Lesson 1: Earth Science Overview
... Earth’s Core The core is the_____________________________________________________________________________. Earth’s core is located _________________________________________ and is made mostly of ___________. The core can be divided into two sections: _________________________________________________ ...
... Earth’s Core The core is the_____________________________________________________________________________. Earth’s core is located _________________________________________ and is made mostly of ___________. The core can be divided into two sections: _________________________________________________ ...
What are the characteristics of Earth`s interior?
... Indirect Evidence • Geologist use indirect evidence to study Earth’s interior – Seismic Waves • Waves produced by earthquakes • Record the waves and study how they travel • Speed of waves and the paths they take reveal that our planet is made up of several layers ...
... Indirect Evidence • Geologist use indirect evidence to study Earth’s interior – Seismic Waves • Waves produced by earthquakes • Record the waves and study how they travel • Speed of waves and the paths they take reveal that our planet is made up of several layers ...
sxES_G6_RNG_ch04-A_070-073.fm
... 19. Wegener’s idea that the continents slowly moved over Earth’s surface became known as 20. Circle the letter of each sentence that supports Wegener’s hypothesis. a. Some continents match up like jigsaw puzzle pieces. b. Different rock structures are found on different continents. c. Fossils of tro ...
... 19. Wegener’s idea that the continents slowly moved over Earth’s surface became known as 20. Circle the letter of each sentence that supports Wegener’s hypothesis. a. Some continents match up like jigsaw puzzle pieces. b. Different rock structures are found on different continents. c. Fossils of tro ...
Earth Science Day 01: Layers of the Earth
... A2: What is the distance traveled by a car in 5 hours (h) if its speed is 35km/h? A. 7 km If the car travels 35 km each hour for 5 hours, the total distance traveled would be 175 km (35 x 5) B. 150 km If the car travels 35 km each hour for 5 hours, the total distance traveled would be 175 km (35 x ...
... A2: What is the distance traveled by a car in 5 hours (h) if its speed is 35km/h? A. 7 km If the car travels 35 km each hour for 5 hours, the total distance traveled would be 175 km (35 x 5) B. 150 km If the car travels 35 km each hour for 5 hours, the total distance traveled would be 175 km (35 x ...
Geodynamics
... Studies of the Earth's Deep Interior (CSEDI). Funding will support basic research on the character and dynamics of the Earth's mantle and core, their influence on the evolution of the Earth as a whole, and on processes operating within the deep interior that affect or are expressed on the Earth's su ...
... Studies of the Earth's Deep Interior (CSEDI). Funding will support basic research on the character and dynamics of the Earth's mantle and core, their influence on the evolution of the Earth as a whole, and on processes operating within the deep interior that affect or are expressed on the Earth's su ...
Earth as a Planet
... we remove these anomalies, we get a smoothed-out shape of the Earth called the geoid, defined as the perfect ellipsoid the planet would assume if it were made completely of liquid. A knowledge of the exact shape of the geoid is essential for accurate map making and navigation, and until the late 195 ...
... we remove these anomalies, we get a smoothed-out shape of the Earth called the geoid, defined as the perfect ellipsoid the planet would assume if it were made completely of liquid. A knowledge of the exact shape of the geoid is essential for accurate map making and navigation, and until the late 195 ...
Chapter 7 Lecture 1
... • Greenhouse gas: molecules with 2 different types of elements (CO2, H2O, CH4) • Not a greenhouse gas: molecules with single or 2 atoms of the same element (O2, N2) ...
... • Greenhouse gas: molecules with 2 different types of elements (CO2, H2O, CH4) • Not a greenhouse gas: molecules with single or 2 atoms of the same element (O2, N2) ...
The Geosphere
... intrusions, and the exhumation of metamorphic rocks are the only means of direct observation we have of the Earth’s interior. Early insights into the deeper portions of the crust were provided by gravity data, which indicated that mountainous regions must be underlain by a thick root of relatively l ...
... intrusions, and the exhumation of metamorphic rocks are the only means of direct observation we have of the Earth’s interior. Early insights into the deeper portions of the crust were provided by gravity data, which indicated that mountainous regions must be underlain by a thick root of relatively l ...
EssayFinal
... The same way in which we observe visible light refracting as it passes into water, do body waves refract as they pass into denser rock within the earth. Scientists have used this observation to theorize the nature and boundaries within the Earth, so after an earthquake we can use this fact to obser ...
... The same way in which we observe visible light refracting as it passes into water, do body waves refract as they pass into denser rock within the earth. Scientists have used this observation to theorize the nature and boundaries within the Earth, so after an earthquake we can use this fact to obser ...
Organizing What You Know About Earth`s Layers
... HINT: in order to correctly label temperature and density, remember: Temperature increases with depth and density decreases with depth. ...
... HINT: in order to correctly label temperature and density, remember: Temperature increases with depth and density decreases with depth. ...
Earth as a System Section 1 Earth`s Interior, continued
... from Earth’s center. Weight and Location • Because the distance between Earth’s surface and its center is greater at the equator than at the poles, the weight of an object at the equator is about 0.3% less than its weight at the North Pole. ...
... from Earth’s center. Weight and Location • Because the distance between Earth’s surface and its center is greater at the equator than at the poles, the weight of an object at the equator is about 0.3% less than its weight at the North Pole. ...
exercise1_figures
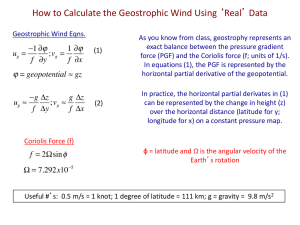
... How to Calculate the Geostrophic Wind Using ‘Real’ Data Geostrophic Wind Eqns. ...
... How to Calculate the Geostrophic Wind Using ‘Real’ Data Geostrophic Wind Eqns. ...
crust - Madison County Schools
... direct evidence from rock samples and indirect evidence from seismic waves. ...
... direct evidence from rock samples and indirect evidence from seismic waves. ...
layers
... • Even the deepest oil wells are only a few kilometers deep, and the diameter of the Earth is 12,756 km. ...
... • Even the deepest oil wells are only a few kilometers deep, and the diameter of the Earth is 12,756 km. ...
EARTH LAYERS PROJECT DUE: Monday September 29, 2014 To
... Pretend that you are about to embark on a journey to the center of the earth. Discuss in detail the type of clothing you will need to wear, the equipment to help you dig your way to the center of the earth. The 8 layers you will go through in their correct order, a brief description and important in ...
... Pretend that you are about to embark on a journey to the center of the earth. Discuss in detail the type of clothing you will need to wear, the equipment to help you dig your way to the center of the earth. The 8 layers you will go through in their correct order, a brief description and important in ...
Unpacking the Content Standards: The following standards appear
... convection, and radiation. E2.2e Explain how energy changes form through Earth systems. (modes) E4.p2I Identify major global wind belts (trade winds, prevailing westerlies, and polar easterlies) and that their vertical components control the global distribution of rainforests and deserts. E4.2 Energ ...
... convection, and radiation. E2.2e Explain how energy changes form through Earth systems. (modes) E4.p2I Identify major global wind belts (trade winds, prevailing westerlies, and polar easterlies) and that their vertical components control the global distribution of rainforests and deserts. E4.2 Energ ...
Planet Earth
... As high-energy particles leak into the lower magnetosphere, they excite molecules near the Earth’s magnetic poles, causing the ...
... As high-energy particles leak into the lower magnetosphere, they excite molecules near the Earth’s magnetic poles, causing the ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... half of the planet at a time. As Earth rotates, levels of solar energy change. The half that faces the sun receives light and heat and is warmer. The half that faces away from the sun is darker and cooler. As Earth rotates, it also moves around the sun. Earth completes one revolution around the sun ...
... half of the planet at a time. As Earth rotates, levels of solar energy change. The half that faces the sun receives light and heat and is warmer. The half that faces away from the sun is darker and cooler. As Earth rotates, it also moves around the sun. Earth completes one revolution around the sun ...
Planetary Geology I
... • Applying what we have learned about Earth's interior to other planets tells us what their interiors are probably like. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Applying what we have learned about Earth's interior to other planets tells us what their interiors are probably like. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Unit 4: Deformation of the Crust
... • Do now: This question may require the use of the Earth Science Reference Tables. In the diagram below which shows a portion of the Earth's crust, what is the relative age of the igneous rock? a) It is older than the limestone but younger than the shale. b) It is younger than the limestone but olde ...
... • Do now: This question may require the use of the Earth Science Reference Tables. In the diagram below which shows a portion of the Earth's crust, what is the relative age of the igneous rock? a) It is older than the limestone but younger than the shale. b) It is younger than the limestone but olde ...
Earth`s Interior
... The deepest man has dug into the Earth is 5 km in the South African gold mines. (This is within the crust.) Here the temperature increases by 10 to 15 ˚C for every kilometer down. We have not actually been to the center of the Earth. So how can we infer what the composition of the Earth’s interior i ...
... The deepest man has dug into the Earth is 5 km in the South African gold mines. (This is within the crust.) Here the temperature increases by 10 to 15 ˚C for every kilometer down. We have not actually been to the center of the Earth. So how can we infer what the composition of the Earth’s interior i ...
History of geodesy
Geodesy (/dʒiːˈɒdɨsi/), also named geodetics, is the scientific discipline that deals with the measurement and representation of the Earth. The history of geodesy began in antiquity and blossomed during the Age of Enlightenment.Early ideas about the figure of the Earth held the Earth to be flat (see flat earth), and the heavens a physical dome spanning over it. Two early arguments for a spherical Earth were that lunar eclipses were seen as circular shadows which could only be caused by a spherical Earth, and that Polaris is seen lower in the sky as one travels South.