6.E.2.2 Plate Tectonics, Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... The Great Rift Valley started forming millions of years ago. It slowly continues to deepen and widen, causing many volcanic eruptions and earthquakes in the area. ...
... The Great Rift Valley started forming millions of years ago. It slowly continues to deepen and widen, causing many volcanic eruptions and earthquakes in the area. ...
Yildirim Dilek is a professor of geology at Miami University and the
... Bergen, Norway, since 1985. He received his D Phil from Oxford University, UK, in 1978. His main research involves the physical volcanology, geochemistry, and petrology of basaltic rocks in ophiolites, island arcs, oceanic islands, and continental flood basalt provinces ranging in age from recent to ...
... Bergen, Norway, since 1985. He received his D Phil from Oxford University, UK, in 1978. His main research involves the physical volcanology, geochemistry, and petrology of basaltic rocks in ophiolites, island arcs, oceanic islands, and continental flood basalt provinces ranging in age from recent to ...
View Chapter 3 of the book
... In contrast to flowing water, flowing ice (i.e. glaciers) does not sort material according to size. As ice melts at the end of a glacier or from an iceberg, the rock material contained in the ice is dumped in an unsorted manner. This results in sediment consisting of a random mixture of material ran ...
... In contrast to flowing water, flowing ice (i.e. glaciers) does not sort material according to size. As ice melts at the end of a glacier or from an iceberg, the rock material contained in the ice is dumped in an unsorted manner. This results in sediment consisting of a random mixture of material ran ...
Earth BootCamp_5.7B_Part 1_AC
... 13. The sides of the Grand Canyon show many different layers of rock. Which statement describes how the Grand Canyon was formed? A. The canyon has a waterfall. B. Big rainstorms washed rocks out of the canyon. C. A flowing river cut into rocks to form the canyon. D. The canyon was formed from the u ...
... 13. The sides of the Grand Canyon show many different layers of rock. Which statement describes how the Grand Canyon was formed? A. The canyon has a waterfall. B. Big rainstorms washed rocks out of the canyon. C. A flowing river cut into rocks to form the canyon. D. The canyon was formed from the u ...
Review 2 – Igneous These questions are a selection pulled from the
... 40) The Icelandic volcanoes are related to plate tectonics because ________. A. they lie on a spreading center where two plates are converging B. they lie on a subduction zone where two plates are converging C. they lie on a spreading center where two plates are moving apart D. they lie along a subd ...
... 40) The Icelandic volcanoes are related to plate tectonics because ________. A. they lie on a spreading center where two plates are converging B. they lie on a subduction zone where two plates are converging C. they lie on a spreading center where two plates are moving apart D. they lie along a subd ...
Most earthquakes are the result of huge pieces of rock in the earth
... The crust of the earth, along with the rigid uppermost part of the mantle, is called the lithosphere. The lithosphere is 18-120 kilometers thick. It covers the earth’s interior and is broken into pieces called plates. The rocks that make up these plates grind, collide, move past one another, and sep ...
... The crust of the earth, along with the rigid uppermost part of the mantle, is called the lithosphere. The lithosphere is 18-120 kilometers thick. It covers the earth’s interior and is broken into pieces called plates. The rocks that make up these plates grind, collide, move past one another, and sep ...
Terrestrial Planets
... suggests the planet may still be geologically active, making Venus one of the few worlds in our solar system that has been volcanically active within the last 3 million years. The evidence comes from the European Space Agency's Venus Express mission, which has been in orbit around the planet since A ...
... suggests the planet may still be geologically active, making Venus one of the few worlds in our solar system that has been volcanically active within the last 3 million years. The evidence comes from the European Space Agency's Venus Express mission, which has been in orbit around the planet since A ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics
... Wegener had so much evidence that the continents had once been joined. Seafloor spreading is a perfect mechanism for moving those continents. It’s really too bad that Alfred Wegener is not here to learn about the theory of plate tectonics. It seems certain that he would be ecstatic! ...
... Wegener had so much evidence that the continents had once been joined. Seafloor spreading is a perfect mechanism for moving those continents. It’s really too bad that Alfred Wegener is not here to learn about the theory of plate tectonics. It seems certain that he would be ecstatic! ...
Powerpoint Jeopardy Five Themes of Geography
... Which term names the type of weathering that changes the size of a rock, but not its composition? Category 4 – 40 points ...
... Which term names the type of weathering that changes the size of a rock, but not its composition? Category 4 – 40 points ...
22.4 Plate Tectonics
... There are about a dozen major tectonic plates. Most major plates contain both continental and oceanic crust. The edges of plates meet at plate boundaries. As the plates move apart, collide, or slide past each other, they cause changes in Earth’s surface. ...
... There are about a dozen major tectonic plates. Most major plates contain both continental and oceanic crust. The edges of plates meet at plate boundaries. As the plates move apart, collide, or slide past each other, they cause changes in Earth’s surface. ...
Test # 2 Study Guide Weathering What is Weathering? - in
... (index minerals) Where do Metamorphic Rocks Occur on Earth? Geologic Time and Dating - Length of Geologic Time - Relative Dating - Absolute Dating Absolute Dating - K-Ar (Potassium-Argon) method is the most widely used (half life of 1.25 b.y.) - K (potassium) occurs in many different minerals - work ...
... (index minerals) Where do Metamorphic Rocks Occur on Earth? Geologic Time and Dating - Length of Geologic Time - Relative Dating - Absolute Dating Absolute Dating - K-Ar (Potassium-Argon) method is the most widely used (half life of 1.25 b.y.) - K (potassium) occurs in many different minerals - work ...
Array Seismology Advances Research Into Earth`s Interior
... possible scale lengths using array methods. In fact, seismic array techniques are often necessary for retrieval of subtle, yet important, deep Earth seismic structures, particularly those containing fine-scale features. While only a handful of investigations over the past few decades have used tradi ...
... possible scale lengths using array methods. In fact, seismic array techniques are often necessary for retrieval of subtle, yet important, deep Earth seismic structures, particularly those containing fine-scale features. While only a handful of investigations over the past few decades have used tradi ...
Weathering
... (index minerals) Where do Metamorphic Rocks Occur on Earth? Geologic Time and Dating - Length of Geologic Time - Relative Dating - Absolute Dating Absolute Dating - K-Ar (Potassium-Argon) method is the most widely used (half life of 1.25 b.y.) - K (potassium) occurs in many different minerals - work ...
... (index minerals) Where do Metamorphic Rocks Occur on Earth? Geologic Time and Dating - Length of Geologic Time - Relative Dating - Absolute Dating Absolute Dating - K-Ar (Potassium-Argon) method is the most widely used (half life of 1.25 b.y.) - K (potassium) occurs in many different minerals - work ...
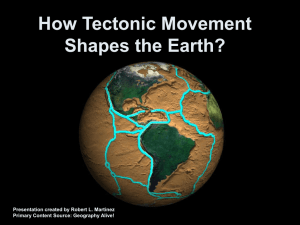
Geography How Tectonic Movement Shapes the Earth 2010
... The Urals slice through Russia from north to south. This long chain of mountains separates the Northern European Plain to the west from the West Siberian Plain to the east. ...
... The Urals slice through Russia from north to south. This long chain of mountains separates the Northern European Plain to the west from the West Siberian Plain to the east. ...
Final Earth Pacing
... energy which is transferred to the Earth by radiation. EEn.1.1.4—Explain how incoming solar energy makes life possible on Earth. ...
... energy which is transferred to the Earth by radiation. EEn.1.1.4—Explain how incoming solar energy makes life possible on Earth. ...
Plate Tectonics through Time Treatise on Geophysics, N. H. Sleep
... Figure 1 The heat flow from the Earth’s mantle is a multibranched function of the potential temperature of the Earth’s interior. Thermal histories are paths on this graph. One model has a monotonic thermal history where the heat flow lies along the transition in branch jumps. The other model jumps b ...
... Figure 1 The heat flow from the Earth’s mantle is a multibranched function of the potential temperature of the Earth’s interior. Thermal histories are paths on this graph. One model has a monotonic thermal history where the heat flow lies along the transition in branch jumps. The other model jumps b ...
Crust
... crust. The crust is Earth’s most external layer out of all the four layers mentioned. The crust consists of two parts the oceanic and continental crust. These crusts hover above the earth’s mantle, which is basically a river of molten rocks that is 2850 km thick. This outer most “coating” is more em ...
... crust. The crust is Earth’s most external layer out of all the four layers mentioned. The crust consists of two parts the oceanic and continental crust. These crusts hover above the earth’s mantle, which is basically a river of molten rocks that is 2850 km thick. This outer most “coating” is more em ...
3 The Theory of Plate Tectonics
... As scientists learned more about sea-floor spreading and magnetic reversals, they formed a theory to explain how continents move. The theory of plate tectonics states that Earth’s lithosphere is broken into many pieces—tectonic plates—that move slowly over the asthenosphere. Tectonic plates move ver ...
... As scientists learned more about sea-floor spreading and magnetic reversals, they formed a theory to explain how continents move. The theory of plate tectonics states that Earth’s lithosphere is broken into many pieces—tectonic plates—that move slowly over the asthenosphere. Tectonic plates move ver ...
tectonic plates - Revision World
... The ocean floors are continually moving, spreading from the centre and sinking at the edges. Where plates meet, huge forces build up causing earthquakes and volcanoes and the formation of fold mountains and deep-sea trenches. ...
... The ocean floors are continually moving, spreading from the centre and sinking at the edges. Where plates meet, huge forces build up causing earthquakes and volcanoes and the formation of fold mountains and deep-sea trenches. ...
Plate Tectonics
... To the east is the North American Plate, which is moving southeast. Los Angeles, located on the Pacific plate, is now 340 miles south of San Francisco, located on the North American plate. In 16 million years, the plates will have moved so much that Los Angeles will be north of San Francisco! ...
... To the east is the North American Plate, which is moving southeast. Los Angeles, located on the Pacific plate, is now 340 miles south of San Francisco, located on the North American plate. In 16 million years, the plates will have moved so much that Los Angeles will be north of San Francisco! ...
Introduction - Science Media Centre of Canada
... noticeable except with sensitive instruments. A magnitude-7 is the cutoff between a moderate and severe earthquake. A magnitude-9 is a really big one and they're extremely rare. As a rule, the larger the magnitude, the rarer the event. Seismologists currently use the Moment Magnitude Scale to measur ...
... noticeable except with sensitive instruments. A magnitude-7 is the cutoff between a moderate and severe earthquake. A magnitude-9 is a really big one and they're extremely rare. As a rule, the larger the magnitude, the rarer the event. Seismologists currently use the Moment Magnitude Scale to measur ...
Powerpoint Presentation (large file)
... evolutionary path from that on Earth • Venus’s high temperature is caused by the greenhouse effect, as the dense carbon dioxide atmosphere traps and retains energy from sunlight. • The early atmosphere of Venus contained substantial amounts of water vapor • This caused a runaway greenhouse effect th ...
... evolutionary path from that on Earth • Venus’s high temperature is caused by the greenhouse effect, as the dense carbon dioxide atmosphere traps and retains energy from sunlight. • The early atmosphere of Venus contained substantial amounts of water vapor • This caused a runaway greenhouse effect th ...
Earthquakes - Science Media Centre of Canada
... noticeable except with sensitive instruments. A magnitude-‐7 is the cutoff between a moderate and severe earthquake. A magnitude-‐9 is a really big one and they're extremely rare. As a rule, the larger ...
... noticeable except with sensitive instruments. A magnitude-‐7 is the cutoff between a moderate and severe earthquake. A magnitude-‐9 is a really big one and they're extremely rare. As a rule, the larger ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.