Ppt - AIS Moodle
... orbit will be a noncircular ellipse. A satellite in an elliptical orbit does not move at a constant speed. ...
... orbit will be a noncircular ellipse. A satellite in an elliptical orbit does not move at a constant speed. ...
Chapter 2
... • Force is a push or pull that one body exerts on another • Example: passing a basketball to a team member requires force • The applied force results in the movement of the object. ...
... • Force is a push or pull that one body exerts on another • Example: passing a basketball to a team member requires force • The applied force results in the movement of the object. ...
chapter - 5 laws of motion
... Q.10. If the speed of stone is increased beyond the maximum permissible value and the string breaks suddenly, which of the following correctly describes the trajectory of the stone after the string breaks (i) the stone moves radially outwards, (ii) the stone flies off tangentially from the instant t ...
... Q.10. If the speed of stone is increased beyond the maximum permissible value and the string breaks suddenly, which of the following correctly describes the trajectory of the stone after the string breaks (i) the stone moves radially outwards, (ii) the stone flies off tangentially from the instant t ...
1. Mass, Force and Gravity
... miles). Recall that five meters is just the vertical distance an initially horizontally moving projectile will fall in the first second of motion. But this implies that if the (horizontal) muzzle velocity were 8,000 meters per second, the downward fall of the cannonball would be just matched by the ...
... miles). Recall that five meters is just the vertical distance an initially horizontally moving projectile will fall in the first second of motion. But this implies that if the (horizontal) muzzle velocity were 8,000 meters per second, the downward fall of the cannonball would be just matched by the ...
Newton’s Laws of Motion
... A book sliding across a table slows down and stops because of the force of friction. ...
... A book sliding across a table slows down and stops because of the force of friction. ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of retardation are removed!! Galileo’s statement is formulated by Newton into the 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of external forces, an object at rest remains at rest and ...
... body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of retardation are removed!! Galileo’s statement is formulated by Newton into the 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of external forces, an object at rest remains at rest and ...
p211c05
... A chute is being built along which crates are to be slid down at constant speed. The coefficient of kinetic friction is k. What angle should the chute make with respect to the horizontal? What is the acceleration of a moving crate if the angle is actually greater than this critical angle? ...
... A chute is being built along which crates are to be slid down at constant speed. The coefficient of kinetic friction is k. What angle should the chute make with respect to the horizontal? What is the acceleration of a moving crate if the angle is actually greater than this critical angle? ...
Document
... A chute is being built along which crates are to be slid down at constant speed. The coefficient of kinetic friction is k. What angle should the chute make with respect to the horizontal? What is the acceleration of a moving crate if the angle is actually greater than this critical angle? ...
... A chute is being built along which crates are to be slid down at constant speed. The coefficient of kinetic friction is k. What angle should the chute make with respect to the horizontal? What is the acceleration of a moving crate if the angle is actually greater than this critical angle? ...
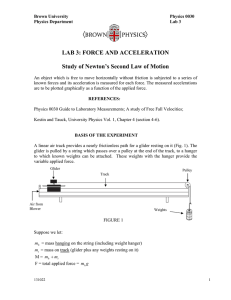
Atwood`s Machine
... For this part of the experiment you will keep the total mass used constant, but move weights from one side to the other. The difference in masses changes. 1. Set up the Atwood’s machine apparatus as shown in Figure 1. Be sure the heavier mass can move at least 40 cm before striking the floor. 2. Con ...
... For this part of the experiment you will keep the total mass used constant, but move weights from one side to the other. The difference in masses changes. 1. Set up the Atwood’s machine apparatus as shown in Figure 1. Be sure the heavier mass can move at least 40 cm before striking the floor. 2. Con ...
A) m s2 B) W s C) J•s D) kg•ms 1. Which unit is
... A small discrepancy between the calculated orbit and the observed orbit of the planet Uranus was noted. It appeared that the sum of the forces on Uranus did not equal its mass times its acceleration, unless there was another force on the planet that was not included in the calculation. Assuming ...
... A small discrepancy between the calculated orbit and the observed orbit of the planet Uranus was noted. It appeared that the sum of the forces on Uranus did not equal its mass times its acceleration, unless there was another force on the planet that was not included in the calculation. Assuming ...
Chapter 3 - "Patterns of Motion"
... – The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. – The unit of force used in the SI system is the Newton (N) – N= kgm/s2 – Force is equal to mass times acceleration • F=ma – Weight is equal to the mass of a ...
... – The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. – The unit of force used in the SI system is the Newton (N) – N= kgm/s2 – Force is equal to mass times acceleration • F=ma – Weight is equal to the mass of a ...