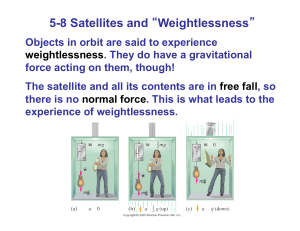
QUESTIONS MC Newton`s Laws
... If your automobile runs out of fuel while you were driving the engine stops but you do not come to an abrupt stop. The concept that most explain why is: A. inertia. B. gravity. C. acceleration. D. resistance. ...
... If your automobile runs out of fuel while you were driving the engine stops but you do not come to an abrupt stop. The concept that most explain why is: A. inertia. B. gravity. C. acceleration. D. resistance. ...
Newton`s Laws - Galileo and Einstein
... the cannonball one second apart. As is explained above, the magnitude a of the acceleration is the length of the small dashed vector on the right, where the other two sides of this long narrow triangle have lengths equal to the speed v of the cannonball. We’ll call this the “vav” triangle, because t ...
... the cannonball one second apart. As is explained above, the magnitude a of the acceleration is the length of the small dashed vector on the right, where the other two sides of this long narrow triangle have lengths equal to the speed v of the cannonball. We’ll call this the “vav” triangle, because t ...
Concept Questions
... legs are separated by a distance d, with one foot uphill and one downhill. The center of mass of the person is at a distance h above the ground, perpendicular to the hillside, midway between the person’s feet. Assume that the coefficient of static friction between the person’s feet and the hill is s ...
... legs are separated by a distance d, with one foot uphill and one downhill. The center of mass of the person is at a distance h above the ground, perpendicular to the hillside, midway between the person’s feet. Assume that the coefficient of static friction between the person’s feet and the hill is s ...
What is a Force?
... An object will remain at rest unless acted upon by an “unbalanced” force. An object in motion will continue with constant speed and direction, unless acted on by an unbalanced force. This law shows how force, mass and acceleration are related as shown in the equation below: Force = mass x accelerati ...
... An object will remain at rest unless acted upon by an “unbalanced” force. An object in motion will continue with constant speed and direction, unless acted on by an unbalanced force. This law shows how force, mass and acceleration are related as shown in the equation below: Force = mass x accelerati ...
rotational kinetic energy
... platform begin to rotate if the man moves from the edge to the centre? (a) 22 rpm ...
... platform begin to rotate if the man moves from the edge to the centre? (a) 22 rpm ...
Circular motion and rotation Uniform circular motion
... Other Effects of Forces Up until now, we’ve focused on forces that speed up or slow down an object. ...
... Other Effects of Forces Up until now, we’ve focused on forces that speed up or slow down an object. ...
Link to Notes - Coweta County Schools
... The Same Force Paradox If the force on each object is the same, then why don’t they experience the same effect in the collision Their masses differ, and therefore they undergo different ...
... The Same Force Paradox If the force on each object is the same, then why don’t they experience the same effect in the collision Their masses differ, and therefore they undergo different ...
1 - mackenziekim
... Determine the tension in the rope during the acceleration of the 5.0-kg mass along the ramp. Determine the speed of projection of the 5.0-kg mass from the top of the ramp. Determine the horizontal range of the 5.0-kg mass from the base of the ramp. ...
... Determine the tension in the rope during the acceleration of the 5.0-kg mass along the ramp. Determine the speed of projection of the 5.0-kg mass from the top of the ramp. Determine the horizontal range of the 5.0-kg mass from the base of the ramp. ...
Two objects are acted on by equal forces for equal times
... Part A-Multiple Choice. 4 points each. Choose the best answer and write it on the line to the left of the question number. ________1. Two ice hockey pucks collide on a frictionless surface. In considering conservation of momentum of the two-puck system, we would break the total momentum into x and ...
... Part A-Multiple Choice. 4 points each. Choose the best answer and write it on the line to the left of the question number. ________1. Two ice hockey pucks collide on a frictionless surface. In considering conservation of momentum of the two-puck system, we would break the total momentum into x and ...
Newton`s Laws - SCHOOLinSITES
... Friction acts on materials that are in contact with each other. It always acts in a direction to oppose motion. The force of friction between surfaces depends on the kinds of materials in contact & how much the surfaces are pressed together. ...
... Friction acts on materials that are in contact with each other. It always acts in a direction to oppose motion. The force of friction between surfaces depends on the kinds of materials in contact & how much the surfaces are pressed together. ...