* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 4: Deformation of the Crust
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
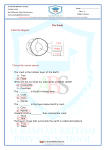
Unit 4: Deformation of the Crust Mr. Ross Brown Brooklyn School for Law and Technology In what ways is the crust deformed? • 31 October 2016 • Do now: This question may require the use of the Earth Science Reference Tables. In the diagram below which shows a portion of the Earth's crust, what is the relative age of the igneous rock? a) It is older than the limestone but younger than the shale. b) It is younger than the limestone but older than the shale. c) It is older than both the limestone and the shale. d) It is younger than both the limestone and the shale. In this unit we will learn about: • How isostatic adjustment causes stress on the crust • How this stress leads to faulting and folding • How mountains formed as a result of plate tectonics and other Earth activity How does the weight of the crust shape the Earth? • 1 November 2016 • Do now: This question may require the use of the Earth Science Reference Tables. This block diagram shows a section of the Earth's crust. The rock layers have not been overturned. I, II, III, IV, and V are locations on the Earth's surface. The deformed rock strata in the block diagram above are primarily the result of: a) Folding b) Faulting c) Ground water d) Volcanism How does the weight of the crust shape the Earth? • We said the crust ‘rides’ on the mantle • Heavier crust (mountains) sink down • Lighter crust rises • Crust presses down, mantle presses up • The balance is called isostasy • Isostatic adjustments lead to bending and deformation Isostatic Adjustments Homework #3 (only 3???) • 1 November 2016 • Define and contrast geologic stress and geologic strain • Name and describe the 3 main types of geological stress