Chapter4.1 - Department of Physics & Astronomy
... collision. Are the following true or false? 1. The force of the car on the truck is equal and opposite to the force of the truck on the car. T 2. The momentum transferred from the truck to the car is equal and opposite to the momentum transferred from the car to the truck. T 3. The change of velocit ...
... collision. Are the following true or false? 1. The force of the car on the truck is equal and opposite to the force of the truck on the car. T 2. The momentum transferred from the truck to the car is equal and opposite to the momentum transferred from the car to the truck. T 3. The change of velocit ...
Chapter 7
... Tangential speed is the thought that as an object is traveling in a circle, with what speed is it traveling linearly. Or a more practical use would be if the object were to break its circular motion, what path would it travel? Linear So what would the initial velocity be of the object as it breaks f ...
... Tangential speed is the thought that as an object is traveling in a circle, with what speed is it traveling linearly. Or a more practical use would be if the object were to break its circular motion, what path would it travel? Linear So what would the initial velocity be of the object as it breaks f ...
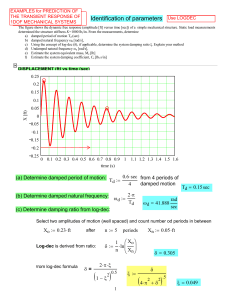
(ft) vs time (sec)
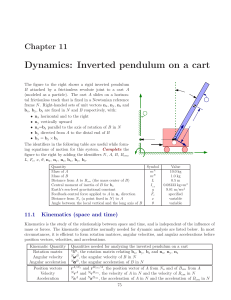
... The car of mass M=500 kg is traveling at constant speed Vo= 50 kilometer/hour when it hits a rigid wall. A spring (K) and a viscous dashpot (C) represent the car front bumper system. The system natural frequency fn=3 Hz, and the dashpot provides critical damping. Disregard friction on the car wheels ...
... The car of mass M=500 kg is traveling at constant speed Vo= 50 kilometer/hour when it hits a rigid wall. A spring (K) and a viscous dashpot (C) represent the car front bumper system. The system natural frequency fn=3 Hz, and the dashpot provides critical damping. Disregard friction on the car wheels ...
Document
... Instruments cannot perform measurements to arbitrary precision. A meter stick commonly has markings 1 millimeter (mm) apart, so distances shorter than that cannot be measured accurately with a meter stick. We report only significant digits—those whose values we feel sure are accurately measured. The ...
... Instruments cannot perform measurements to arbitrary precision. A meter stick commonly has markings 1 millimeter (mm) apart, so distances shorter than that cannot be measured accurately with a meter stick. We report only significant digits—those whose values we feel sure are accurately measured. The ...
New P20 workbook
... 2. A cannon is fired at an angle of 60.0˚ from the horizontal. The shell has a velocity of 50.0 m/s when it leaves the barrel. a. What is the shell’s initial vertical velocity? (43.3 m/s) b. How long does it take the shell to reach its maximum height? (4.41 s) c. How long is the shell in the air? (8 ...
... 2. A cannon is fired at an angle of 60.0˚ from the horizontal. The shell has a velocity of 50.0 m/s when it leaves the barrel. a. What is the shell’s initial vertical velocity? (43.3 m/s) b. How long does it take the shell to reach its maximum height? (4.41 s) c. How long is the shell in the air? (8 ...
Ch11a Powerpoint
... Motion is the act or process of changing place or position with respect to some reference object. At rest or in motion depends totally on the reference. Sleeping passenger in a flying airplane: At rest in reference to the airplane. In motion in reference to the earth. ...
... Motion is the act or process of changing place or position with respect to some reference object. At rest or in motion depends totally on the reference. Sleeping passenger in a flying airplane: At rest in reference to the airplane. In motion in reference to the earth. ...
Example
... Acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Earth g = 9.81 m/s2 This number is an average and can change slightly depending on where you are on the earth (distance from the centre of the earth) All objects have the same acceleration due to gravity in a vacuum. In a vacuum where there is no ...
... Acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Earth g = 9.81 m/s2 This number is an average and can change slightly depending on where you are on the earth (distance from the centre of the earth) All objects have the same acceleration due to gravity in a vacuum. In a vacuum where there is no ...