tomography [King, 2001; Wortel and Spakman, 2000; Zhao, 2004]. [13] The use of numerical models (like the ones presented here) is central in the study o ...
MS Plate Tectonics
... Deep sea trenches are found near chains of active volcanoes. These volcanoes can be at the edges of continents or in the oceans. Trenches are the deepest places on Earth. The deepest trench is the Mariana Trench in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. This trench plunges about 11 kilometers (35,840 feet) ...
... Deep sea trenches are found near chains of active volcanoes. These volcanoes can be at the edges of continents or in the oceans. Trenches are the deepest places on Earth. The deepest trench is the Mariana Trench in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. This trench plunges about 11 kilometers (35,840 feet) ...
Earthquakes and volcanoes CH. 11
... • When these plates move around, they collide, move apart, or slide past each other. • The movement of these plates can cause vibrations known as earthquakes and can create conditions that cause volcanoes to form. ...
... • When these plates move around, they collide, move apart, or slide past each other. • The movement of these plates can cause vibrations known as earthquakes and can create conditions that cause volcanoes to form. ...
Worksheet as a MS Word file ( format)
... appeared that the oceanic lithosphere should be older with greater distance from the center of the mid-ocean ridge where it first formed By matching the reversal history to the magnetic patterns under the sea, and assuming seafloor spreading, the age of a particular piece of oceanic lithosphere coul ...
... appeared that the oceanic lithosphere should be older with greater distance from the center of the mid-ocean ridge where it first formed By matching the reversal history to the magnetic patterns under the sea, and assuming seafloor spreading, the age of a particular piece of oceanic lithosphere coul ...
expedition 8 worksheet as a pdf
... appeared that the oceanic lithosphere should be older with greater distance from the center of the mid-ocean ridge where it first formed By matching the reversal history to the magnetic patterns under the sea, and assuming seafloor spreading, the age of a particular piece of oceanic lithosphere coul ...
... appeared that the oceanic lithosphere should be older with greater distance from the center of the mid-ocean ridge where it first formed By matching the reversal history to the magnetic patterns under the sea, and assuming seafloor spreading, the age of a particular piece of oceanic lithosphere coul ...
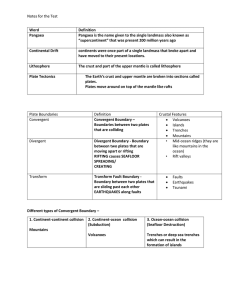
Notes for the Test Word Definition Pangaea Pangaea is the name
... Pangaea is the name given to the single landmass also known as “supercontinent” that was present 200 million years ago ...
... Pangaea is the name given to the single landmass also known as “supercontinent” that was present 200 million years ago ...
Document
... _____ 11. When rock is heated, it becomes less dense and tends to a. rise. b. sink. c. move sideways. d. erupt. _____ 12. When rock cools, it becomes more dense and tends to a. rise to the surface. b. sink below the surface. c. move sideways. d. push against the surface. 13. Density changes in the a ...
... _____ 11. When rock is heated, it becomes less dense and tends to a. rise. b. sink. c. move sideways. d. erupt. _____ 12. When rock cools, it becomes more dense and tends to a. rise to the surface. b. sink below the surface. c. move sideways. d. push against the surface. 13. Density changes in the a ...
Plate tectonics
... Two– and three–dimensional imaging of Earth’s interior (seismic tomography) shows a varying lateral density distribution throughout the mantle. Such density variations can be material (from rock chemistry), mineral (from variations in mineral structures), or thermal (through thermal expansion and co ...
... Two– and three–dimensional imaging of Earth’s interior (seismic tomography) shows a varying lateral density distribution throughout the mantle. Such density variations can be material (from rock chemistry), mineral (from variations in mineral structures), or thermal (through thermal expansion and co ...
introduction to plate tectonics
... separated by an ocean floor that is being subducted under one continent and that lacks a spreading axis to create new oceanic crust. As the sea floor is subducted, the ocean becomes narrower and narrower until the continents eventually collide and destroy or close the ocean basin. Eventually a mount ...
... separated by an ocean floor that is being subducted under one continent and that lacks a spreading axis to create new oceanic crust. As the sea floor is subducted, the ocean becomes narrower and narrower until the continents eventually collide and destroy or close the ocean basin. Eventually a mount ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics Directed Reading A
... _____ 11. When rock is heated, it becomes less dense and tends to a. rise. b. sink. c. move sideways. d. erupt. _____ 12. When rock cools, it becomes more dense and tends to a. rise to the surface. b. sink below the surface. c. move sideways. d. push against the surface. 13. Density changes in the a ...
... _____ 11. When rock is heated, it becomes less dense and tends to a. rise. b. sink. c. move sideways. d. erupt. _____ 12. When rock cools, it becomes more dense and tends to a. rise to the surface. b. sink below the surface. c. move sideways. d. push against the surface. 13. Density changes in the a ...
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks
... Made extensive studies of fossil assemblages and used geologic principles to formulate Correlation Techniques to find continuances of eroded layers. Using his findings, he developed the “Principle of Biologic Succession”. The Principle of Biologic Succession states: “…Life of each age in the ear ...
... Made extensive studies of fossil assemblages and used geologic principles to formulate Correlation Techniques to find continuances of eroded layers. Using his findings, he developed the “Principle of Biologic Succession”. The Principle of Biologic Succession states: “…Life of each age in the ear ...
Earth and Space Science Quarterly Pre/Post Assessment
... A line of volcanoes occurs along the western coast of South America, near location 4. Based on the information about plate movement on the map, which process explains the formation of these volcanoes? A. subducting of one plate under the other causing melting of the lower plate B. sliding of one pla ...
... A line of volcanoes occurs along the western coast of South America, near location 4. Based on the information about plate movement on the map, which process explains the formation of these volcanoes? A. subducting of one plate under the other causing melting of the lower plate B. sliding of one pla ...
Motion
... • They can be exposed at Earth’s surface due to uplift and erosion and are classified based on their size, shape, and relationship to surrounding rocks. ...
... • They can be exposed at Earth’s surface due to uplift and erosion and are classified based on their size, shape, and relationship to surrounding rocks. ...
Geology 101 chapter2 Plate tectonics
... and oceanic crust move together Seafloor separates at oceanic ridges where new crust forms from upwelling and cooling magma, and the new crust moves laterally away from the ridge ...
... and oceanic crust move together Seafloor separates at oceanic ridges where new crust forms from upwelling and cooling magma, and the new crust moves laterally away from the ridge ...
worksheets extreme earth
... - Saucepan, saucepan, 1,2,3 opacity, opacity, disappear. - If the saucepan is not opaque, what does it look like now? - Now the saucepan is transparent. - We can see the water inside. - What is the water doing? - The water is ______ up and down, ___ and _____, ____ and ______. - The movement is call ...
... - Saucepan, saucepan, 1,2,3 opacity, opacity, disappear. - If the saucepan is not opaque, what does it look like now? - Now the saucepan is transparent. - We can see the water inside. - What is the water doing? - The water is ______ up and down, ___ and _____, ____ and ______. - The movement is call ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.