Physics Final Review Problems 2014 *Note: the following problems
... e) Be able to do the above with graphical representations as well (position vs time graphs, velocity vs time graphs) f) Calculate velocity, position, and acceleration using the appropriate formulas. 1. What is the difference between distance and displacement? Speed and velocity? 2. What type of moti ...
... e) Be able to do the above with graphical representations as well (position vs time graphs, velocity vs time graphs) f) Calculate velocity, position, and acceleration using the appropriate formulas. 1. What is the difference between distance and displacement? Speed and velocity? 2. What type of moti ...
Physics Final Review Problems 2013 *Note: the following problems
... e) Be able to do the above with graphical representations as well (position vs time graphs, velocity vs time graphs) f) Calculate velocity, position, and acceleration using the appropriate formulas. 1. What is the difference between distance and displacement? Speed and velocity? 2. What type of moti ...
... e) Be able to do the above with graphical representations as well (position vs time graphs, velocity vs time graphs) f) Calculate velocity, position, and acceleration using the appropriate formulas. 1. What is the difference between distance and displacement? Speed and velocity? 2. What type of moti ...
quiz practice worksheet
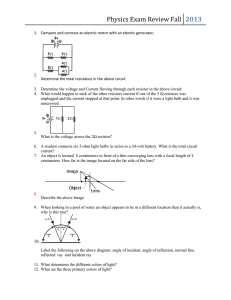
... 1. What is the force acting on an object with a mass of 24g and an acceleration of 6.25 m/s2? 2. What is the mass of a falling rock if it produces a force of 170N? 3. What force is required to bring a 1000Kg car to rest from a speed of 90km/hr in 45 meters? 4. A rifle bullet which travels at 360 m/s ...
... 1. What is the force acting on an object with a mass of 24g and an acceleration of 6.25 m/s2? 2. What is the mass of a falling rock if it produces a force of 170N? 3. What force is required to bring a 1000Kg car to rest from a speed of 90km/hr in 45 meters? 4. A rifle bullet which travels at 360 m/s ...
Ch5CTa
... Answer: Both cars have the same acceleration. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity: a = dv/dt. Both cars have a velocity vector which is changing in the same way. (Since this is circular motion with constant speed, the direction of the acceleration is toward the center of the circle and th ...
... Answer: Both cars have the same acceleration. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity: a = dv/dt. Both cars have a velocity vector which is changing in the same way. (Since this is circular motion with constant speed, the direction of the acceleration is toward the center of the circle and th ...
Additional Midterm Review Questions
... The Work-Energy Theorem and Kinetic Energy 39. In which one of the following situations is zero net work done? (a) A ball rolls down an inclined plane. (b) A physics student stretches a spring. (c) A projectile falls toward the surface of Earth. (d) A box is pulled across a rough floor at constant v ...
... The Work-Energy Theorem and Kinetic Energy 39. In which one of the following situations is zero net work done? (a) A ball rolls down an inclined plane. (b) A physics student stretches a spring. (c) A projectile falls toward the surface of Earth. (d) A box is pulled across a rough floor at constant v ...
Properties of Uniform Circular Motion
... This inward acceleration can be demonstrated with a cork accelerometer. The cork will move toward the direction of the acceleration. For an object moving in a circle, there must be an inward force acting upon it in order to cause its inward acceleration. This is sometimes referred to as the centrip ...
... This inward acceleration can be demonstrated with a cork accelerometer. The cork will move toward the direction of the acceleration. For an object moving in a circle, there must be an inward force acting upon it in order to cause its inward acceleration. This is sometimes referred to as the centrip ...
Motion Study Guide
... 16. A steel ball whose mass is 2.0 kg is rolling at a rate of 2.8 m/s. What is its momentum? p = mv = (2.0 kg)(2.8 m/s) = 5.6 kg*m/s 17. A race car leaves the starting line and travels 36000 m in the first 600 seconds of the race. They are then forced to take a pit stop and don’t go anywhere for 250 ...
... 16. A steel ball whose mass is 2.0 kg is rolling at a rate of 2.8 m/s. What is its momentum? p = mv = (2.0 kg)(2.8 m/s) = 5.6 kg*m/s 17. A race car leaves the starting line and travels 36000 m in the first 600 seconds of the race. They are then forced to take a pit stop and don’t go anywhere for 250 ...
HW#5a Page 1 of 4 For circular motion, we know that the total force
... Translating this to the boxes above gives ax = 1.4 m/s , ay = 0 for m1, and ax = 0, ay = -1.4 m/s2 for m2. We note that the tension is less than the weight of m2, m2g=49 N. This agrees with the drawing, where the weight overcomes the tension and makes m2 accelerate downwards. (b) Suppose m1 = 0. The ...
... Translating this to the boxes above gives ax = 1.4 m/s , ay = 0 for m1, and ax = 0, ay = -1.4 m/s2 for m2. We note that the tension is less than the weight of m2, m2g=49 N. This agrees with the drawing, where the weight overcomes the tension and makes m2 accelerate downwards. (b) Suppose m1 = 0. The ...
Chapter 6 Notes Circular Motion and Gravity
... A curved path requires an inward pull. centripetal force: the force needed to make an object follow a curved path Centripetal force is the force perpendicular to the velocity of an object moving along a curved path. The centripetal force is the force directed toward the center of the curvature of th ...
... A curved path requires an inward pull. centripetal force: the force needed to make an object follow a curved path Centripetal force is the force perpendicular to the velocity of an object moving along a curved path. The centripetal force is the force directed toward the center of the curvature of th ...
Physical Science Final Study Guide I KEY Name __ ___
... 20. Identify the velocity and acceleration of the object for the following points. (show work, include units) ...
... 20. Identify the velocity and acceleration of the object for the following points. (show work, include units) ...
Physics GCSE Year 9
... Explain that inertial mass is a measure of how difficult it is to change the velocity of an object (including from rest) and know that it is defined as the ratio of force over acceleration. Investigate the relationship between force, mass and acceleration ...
... Explain that inertial mass is a measure of how difficult it is to change the velocity of an object (including from rest) and know that it is defined as the ratio of force over acceleration. Investigate the relationship between force, mass and acceleration ...
Dyanmics I slides
... » Some motion is natural for the sublunar elements, rectilinear motion to or away from the earth's center for the supralunar quintessence, circular motion » All other motion is violent, and requires a mover • [Anselm's nth proof of the existence of God] • Because motion exists, there must be a self- ...
... » Some motion is natural for the sublunar elements, rectilinear motion to or away from the earth's center for the supralunar quintessence, circular motion » All other motion is violent, and requires a mover • [Anselm's nth proof of the existence of God] • Because motion exists, there must be a self- ...