Measuring Motion
... O Compare balanced and unbalanced forces. O Describe how unbalanced forces cause changes in ...
... O Compare balanced and unbalanced forces. O Describe how unbalanced forces cause changes in ...
Answers to Sample exam 2004
... A lab cart is set in motion, by hand, on a frictionless incline. Once the cart has been given its motion, only the force of gravity acts on it, and thus gravity controls its velovity on the incline. The three `velocity Vs time` curves presented in the graph below result from three different angles f ...
... A lab cart is set in motion, by hand, on a frictionless incline. Once the cart has been given its motion, only the force of gravity acts on it, and thus gravity controls its velovity on the incline. The three `velocity Vs time` curves presented in the graph below result from three different angles f ...
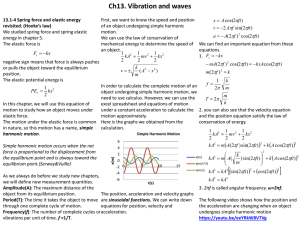
13.1-4 Spring force and elastic energy revisited. (Hooke’s law)
... equilibrium point.(Serway&Vuille) ...
... equilibrium point.(Serway&Vuille) ...
Slide 1 - apphysicswarren
... object can be described using polar coordinates—r and θ— rather than x and y. The figure at left gives the conversion between the two descriptions. ...
... object can be described using polar coordinates—r and θ— rather than x and y. The figure at left gives the conversion between the two descriptions. ...
physics - Bharatiya Vidya Bhavans School
... 12. Derive the relation Ʈ =Iα for the rotation of particle about the fixed axis. 13. (i) With the help of a suitable diagram, show that in an elastic one- dimensional collision, the relative velocity of approach is equal to the relative velocity of separation after the collision . 14. Explain the te ...
... 12. Derive the relation Ʈ =Iα for the rotation of particle about the fixed axis. 13. (i) With the help of a suitable diagram, show that in an elastic one- dimensional collision, the relative velocity of approach is equal to the relative velocity of separation after the collision . 14. Explain the te ...
Newtons laws and Friction spring 2010
... There’s earthly gravity (the earth & objects are attracted to each other) There’s universal gravity (attraction between heavenly bodies like the Sun and moon) No matter what kind of gravity you speak, two variables influence the strength of this attractive force: Object’s mass Distance between objec ...
... There’s earthly gravity (the earth & objects are attracted to each other) There’s universal gravity (attraction between heavenly bodies like the Sun and moon) No matter what kind of gravity you speak, two variables influence the strength of this attractive force: Object’s mass Distance between objec ...
File - Mrs. Phillips` Physical Science Webpage
... constant velocity, and objects at rest tend to stay at rest, unless acted upon by an outside force. ...
... constant velocity, and objects at rest tend to stay at rest, unless acted upon by an outside force. ...
Study Sheet for Chemistry and Physics Chemistry Atomic Structure
... space reasons only. Most ALL of your METALS are to the left of the staircase (except Hydrogen). ALL of you nonmetals are to the right of the staircase. The metalloids are located along the staircase and they have properties of metals and nonmetals. Valence Electrons can be found relatively easy by l ...
... space reasons only. Most ALL of your METALS are to the left of the staircase (except Hydrogen). ALL of you nonmetals are to the right of the staircase. The metalloids are located along the staircase and they have properties of metals and nonmetals. Valence Electrons can be found relatively easy by l ...
Physics 106P: Lecture 1 Notes
... So far we only talked about the magnitude of these vectors. But as vectors they also have a direction. Both angular velocity and acceleration point along the rotation axis. ...
... So far we only talked about the magnitude of these vectors. But as vectors they also have a direction. Both angular velocity and acceleration point along the rotation axis. ...
Sections 13.1-13.4 - University of Mary Hardin–Baylor
... It is important to understand the difference between the mass and weight of a body! Mass is an absolute property of a body. It is independent of the gravitational field in which it is measured. The mass provides a measure of the resistance of a body to a change in velocity, as defined by Newton’s se ...
... It is important to understand the difference between the mass and weight of a body! Mass is an absolute property of a body. It is independent of the gravitational field in which it is measured. The mass provides a measure of the resistance of a body to a change in velocity, as defined by Newton’s se ...
Circular Motion - Effingham County Schools
... torques are equal and no net rotation will occur. The kids can balance! ...
... torques are equal and no net rotation will occur. The kids can balance! ...
Newton`s Second Law - Philadelphia University
... It is important to understand the difference between the mass and weight of a body! Mass is an absolute property of a body. It is independent of the gravitational field in which it is measured. The mass provides a measure of the resistance of a body to a change in velocity, as defined by Newton’s se ...
... It is important to understand the difference between the mass and weight of a body! Mass is an absolute property of a body. It is independent of the gravitational field in which it is measured. The mass provides a measure of the resistance of a body to a change in velocity, as defined by Newton’s se ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... Identify forces and draw a Free Body Diagram Begin to solve 1D and 2D problems with forces in equilibrium and non-equilibrium (i.e., acceleration) using Newton’s 1st and 2nd laws. ...
... Identify forces and draw a Free Body Diagram Begin to solve 1D and 2D problems with forces in equilibrium and non-equilibrium (i.e., acceleration) using Newton’s 1st and 2nd laws. ...
Lecture12
... rotate freely about its axis is accelerated by hanging a 240 kg mass from the end by a string which is wrapped about the cylinder. a) Find the linear acceleration of the mass. 4.36 m/s2 b) What is the speed of the mass after it has dropped 2.5 m? 4.67 m/s ...
... rotate freely about its axis is accelerated by hanging a 240 kg mass from the end by a string which is wrapped about the cylinder. a) Find the linear acceleration of the mass. 4.36 m/s2 b) What is the speed of the mass after it has dropped 2.5 m? 4.67 m/s ...
Document
... An airplane is capable of moving 200 mph in still air. A wind blows directly from the North at 50 mph. The airplane accounts for the wind (by pointing the plane somewhat into the wind) and flies directly east relative to the ground. What is the plane’s resulting ground speed? In what direction is th ...
... An airplane is capable of moving 200 mph in still air. A wind blows directly from the North at 50 mph. The airplane accounts for the wind (by pointing the plane somewhat into the wind) and flies directly east relative to the ground. What is the plane’s resulting ground speed? In what direction is th ...
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 4
... • If the net force exerted on an object is zero, its velocity remains constant (both magnitude and direction). • Objects at rest feel no net force • Objects moving with constant velocity feel no net force • No net force means ...
... • If the net force exerted on an object is zero, its velocity remains constant (both magnitude and direction). • Objects at rest feel no net force • Objects moving with constant velocity feel no net force • No net force means ...